Venezuelan lowland rabbit
The Venezuelan lowland rabbit (Sylvilagus varynaensis), also known as the Barinas wild rabbit, is a cottontail rabbit species found in western Venezuela.[2] Its diet consists in large measure of plants of the genus Sida.[1] It is found in lowland savannas close to dry forests within the Llanos ecoregion.[1] It is the largest of only three leporids known from South America.[2] Head and body length is about 44 cm, with females being slightly larger.[1] Reproduction takes place over three quarters of the year, with an average of 2.6 embryos per litter, but most commonly during September through December. The gestation period is 35 days.[1] Possible threats to the species include habitat destruction by deforestation and agricultural conversion, competition with grazing livestock and hunting.[1]
| Venezuelan lowland rabbit | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Lagomorpha |
| Family: | Leporidae |
| Genus: | Sylvilagus |
| Species: | S. varynaensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Sylvilagus varynaensis Durant & Guevara, 2001 | |
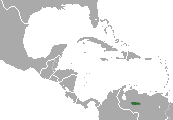 | |
| Venezuelan lowland rabbit range | |
References
- Durant, P. & Guevara, M. A. (2008). "Sylvilagus varynaensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T41311A10439391. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T41311A10439391.en. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- Hoffman, R.S.; Smith, A.T. (2005). "Order Lagomorpha". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 211. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
