Washington State Route 202
State Route 202 (SR 202) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Washington, serving part of the Seattle metropolitan area. It runs southeasterly for 31 miles (50 km) in the Eastside region of King County, connecting Woodinville, Redmond, Fall City, and North Bend. The highway begins at SR 522 in Woodinville, intersects SR 520 in Redmond and SR 203 in Fall City, and terminates at Interstate 90 (I-90) in North Bend. The entire highway is designated as the Cascade Valleys Scenic Byway, a state scenic and recreational highway.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cascade Valleys Scenic Byway | ||||
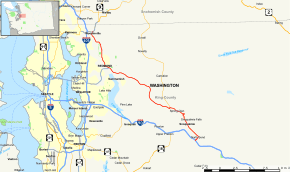 Map of western King County, with SR 202 is highlighted in red. | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Auxiliary route of US 2 | ||||
| Defined by RCW 47.17.385 | ||||
| Maintained by WSDOT | ||||
| Length | 30.53 mi[1] (49.13 km) | |||
| Existed | 1964[2]–present | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| West end | ||||
| East end | ||||
| Location | ||||
| Counties | King | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
Railroads and roads in the Sammamish River and Snoqualmie River valleys, where modern-day SR 202 runs, were built during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The early roads were incorporated into the Yellowstone Trail in the 1910s and became a state highway in 1925. SR 202 was established in 1964 as part of a new state highway system, running from Woodinville to Monroe; SR 522 was designated to the Woodinville–North Bend highway, continuing west to Seattle. By 1970, the designations were reversed, with SR 202 moved to the Woodinville–North Bend highway, and SR 522 moved to the Bothell–Monroe highway.
Route description

SR 202 begins at an interchange with SR 522 northwest of downtown Woodinville and east of the I-405 interchange. The highway travels south on 131st Avenue NE, crossing under a railroad overpass, before turning west onto NE 175th Street. SR 202 then crosses a railroad grade crossing and bridges the Sammamish River, before turning south onto Redmond–Woodinville Road. The highway travels south along the west side of the Sammamish River valley into Woodinville wine country, a district of wineries and tasting rooms south of Woodinville.[3] SR 202 turns east onto NE 145th Street and crosses over the Sammamish River, and then enters the first in a series of three roundabouts that turn the highway southward.[4][5]
SR 202 continues south along the east side of the rural Sammamish River valley and passes Sammamish River Regional Park before entering the city of Redmond. The highway travels along the western end of Education Hill and turns due south onto 164th Avenue NE while approaching downtown Redmond. SR 202 turns east onto Redmond Way at the terminus of former SR 908 and passes through Downtown Redmond near the Redmond Town Center.[6] The street crosses over Bear Creek and under a freeway interchange with SR 520 before turning southeast.[7] SR 202 continues along the edge of Marymoor Park near the north shore of Lake Sammamish, leaving Redmond and briefly entering the city of Sammamish.[5][8]
SR 202 continues into unincorporated King County, traveling east and south around the Sammamish Plateau by following the course of Patterson Creek. The highway turns east at Duthie Hill and passes through Fall City, turning north to cross the Snoqualmie River. At the north end of the bridge, SR 202 intersects SR 203 in a roundabout, forming the latter's terminus. The highway continues southeast along the Snoqualmie River, passing Fall City Airport and crossing Tokul Creek via a long hairpin turn. SR 202 passes Snoqualmie Falls, enters a roundabout at Tokul Road, and travels south across the Snoqualmie River towards downtown Snoqualmie. From Snoqualmie, it travels southeast through the Three Forks lowlands and crosses the South Fork Snoqualmie River into North Bend. The highway turns southwest onto Bendigo Boulevard and travels through the city's downtown, exiting via a crossing of the South Fork Snoqualmie River. SR 202 passes the North Bend Premium Outlets mall and intersects I-90, where it terminates at a partial dumbbell interchange.[5][8][9]
SR 202 is maintained by the Washington State Department of Transportation (WSDOT), who conduct an annual survey on its highways to measure traffic volume in terms of average annual daily traffic. In 2016, WSDOT calculated that 40,000 vehicles used SR 202 at its western terminus in Woodinville and 7,500 vehicles used it in Woodinville wine country, the highest and lowest counts along the highway, respectively.[10] The entire highway is also designated as the Cascade Valleys Scenic Byway, a state scenic and recreational highway and heritage corridor.[11][12][13]
History
