Vyborg Castle
Vyborg Castle (Russian: Выборгский замок, Finnish: Viipurin linna, Swedish: Viborgs fästning) is a Swedish-built medieval fortress around which the town of Vyborg (today in Russia) evolved. The first record of the castle dates back to 1293. Currently it serves as a museum.
| Vyborg Castle | |
|---|---|
| Native names Russian: Выборгский замок Finnish: Viipurin linna Swedish: Viborgs slott | |
 View of the Vyborg Castle | |
| Type | Medieval castle |
| Location | Vyborg, Leningrad Oblast, Russia |
| Coordinates | 60°42′57″N 28°43′45″E |
| Built | 1293 |
| Built for | Torkel Knutsson |
| Current use | Museum |
 Location of Vyborg Castle in Leningrad Oblast | |
General
Vyborg Castle was one of the three major castles of Finland. It was built as the easternmost outpost of the medieval Kingdom of Sweden: it is located on the Karelian Isthmus, on a little islet in the innermost corner of the Gulf of Finland, in a tight strait which connects Suomenvedenpohja to the Bay of Viipuri. It was originally constructed in the 1290s on the site of Karelian fortress after the Third Swedish Crusade to Finland.[1] The town was originally located inside the outer fortifications of the castle, at the fortress island, but it had to be moved to its present location off of the island because of lack of space.
Iron Age History
V. A. Tjulanevs excavations in 1980`s indicated that a Karelian fortress pre-dated the castle built by the Swedes in 1293. The oldest layers of occupation have been discovered in the so-called Smith`s Courtyard. A man-made breastwork of sand with timber posts was found from this area. Also charred remains of buildings, which some were linked to the breastwork, were also found. Tjulenev suggests that the Karelian fort had a wooden tower. Tjulanev's several finds from the area include a bent sword which was dated to the period between 1130-1200.[1]
Medieval history
Construction of the next phase of the fortress started in 1293 by orders of Torkel Knutsson, Lord High Constable of Sweden, who in the 1290s made a supposed crusade against Karelia, the Third Swedish Crusade. The crusade was part of the ongoing Swedish–Novgorodian Wars, against the Russians of the Novgorod Republic. Knutsson chose the location of the new fortress to control the Bay of Vyborg, which was bordered by trading sites long used by the local population. From the bay, a navigable river passage goes inland, ultimately connecting the place with several districts, lakes, and, indirectly by portage, with rivers flowing into Lake Ladoga.
The three high-medieval Finnish "castle fiefs" were ruled until the 1360s from the castles of Turku (formerly Åbo in Swedish), Hämeenlinna (Tavastehus), and Vyborg (Viborg).
In 1364, Albert III of Mecklenburg was proclaimed king of Sweden, and in accordance with the German model he began to divide the castle fiefs, which were immense in Finland, into smaller provinces. In some instances, these new, smaller provinces were given separate bailiffs' residences which have since disappeared; this was the case with the Linnavuori castle mound in Porvoo (Borgå) and the castle of Korsholm in Ostrobothnia, near the modern-day city of Vaasa which was founded later. Only earthworks remain at these sites, but in two places, still-extant though now ruined stone strongholds were built: Raseborg Castle, in western Uusimaa (west of Helsinki), and Kastelholm Castle, in the Åland Islands.
The castle became the stronghold of the Swedish realm in the Karelian region. Throughout the centuries, it was the first defence of the kingdom against Russians. Its military and strategic status in the late Middle Ages was second only to the fortified capital Stockholm.
The castle and the large surrounding fief became a virtually autonomous principality. Its governors were usually enfeoffed with the incomes of the county. The fief of Viborg became known as a margraviate. Its governors were generally from the most powerful families of the kingdom. They enjoyed large administrative powers at a significant distance from the capital. These realities made them practically independent rulers. The castle of Savonlinna, Olavinlinna (built in the 1470s), was usually subjugated to Viborg.
Prominent men who held Viborg as their fief included Bo Jonsson (Grip), Christer Nilsson Vasa (1417–42), Karl Knutsson Bonde (1442–48, the future king), Eric Axelsson Tott (1457–81), Knut Posse (1495–97), Sten Sture the Elder (1497–99, between his regencies), Eric Bielke, and Count John of Hoya. Particularly in the 1440s and the late 15th century, the fortresses were further enlarged.
The first mention of firearms in Finland relates to Viborg castle in 1429. During the Middle Ages the Russians repeatedly besieged the castle, most famously in 1495 during the Russo-Swedish War (1495–97) while Knut Posse was governor of the castle. The situation of the defenders looked hopeless, but they were saved by the Viborg blast on 30 November 1495 (St. Andrew's Day), a mysterious explosion which scared the Russians away after they believed they had seen a Saint Andrew's cross in the sky.
 Simulation of Viborg castle ablaze in 1710, after the Russian attack in the Great Northern War.
Simulation of Viborg castle ablaze in 1710, after the Russian attack in the Great Northern War.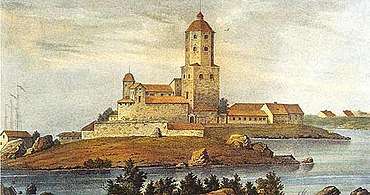 Torsten Wilhelm Forstén: Vyborg Castle 1840
Torsten Wilhelm Forstén: Vyborg Castle 1840
Modern history
In the 16th century, much was renovated and additions were made. In the 17th century, the castle was allowed to decay, as Russian danger was lessened and the border was further eastwards.
Viborg was taken by the Russians in 1710, but passed back to Finnish hands in 1812 when all of Old Finland was attached to the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland. The castle owes its present appearance to extensive restorations undertaken in the 1890s. The military of the Russian Empire used the castle until 1918 for housing administration.
Viipuri belonged to the newly independent Republic of Finland between 1917–40 and again 1941–44. As a result of border changes in World War II it was annexed by the Soviet Union in 1944.
Architecture
The main castle, located in the eastern part of the islet on its highest hill, has an irregular four-cornered layout, with the immense tower of St. Olav (Pyhän Olavin torni in Finnish) as its biggest section. It is 3–4 storeys tall, varying in places. Outer defensive works surround the main castle, following the islet's coastlines.
 View of the castle
View of the castle Walls of the castle
Walls of the castle St. Olav Tower
St. Olav Tower
See also
References
- Taavitsainen, Jussi-Pekka (1990). Ancient Hillforts of Finland. Suomen muinaismuistoyhdistyksen aikakausikirja 94. p. 240.
- Medieval castles of Finland, by Dr Carl Jacob Gardberg, state archaeologist
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vyborg Castle. |
- Photos Vyborg Castle
- Vyborg Castle, Vyborg Castle State Museum (Vyborg)
- The Association of Castles and Museums around the Baltic Sea
