Von Kármán swirling flow
Von Kármán swirling flow is a flow created by a uniformly rotating infinitely long plane disk, named after Theodore von Kármán who solved the problem in 1921.[1] This problem is used as a model for centrifugal fans or compressors. This flow is classified under the category of steady flows in which vorticity generated at a solid surface is prevented from diffusing far away by an opposing convection, the other examples being the Blasius boundary layer with suction, stagnation point flow etc.
Flow description
Consider a plane disk of infinite radius rotating at a constant angular velocity in fluid which is initially rest everywhere. The outward radial motion of the fluid near the disk due to the centrifugal force must be accompanied by an inward axial motion of the fluid towards the disk to conserve mass. Theodore von Kármán[1] noticed that the governing equations and the boundary conditions allow a solution such that and are functions of only, where are the velocity components in cylindrical coordinate with being the axis of rotation and represents the plane disk. Due to symmetry, pressure of the fluid can depend only on radial and axial coordinate . Then the continuity equation and the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations reduce to
No rotation at infinity
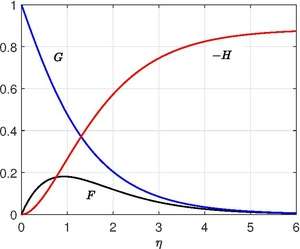
Since there is no rotation at large , becomes independent of resulting in . Hence and .
Here the boundary conditions for the fluid are
Self-similar solution is obtained by introducing following transformation,[2]
The self-similar equations are
with boundary conditions for the fluid are
The coupled ordinary differential equations need to be solved numerically and an accurate solution is given by Cochran(1934).[3] The inflow axial velocity at infinity obtained from the numerical integration is , so the total outflowing volume flux across a cylindrical surface of radius is . The tangential stress on the disk is . Neglecting edge effects, the torque exerted by the fluid on the disk with large () but finite radius is
The factor is added to account for both sides of the disk. From numerical solution, torque is given by . The torque predicted by the theory is in excellent agreement with the experiment on large disks up to the Reynolds number of about , the flow becomes turbulent at high Reynolds number.[4]
Rigid body rotation at infinity
This problem was addressed by George Keith Batchelor(1951).[5] Let be the angular velocity at infinity. Now the pressure at is . Hence and .
Then the boundary conditions for the fluid are
Self-similar solution is obtained by introducing following transformation,
The self-similar equations are
with boundary conditions for the fluid is
The solution is easy to obtain only for i.e., the fluid at infinity rotates in the same sense as the plate. For , the solution is more complex, in the sense that many-solution branches occur. Evans(1969)[6] obtained solution for the range . Zandbergen and Dijkstra[7][8] showed that the solution exhibits a square root singularity as and found a second-solution branch merging with the solution found for . The solution of the second branch is continued till , at which point, a third-solution branch is found to emerge. They also discovered an infinity of solution branches around the point . Bodoyni(1975)[9] calculated solutions for large negative , showed that the solution breaks down at . If the rotating plate is allowed to have uniform suction velocity at the plate, then meaningful solution can be obtained for .[4]
For ( represents solid body rotation, the whole fluid rotates at the same speed) the solution reaches the solid body rotation at infinity in an oscillating manner from the plate. The axial velocity is negative for and positive for . There is an explicit solution when .
Nearly rotating at the same speed,
Since both boundary conditions for are almost equal to one, one would expect the solution for to slightly deviate from unity. The corresponding scales for and can be derived from the self-similar equations. Therefore,
To the first order approximation(neglecting ), the self-similar equation [10] becomes
with exact solutions
These solution are similar to an Ekman layer[10] solution.
Two rotating coaxial disks
This problem was addressed by George Keith Batchelor(1951),[5] Keith Stewartson(1952)[13] and many other researchers. Here the solution is not simple, because of the additional length scale imposed in the problem i.e., the distance between the two disks. In addition, the uniqueness and existence of a steady solution are also depend on the corresponding Reynolds number .