The Sammamish River valley was settled in the late 19th century and served by the Seattle, Lake Shore and Eastern Railroad, built in 1889 from Bothell to North Bend,[14] traveling through Redmond, Issaquah, Fall City, and Snoqualmie.[15] By 1902, several wagon roads were built along the railroad, including a road between Fall City and North Bend,[16][17] which was incorporated into the Sunset Highway when it was designated as a state highway in 1909.[18] The road from Redmond to North Bend became part of the national Yellowstone Trail in the 1910s,[19] including a section near Redmond that was paved with bricks in 1913.[20][21] A portion of the Yellowstone Trail, along with unpaved roads from Redmond to Bothell, were designated as a state highway in 1925.[22][23] The highway was paved in the late 1920s,[16] and was incorporated into the Seattle–Fall City branch of the Sunset Highway (Primary State Highway 2) in 1937.[24][25] After the opening of the North Bend bypass in 1941, the branch highway was extended to North Bend over the former Sunset Highway.[26][27]
In 1963, the Washington State Legislature commissioned a new state highway numbering system to ease confusion over similarly-numbered routes. The new system debuted in 1964, assigning State Route 522 (SR 522) to the Seattle–Bothell–North Bend highway, and State Route 202 (SR 202) to a proposed branch of the Stevens Pass Highway between Monroe and Bothell.[28][29] By 1970, SR 522 was moved to the completed Bothell–Monroe highway, retaining the Seattle–Bothell portion, while SR 202 was designated to the remaining highway from Woodinville (east of Bothell) to North Bend.[30][31]
SR 202 was extended 0.62 miles (1 km) southwest of downtown North Bend to a new interchange with I-90 in 1978, after it was moved to a freeway bypass of North Bend.[32][33] The area around the new interchange was annexed by the city of North Bend prior to the opening of the I-90 bypass,[34] and a factory outlet mall opened at the interchange in 1990.[35] Since the early 2000s, the Washington State Department of Transportation (WSDOT) has built several roundabouts on SR 202 in Woodinville,[4] Snoqualmie,[36] Fall City,[37] and North Bend,[38] in an effort to improve the road's safety as traffic increases along the corridor.[39] Another section of SR 202 between Redmond and Sammamish was widened in 2008 to accommodate additional traffic and included the construction of a new flyover ramp at the SR 520 interchange.[40] In 2007, WSDOT also studied possible improvements to SR 202 in the Sammamish area, recommending the construction of new lanes, traffic signals, guardrails, and other projects.[41] The study's recommended projects would cost an estimated $52.9 million to complete, and were not funded by the state government.[42]
Major intersections
The entire highway is in King County.
| Location | mi[1] | km | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woodinville | 0.00 | 0.00 | Interchange | ||
| Redmond | 6.97 | 11.22 | Redmond Way | Former SR 908 | |
| 7.70 | 12.39 | Interchange | |||
| Fall City | 21.77 | 35.04 | Roundabout | ||
| North Bend | 30.53 | 49.13 | Interchange | ||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
References
- Multimodal Planning Division (February 4, 2020). State Highway Log Planning Report 2019, SR 2 to SR 971 (PDF) (Report). Washington State Department of Transportation. pp. 1144–1157. Retrieved May 16, 2020.
- "47.17.385: State route No. 202". Revised Code of Washington. Washington State Legislature. 1970. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- Whitely, Peyton (May 10, 2006). ""Wine village" plan growing". The Seattle Times. p. B1. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- Whitely, Peyton (February 10, 2006). "Woodinville intersection to be redone — in a roundabout way". The Seattle Times. p. B3. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- Google (June 3, 2017). "State Route 202" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- "SR 202: Junction SR 202 Couplet Redmond" (PDF). Washington State Department of Transportation. July 27, 2010. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- "SR 520: Junction SR 202" (PDF). Washington State Department of Transportation. March 31, 2011. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- Washington State Department of Transportation (2014). Washington State Highways, 2014–2015 (PDF) (Map). Olympia: Washington State Department of Transportation. Retrieved June 3, 2017. (Inset map)
- "SR 90 - Exit 31: Junction SR 202/Bendigo Blvd" (PDF). Washington State Department of Transportation. April 23, 2012. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- 2016 Annual Traffic Report (PDF) (Report). Washington State Department of Transportation. 2017. pp. 161–162. Retrieved May 31, 2017.
- "Washington State's Scenic Byways & Road Trips" (PDF). Washington State Department of Transportation. 2012. pp. 46–47. Retrieved July 17, 2017.
- "RCW 47.39.020: Designation of portions of existing highways and ferry routes as part of system". Revised Code of Washington. Washington State Legislature. Retrieved July 17, 2017.
- Burgess, Rebecca (May 19, 1997). "Volunteers push to preserve SR 202 corridor". Snoqualmie Valley Reporter. p. A3.
