Zlín Z 526
The Zlin Z-526 Akrobat is a Czech sports plane used in aerobatics.
| Zlin Z-526 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Sports plane |
| Manufacturer | Zlin Aircraft |
| First flight | 1959 |
| Number built | 1,400+ |
History
The Z-526 was originally designed by Zlin Aircraft in 1959. Its two-seat version is called the Trener-Master
The Z 526's layout was organized with the pilot in the rear, and the student in front. The aircraft could be equipped also with tip tanks and a constant speed propeller. The Z-526F was introduced in 1968 and was equipped with a 135 kW (180 hp) Avia M 137A engine, the export version Z-526L differing by being equipped with a 150 kW (200 hp) Lycoming AEIO-360 flat-four. Single-seat versions included the Z-526A, Z-526AS, and the Z-526AFS.
The Z-526 AFM was built between 1981 and 1984 and was powered by a 155 kW (210 hp) Avia M337 engine, had tip tanks and a lengthened fuselage. The aircraft was later developed into the Zlin Z-726.
More than 1,400 Z-526s were manufactured, many for military and private flying schools.
Variants
- Z-526
- Two-seat version
- Z-526A
- Single-seat version
- Z-526AF
- Single-seat version
- Z-526AFS
- Single-seat version
- Z-526AFM Condor
- powered by an Avia M337 inverted six-cylinder engine giving 210hp(157kW)
Specifications (Z-526 Trener-Master)
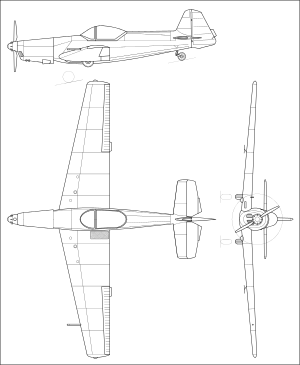
Data from Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1968–69[1]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2 (526A / 526F - 1)
- Length: 7.8 m (25 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 10.6 m (34 ft 9 in)
- Height: 2.06 m (6 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 15.45 m2 (166.3 sq ft)
- Airfoil: root: NACA 2418; tip: NACA 4412[2]
- Empty weight: 680 kg (1,499 lb)
- Z 526A 650 kg (1,430 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 975 kg (2,150 lb) (trainer)
- 940 kg (2,070 lb) (aerobatic)
- Z 526A 830 kg (1,830 lb) (aerobatic)
- Fuel capacity: 2x 45 l (12 US gal; 9.9 imp gal) tanks in the wing roots, with a 7 l (1.8 US gal; 1.5 imp gal) gravity collector tank in the fuselage.
- Powerplant: 1 × Walter Minor 6-III 6-cylinder air-cooled inverted in-line piston engine, 120 kW (160 hp) (later variants 155 kW (208 hp) Avia M337)
- Propellers: 2-bladed V 503, 1.9 m (6 ft 3 in) diameter constant-speed propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 220 km/h (140 mph, 120 kn) at sea level
- Cruise speed: 208 km/h (129 mph, 112 kn) (70% power)
- Landing speed: 78 km/h (48 mph; 42 kn)
- Never exceed speed: 320 km/h (200 mph, 170 kn)
- Range: 580 km (360 mi, 310 nmi)
- Ferry range: 610 km (380 mi, 330 nmi) with wing-tip tanks
- Service ceiling: 5,000 m (16,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 5 m/s (980 ft/min) at sea level
- Take-off run: 220 m (720 ft)
- Landing run: 135 m (443 ft)
References
- Taylor, John W.R., ed. (1968). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1968–69. London: Sampson Low, Marston & Company. p. 26.
- Lednicer, David. "The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage". m-selig.ae.illinois.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Zlin Z-526. |