Then the boundary conditions for the fluid are
In terms of , the upper wall location is simply . Thus, instead of the scalings
used before, it is convenient to introduce following transformation,
so that the governing equations become
with six boundary conditions
and the pressure is given by
Here boundary conditions are six because pressure is not known either at the top or bottom wall; is to be obtained as part of solution. For large Reynolds number , Batchelor argued that the fluid in the core would rotate at a constant velocity, flanked by two boundary layers at each disk for and there would be two uniform counter-rotating flow of thickness for . However, Stewartson predicted that for the fluid in the core would not rotate at , but just left with two boundary layers at each disk. It turns out, Stewartson predictions were correct.
There is also an exact solution if the two disks are rotating about different axes but for .
Applications
Von Kármán swirling flow finds its applications in wide range of fields, which includes rotating machines, filtering systems, computer storage devices, heat transfer and mass transfer applications, combustion-related problems, planetary formations, geophysical applications etc.
References
- Von Kármán, Theodore (1921). "Über laminare und turbulente Reibung" (PDF). Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik. 1 (4): 233–252. doi:10.1002/zamm.19210010401.
- Landau, Lev D. Fluid Mechanics. ISBN 978-0750627672.
- Cochran, W.G. (1934). "The flow due to a rotating disc". Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. 30.
- Schlichting, Hermann (1960). Boundary Layer Theory. New York: McGraw-hill.
- Batchelor, George Keith (1951). "Note on a class of solutions of the Navier–Stokes equations representing steady rotationally-symmetric flow". The Quarterly Journal of Mechanics and Applied Mathematics. 4: 29–41. doi:10.1093/qjmam/4.1.29.
- Evans, D. J. "The rotationally symmetric flow of a viscous fluid in the presence of an infinite rotating disc with uniform suction." The Quarterly Journal of Mechanics and Applied Mathematics 22.4 (1969): 467-485.
- Zandbergen, P. J., and D. Dijkstra. "Non-unique solutions of the Navier-Stokes equations for the Karman swirling flow." Journal of engineering mathematics 11.2 (1977): 167-188.
- Dijkstra, D., and P. J. Zandbergen. "Some further investigations on non-unique solutions of the Navier-Stokes equations for the Karman swirling flow." Archiv of Mechanics, Archiwum Mechaniki Stosowanej 30 (1978): 411-419.
- Bodonyi, R. J. "On rotationally symmetric flow above an infinite rotating disk." Journal of Fluid Mechanics 67.04 (1975): 657-666.
- Batchelor, George Keith (2000). An introduction to fluid dynamics. Cambridge university press. ISBN 978-0521663960.
- Drazin, Philip G., and Norman Riley. The Navier–Stokes equations: a classification of flows and exact solutions. No. 334. Cambridge University Press, 2006.
- Hewitt, R. E., P. W. Duck, and M. R. Foster. "Steady boundary-layer solutions for a swirling stratified fluid in a rotating cone." Journal of Fluid Mechanics 384 (1999): 339-374.
- Stewartson, K. (1953). "On the flow between two rotating coaxial disks". Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. 49 (2): 333. doi:10.1017/S0305004100028437.
Bibliography
- Von Kármán, Theodore (1921). "Über laminare und turbulente Reibung" (PDF). Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik. 1 (4): 233–252. doi:10.1002/zamm.19210010401.
- Batchelor, George Keith (1951). "Note on a class of solutions of the Navier-Stokes equations representing steady rotationally-symmetric flow". The Quarterly Journal of Mechanics and Applied Mathematics. 4: 29–41. doi:10.1093/qjmam/4.1.29.
- Stewartson, K. (1953). "On the flow between two rotating coaxial disks". Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. 49 (2): 333. doi:10.1017/S0305004100028437.
- Batchelor, George Keith (2000). An introduction to fluid dynamics. Cambridge university press. ISBN 978-0521663960.
- Landau, Lev D. Fluid Mechanics. ISBN 978-0750627672.
- Schlichting, Hermann (1960). Boundary Layer Theory. New York: McGraw-hill.