White-throated round-eared bat
The white-throated round-eared bat (Lophostoma silvicolum) is a South and Central American bat species[2] found from Honduras to Bolivia, Paraguay and Brazil. It creates roosts inside the nests of the termite, Nasutitermes corniger. It thrives on a mainly insect-based diet, focusing on the surfaces of foliage to hunt, and also eats fruit and pollen.[3] It has a very wide range and is a common species over much of that range, so the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".[1]
| White-throated round-eared bat | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Phyllostomidae |
| Genus: | Lophostoma |
| Species: | L. silvicolum |
| Binomial name | |
| Lophostoma silvicolum D'Orbigny, 1836 | |
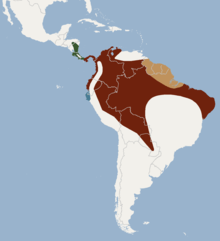 | |
| Distribution of the white-throated round-eared bat Red = L.s.silvicolum | |
Taxonomy
This species was first described in 1836 by the French naturalist Alcide d'Orbigny. Four subspecies are recognised:[2]
- L.s.silvicolum: southern Panama, Colombia, Venezuela, eastern and north-eastern Brazil, eastern and north-eastern Ecuador, eastern Peru, central and northern Bolivia and Paraguay
- L.s.centralis: southern Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and northern Panama;
- L.s.laephotis: Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana and northeastern Brazil;
- L.s.occidentalis: northeastern Peru and southeastern Ecuador.
Description

Lophostoma silvicolum is a medium-sized bat with a forearm length of 50 mm (2.0 in) or more, long, soft fur on its body and very short fur on its face. The dorsal parts of the pelage are grey or greyish-brown frosted by hairs with white tips, while the ventral parts are light greyish-brown and the throat is entirely white. The muzzle is naked, the nose-leaf is lanceolate, with the front portion completely fused to the upper lip. On the chin there is a furrow in the centre surrounded by rows of small warts. The ears are large with rounded margins, and the tail extends half way to the interfemoral membrane. Populations in Ecuador have conspicuous white patches behind the ears.[4][5]
Distribution and habitat
Lophostoma silvicolum is native to Central America and the northern half of South America, to the east of the Andes. It is absent from much of the Amazon basin. It occurs in forests of various types, in forest clearings and over agricultural land. It tends to avoid creeks.[1]
Ecology
Lophostoma silvicolum feeds mainly on insects, gleaning them from the upper surface of leaves while in flight, but supplements this diet with fruits.[4] It roosts in cavities hollowed out by the males in the base of active termite mounds.[6] Advantages to the bat of using such a location include a reduction of competition with other bat species for roosting sites, a reduction in parasites, a reduction in predation and a constant microclimate. On Barro Colorado Island, Panama, the nests used are exclusively those of Nasutitermes corniger, and up to nineteen bats have been found in one roost; active roost construction is extremely rare among bats.[6]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lophostoma silvicolum. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Lophostoma silvicolum |
- Barquez, R.; Diaz, M.; Pineda, W.; Rodriguez, B. (2016). "Lophostoma silvicolum". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T88149202A22041651. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T88149202A22041651.en.
- Simmons, N.B. (2005). "Order Chiroptera". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 406. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- "Mamíferos del Ecuador". bioweb.bio. Retrieved 2019-09-04.
- Gardner, Alfred L. (2008). Mammals of South America, Volume 1: Marsupials, Xenarthrans, Shrews, and Bats. University of Chicago Press. pp. 265–270. ISBN 978-0-226-28242-8.
- Reid, Fiona A. (2009). A field guide to the Mammals of Central America and Southeast Mexico. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195343236.
- Dechmann, D.K.N.; Kalko, E.K.V.; König, B.; Kerth, G. (2005). "Mating system of a Neotropical roost-making bat: the white-throated, round-eared bat, Lophostoma silvicolum (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae)" (PDF). Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 58 (3): 316–325. doi:10.1007/s00265-005-0913-y.
