Eastern whip-poor-will
The eastern whip-poor-will (Antrostomus vociferus) is a medium-sized (22–27 cm) nightjar from North America. The whip-poor-will is commonly heard within its range, but less often seen because of its camouflage. It is named onomatopoeically after its song.[2]
| Eastern whip-poor-will | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Adult male | |
| Namesake vocalization | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Caprimulgiformes |
| Family: | Caprimulgidae |
| Genus: | Antrostomus |
| Species: | A. vociferus |
| Binomial name | |
| Antrostomus vociferus Wilson, 1812 | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Caprimulgus vociferus Wilson, 1812 | |
Description

This medium-sized nightjar measures 22–27 cm (8.7–10.6 in) in length, spans 45–50 cm (18–20 in) across the wings and weighs 42–69 g (1.5–2.4 oz).[3] Further standard measurements are a wing chord of 14.7 to 16.9 cm (5.8 to 6.7 in), a tail of 10.5 to 12.8 cm (4.1 to 5.0 in), a bill of 1 to 1.4 cm (0.39 to 0.55 in) and a tarsus of 1.5 to 1.8 cm (0.59 to 0.71 in).[4] Adults have mottled plumage: the upperparts are grey, black and brown; the lower parts are grey and black. They have a very short bill and a black throat. Males have a white patch below the throat and white tips on the outer tail feathers; in the female, these parts are light brown.
This bird is sometimes confused[5] with the related chuck-will's-widow (Antrostomus carolinensis) which has a similar but lower-pitched and slower call.
Ecology
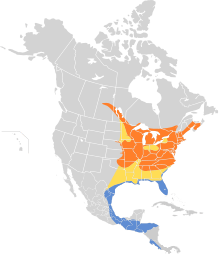
Eastern whip-poor-wills breed in deciduous or mixed woods across central and southeastern Canada and the eastern United States, and migrate to the southeastern United States and to eastern Mexico and Central America for the winter. These birds forage at night, catching insects in flight, and normally sleep during the day. Eastern whip-poor-wills nest on the ground, in shaded locations among dead leaves, and usually lay two eggs at a time. The bird will commonly remain on the nest unless almost stepped upon.
The eastern whip-poor-will is becoming locally rare. Several reasons for the decline are proposed, such as loss of early successional forest habitat, habitat destruction, predation by feral cats and dogs, and poisoning by insecticides, but the actual causes remain elusive.[6][7] Even with local populations endangered, the species as a whole is not considered globally threatened due to its large range.[8][9]
The whip-poor-will has been split into two species. Eastern populations are now referred to as the eastern whip-poor-will. The disjunct population in southwestern United States and Mexico is now referred to as the Mexican whip-poor-will, Antrostomus arizonae. The two populations were split based on range, different vocalizations, different egg coloration, and DNA sequencing showing differentiation.[10]
Conservation
In 2017, the eastern whip-poor-will was uplisted from least concern to near threatened on the IUCN Red List, on the basis that based on citizen science observations, populations of the eastern whip-poor-will had declined by over 60% between 1970 and 2014.[11] This decline is likely due to decreased forest disturbance and early successional forest habitat, pesticides and intensified agriculture, both of which have led to heavy declines in the flying insect populations that the eastern whip-poor-will depends on, as well as habitat loss. BirdLife International has stated that initiatives like the Conservation Reserve Program will be crucial in conserving the species and reversing its decline.[12][13]
Cultural references
Due to its song, the eastern whip-poor-will is the topic of numerous legends. A New England legend says the whip-poor-will can sense a soul departing, and can capture it as it flees. This is used as a plot device in H. P. Lovecraft's story The Dunwich Horror. Lovecraft based this idea on information of local legends given to him by Edith Miniter of North Wilbraham, Massachusetts when he visited her in 1928. This is likely related to an earlier Native American and general American folk belief that the singing of the birds is a death omen.[14] This is also referred by Whip-poor-will, a short story by James Thurber, in which the constant nighttime singing of a whip-poor-will results in maddening insomnia of the protagonist Mr Kinstrey who eventually loses his mind and kills everyone in his house, including himself. The bird also features, however, in The Runaway Slave at Pilgrim's Point, a poem by the English poet Elizabeth Barrett Browning, in which the outcast speaker asks: "Could the whip-poor-will or the cat of the glen/Look into my eyes and be bold?"[15]
