Vertical Offshore Reference Frames
Vertical Offshore Reference Frames (VORF) is a set of high resolution surfaces which together define the vertical datum for hydrographic surveying and charting in the United Kingdom and Ireland.[1] The following surfaces are included:
- Chart Datum (CD)
- Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT)
- Mean Sea Level (MSL)
- Mean Low Water Springs (MLWS)
- Mean High Water Springs (MHWS)
- Highest Astronomical Tide (HAT)
- Land datums including Ordnance Datums Newlyn, Belfast and Poolbeg
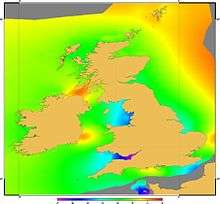
All the surfaces are modelled with respect to the terrestrial reference frame used for satellite navigation (GNSS) positioning, ETRS89. Thus VORF directly permits the use of high precision GNSS in hydrographic survey, and also allows the capability of transforming vertical data between the different datums.
Development
The VORF project started in 2005 as a collaborative research project, sponsored by the UKHO, with a consortium comprising Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory, DTU, and led by University College London.[2] It was delivered to the UKHO in 2008. VORF was developed using satellite altimetry, tide gauge observations, geoid and tidal modelling, and GNSS observations. VORF meets its target inshore accuracy of 10 cm in most of the domain of applicability.[3]
References
- "Vertical Offshore Reference Frames". Ucl.ac.uk. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- "Joining Up Land and Sea". Hydro-international.com. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- Iliffe, J. C.; Ziebart, M. K.; Turner, J. F.; Talbot, A. J.; Lessnoff, A. P. (2013). "Accuracy of vertical datum surfaces in coastal and offshore zones". Survey Review. 45 (331): 254–262. doi:10.1179/1752270613Y.0000000040.