- Stein, Alan J. (November 9, 1998). "Redmond — Thumbnail History". HistoryLink. Retrieved July 2, 2017.
- "Washington" (Map). Cram's Standard American Railway System Atlas of the World. George F. Cram Company. 1901. pp. 410–411. OCLC 58932862. Retrieved July 2, 2017 – via David Rumsey Historical Map Collection.
- "Washington State's Historic State Roads: Historic Context for Island, Snohomish, King, Pierce, and Kitsap Counties" (PDF). Washington State Department of Archaeology and Historic Preservation. January 2014. pp. 144–146. Retrieved July 2, 2017.
- United States Geological Survey (October 1897). Washington: Snohomish Quadrangle (Map). 1:125,000. Reston, VA: United States Geological Survey. Retrieved July 2, 2017 – via Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection.
- Map of the state of Washington Showing State Roads—Located and Proposed (Map). Washington State Highway Commission. 1909. Retrieved July 2, 2017 – via Washington State Archives.
- "How the Roads Are". The Seattle Times. September 7, 1919. p. 4.
- Whyte, Murray (February 2, 1997). "Follow the red brick road". The Seattle Times. p. B3. Retrieved July 2, 2017.
- Red Brick Road Condition Assessment (Report). King County Department of Transportation. December 22, 2015. pp. 7–8. Retrieved July 2, 2017.
- "Chapter 26: Primary and Secondary State Highways" (PDF). Session Laws of the State of Washington, 1925. Washington State Legislature. February 18, 1925. pp. 59–60. Retrieved July 2, 2017.
- Rand McNally Official 1925 Auto Trails Map of Washington and Oregon (Map). Rand McNally and Company. 1925. Retrieved July 2, 2017 – via David Rumsey Historical Map Collection.
- "Chapter 190: Establishment of Primary State Highways" (PDF). Session Laws of the State of Washington, Twenty-Fifth Session. Washington State Legislature. March 17, 1937. p. 934. Retrieved June 1, 2017.
- Washington State Department of Highways; Rand McNally (1939). Highways of the State of Washington (Map). Olympia: Washington State Department of Highways. Retrieved July 2, 2017 – via Washington Secretary of State.
- "North Bend 'Creaks' a Bit; Moves Over for New Road". The Seattle Times. August 17, 1941. p. 11.
- Washington State Department of Highways; Rand McNally (1944). Highways of the State of Washington (Map). Olympia: Washington State Department of Highways. Retrieved July 2, 2017 – via David Rumsey Historical Map Collection.
- Prahl, C. G. (December 1, 1965). "Identification of State Highways" (PDF). Washington State Highway Commission. Retrieved June 2, 2017.
- "To End Confusion: Highways Given Different Numbers". The Seattle Times. January 26, 1964. p. 24.
- "Chapter 51: State Highways—Route Numbers" (PDF). Session Laws of the State of Washington, 1970 1st extraordinary session. Washington State Legislature. February 24, 1970. pp. 367, 380. Retrieved June 1, 2017.
- "Hearing planned on Snoqualmie Falls left turn". The Seattle Times. December 9, 1970. p. A7.
- "Annual Traffic Report, 1980" (PDF). Washington State Department of Transportation. 1980. p. 135. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- Wilson, Marshall (October 25, 1978). "It only hurts a little while, they hope". The Seattle Times. p. H1.
- Corsaletti, Louis T. (June 1, 1977). "North Bend plan: Does it reflect what people want?". The Seattle Times. p. H10.
- Corsaletti, Louis T. (August 9, 1990). "North Bend's growth prompts new hiring". The Seattle Times. p. B3.
- Cornwell, Paige (August 13, 2015). "Snoqualmie Tribe says city is building on sacred ground". The Seattle Times. p. B6. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- "SR 202 - Preston Fall City Road and Jct SR 203 - Complete July 2008". Washington State Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on August 26, 2008. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- "Two-lane Roundabout Open on SR 202 at I-90 in North Bend" (Press release). Washington State Department of Transportation. September 27, 2007. Archived from the original on December 30, 2009. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- "Tokul Roundabout: Frequently Asked Questions". City of Snoqualmie. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- Giroux, Wendy (September 23, 2008). "Gregoire, officials, commuters tout success of 202 improvements". Redmond Reporter. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- "State Route 202 Corridor Planning Study: Sahalee Way NE to Duthie Hill Road/292nd Avenue SE" (PDF). Washington State Department of Transportation. July 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 2, 2012. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- "SR 202 - Sahalee Way to Duthie Hill Road Corridor Study - Complete July 2009". Washington State Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on March 5, 2013. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