It is also frequently used as an auditory symbol of rural America, as in Washington Irving's story The Legend of Sleepy Hollow, or as a plot device. For example, William Faulkner's short story, "Barn Burning", makes several mentions of whip-poor-wills, e.g.: "and then he found that he had been asleep because he knew it was almost dawn, the night almost over. He could tell that from the whip-poor-wills. They were everywhere now among the dark trees below him, constant and inflectioned and ceaseless, so that, as the instant for giving over to the day birds drew nearer and nearer, there was no interval at all between them."[16]
"The Mountain Whippoorwill" is a poem written by Stephen Vincent Benet about a fiddling contest, won by Hillbilly Jim, who refers to his fiddle as a whip-poor-will and identifies the bird with the lonely and poor but vibrant life of the mountain people. American poet Robert Frost described the sound of a whip-poor-will in the fourth stanza of his 1915 poem "Ghost House". This is notable in Frost's use of assonance, in "The whippoorwill is coming to shout / And hush and cluck and flutter about."[17]
In the 1934 Frank Capra film It Happened One Night, before Clark Gable's character Peter Warne reveals his name to Ellie Andrews (Claudette Colbert), he famously says to her: "I am the whip-poor-will that cries in the night".[18]
Elton John and Bernie Taupin's 1975 song "Philadelphia Freedom" features a flute mimicking the call of the eastern whip-poor-will and includes the lyrics "I like living easy without family ties, till the whippoorwill of freedom zapped me right between the eyes."[19]
The Pennsylvania-based Indie rock band Dr Dog released their song "Lonesome" on their 2012 album "Be the void", featuring the passage "I had my fill of the Whippoorwill / When he broke into song I shot him".[20]
The song, "Cockeyed Optimist", sung by Nellie Forbush in Rodger's and Hammerstein's South Pacific, mentions such bird, singing, "But every whip-poor-will / Is selling me a bill/ And telling me it just ain't so!"[21]
In the novel Slapstick by Kurt Vonnegut, the narrator hears the call of a whip-poor-will, which the narrator referred to as a child as "The Nocturnal Goatsucker".[22]
References
- BirdLife International. 2018. Antrostomus vociferus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T22736393A131617918. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22736393A131617918.en. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
- "Call recording".
- "Whip-poor-will". All About Birds.
- Holyoak, D.T. (2001). Nightjars and their Allies: the Caprimulgiformes. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-854987-1.
- For example, Henninger (1906) combines the old scientific name of C. carolinensis with the common name "whip-poor-will". As C. carolinensis does not occur in the area discussed, he obviously refers to C. vociferus. In other cases, the specific identity of birds may not be determinable.
- MWP (2008)
- "Tracking the Mysterious Whip-Poor-Will". WPI. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- BLI (2004)
- "Eastern Whip-poor-will Life History, All About Birds, Cornell Lab of Ornithology". www.allaboutbirds.org. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- Chesser, R. T.; Banks, R. C.; Barker, F. K.; Cicero, C.; Dunn, J. L.; Kratter, A. W.; Lovette, I. J.; Rasmussen, P. C.; Remsen Jr, J. V.; Rising, J. D.; Stotz, D. F.; Winker, K. (2010). "Fifty-first supplement to the American Ornithologists' Union Check-list of North American Birds". Auk. 127 (3): 726–744. doi:10.1525/auk.2010.127.3.726.
- Hooper, Wayne. "Sadly, call of whip-poor-will is being heard less". seacoastonline.com. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- International, BirdLife. "Red List: Northern Bald Ibis, Pink Pigeon making a comeback". BirdLife. Retrieved 23 November 2018.
- "Are Whip-poor-will populations declining? What can we do about it?". All About Birds. 1 April 2009. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- Encyclopedia of Superstitions, p. 716.
- Elizabeth Barrett Browning. "The Runaway Slave at Pilgrim's Point. Lines 55-56".
- Faulkner, William. "Barn Burning". rajuabju.com. Archived from the original on 21 May 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2011.
- Robert Frost. "A Boy's Will. 2. Ghost House".
- "Quotes from "It Happened One Night"" – via www.imdb.com.
- "American Certifications - Philadelphia Freedom" Recording Industry of America
- "Lyrics containing the term: whippoorwill". www.lyrics.com. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- https://genius.com/12259719
- Vonnegut, Kurt (1976). Slapstick, or Lonesome No More!. New York, N.Y. 10017: Dell Publishing Co., Inc. pp. 105–106. ISBN 0440580099.CS1 maint: location (link)
15. Whippoorwill a US Country Album by Blackberry Smoke featuring the title song, available on Earache Records Ltd.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to Caprimulgus vociferus |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Caprimulgus vociferus. |
- Whip-poor-will Species Account - Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- Whip-poor-will - Caprimulgus vociferus - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter