Warrington rail crash
The Warrington rail crash occurred at Walton Junction just south of the town of Warrington in Lancashire on 29 June 1867. The collision involved a passenger train running into the back of a coal train. Eight people were killed and 33 injured. The accident resulted in changes being made to the management of points and signals.
| Warrington rail crash | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Date | 29 June 1867 11:35 |
| Location | Walton Junction, near Warrington Bank Quay railway station |
| Coordinates | 53.3615°N 2.6253°W |
| Country | England |
| Line | London and North Western Railway |
| Cause | Points incorrectly set |
| Statistics | |
| Trains | 2 |
| Passengers | 300 |
| Deaths | 8 |
| Injured | 33 |
| List of UK rail accidents by year | |
Location
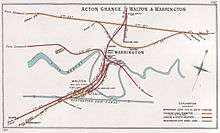
In 1867 Walton Junction was located about 1 mi (1.6 km) south of Warrington Bank Quay station just beyond Walton Bridge over the River Mersey. The junction was where the Birkenhead Railway mainline diverged from the London and North Western Railway.[1]
However, in less than 30 years after the accident the junction was made obsolete with the construction of the Manchester Ship Canal. In the 1890s a single four-track bridge was built to carry the lines of both the LNWR and the Birkenhead Junction Railway (co-owned by the LNWR and Great Western Railways) over the waterway. The Birkenhead Railway lines were consolidated into the LNWR to avoid the unnecessary cost of building separate bridges.
As the new tracks ran to the north of the original Chester-to-Birkenhead mainline on which the accident happened, the old Walton Junction ceased to have through trains and became part of a branch to a marshalling yard.
Accident
The 10:23 Liverpool Lime Street to London Euston service, which was running 10 minutes late, left Warrington Bank Quay station at 11:35 for Crewe. On approach to Walton Junction, the driver saw that a coal train ahead was being shunted onto the Chester line, but did not reduce speed because he thought that the line would be clear. However, the points were not switched back to the Crewe line, causing the London-bound passenger service to plough into the rear of the coal train. Five people were killed at the scene. Three others died later of their injuries. A further 33 were injured.
The coroner gave the following verdict: "We are unanimously of opinion that the deceased came to their deaths by neglect of duty on the part of John Rowson, pointsman, and at the same time we wish to recommend to the railway company the adoption of a new system of signalling and points at Walton Junction." Rowson was later charged with manslaughter in July 1867.
Legacy
The Board of Trade enquiry recommended that the British railway network should adopt a system whereby points were interlocked with signals.[2] This ensures that a train can only be signalled into a section when the correct route has been set for it.
References
Sources
- Official Accident report
- The Times 1867 :
- 1 July page 10 "Dreadful Railway Accident"
- 2 July page 12 "The Accident near Warrington"
- 6 July page 14 "The Fatal Railway Collision at Warrington"
- 10 July page 5 "The Fatal Railway Collision near Warrington"