Yokosuka K1Y
The Yokosuka K1Y, also known as the Navy Type 13 Trainer, was a Japanese single-engined biplane trainer of the 1920s. Designed by the Japanese Navy Arsenal at Yokosuka, over 100 were built by several manufacturers, the type being used by the Imperial Japanese Navy well into the 1930s.
| K1Y | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Trainer |
| National origin | Japan |
| Manufacturer | Yokosuka Naval Air Technical Arsenal |
| First flight | 1925 |
| Introduction | 1925 |
| Primary user | Imperial Japanese Navy |
| Number built | ~104 |
Design and development
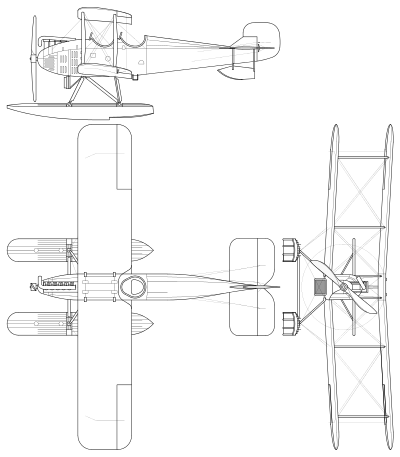
In 1924, the Yokosuka Naval Air Technical Arsenal was tasked with designing a replacement for the Imperial Japanese Navy's Yokosuka I-go Ko-gata and Avro 504 floatplane trainers. The resultant design was a single-engined two-bay biplane of fabric-covered wooden construction. It was powered by a Gasuden-built 130 horsepower (97 kW) Benz six-cylinder water cooled inline engine, and could be fitted with either a conventional landing gear or floats. It first flew in 1925 and was accepted into service as the Navy Type 13 Trainer,[nb 1] with the short system designation E1Y.[2]
Operational history
After acceptance in October 1925, about 40 were built by Nakajima,[3] with 48 more built by Kawanishi from 1928 to 1928 to 1932,[4] and 10 by Watanabe in 1933–34, which together with six aircraft built by Yokosuka, gave a total of about 104.[2] The type remained the standard floatplane trainer of the Imperial Japanese Navy until it was replaced by the Yokosuka K4Y from 1933,[5] although a few remained in use until the early years of the Second World War.[2]
Variants
Operators
Specifications (K1Y2 seaplane)
Data from Japanese Aircraft 1910-1941[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 8.68 m (28 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 10.205 m (33 ft 6 in)
- Height: 3.47 m (11 ft 5 in)
- Wing area: 32.65 m2 (351.4 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 872 kg (1,922 lb)
- Gross weight: 1,056 kg (2,328 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Gasuden Benz six-cylinder air-cooled inline engine, 97 kW (130 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 130 km/h (81 mph, 70 kn)
- Endurance: 3 hr
- Time to altitude: 42 min to 2,000 m (6,600 ft)
Notes
- The type number was the year of the Taishō Emperor's reign of the requirement, i.e. Type 13 = 1924[1]
- Mikesh and Abe 1990, pp. 2, 286.
- Mikesh and Abe 1990, p. 273
- Mikesh and Abe 1990, p. 222.
- Mikesh and Abe 1990, p. 135.
- Mikesh and Abe 1990, p. 277.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yokosuka K1Y. |
- Mikesh, Robert and Shorzoe Abe. Japanese Aircraft 1910-1941. London:Putnam, 1990. ISBN 0 85177 840 2.