Ueno Route
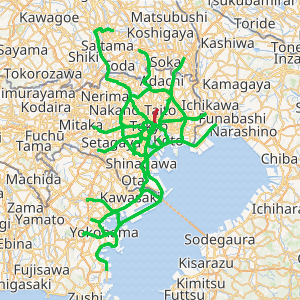
The Ueno Route (上野線, Ueno-sen), signed as Route 1, is one of the tolled routes of the Shuto Expressway system serving the Greater Tokyo Area. It is one two expressways signed as Route 1 in the system, the other expressway signed as Route 1 is the Haneda Route. The route is a 4.4-kilometer (2.7 mi) long radial highway running northeast from the ward of Chūō in central Tokyo to the ward of Taitō. It connects Tokyo's Inner Circular Route in central Tokyo to the Ueno area and Ueno Station, a major rail hub, and National Route 4, which connects the Kantō region to the Tōhoku region.
首都高速1号上野線 | |
|---|---|
| |
| Route information | |
| Maintained by Metropolitan Expressway Company Limited | |
| Length | 4.4 km (2.7 mi) |
| Existed | 1963–present |
| Major junctions | |
| South end | Edobashi Junction in Chūō, Tokyo |
| North end | Iriya entrance/exit in Taitō, Tokyo |
| Highway system | |
| National highways of Japan Expressways of Japan | |
Route description
The Ueno Route begins at Edobashi Junction with the Inner Circular Route in Chūō City as an indirect continuation north for the Haneda Route, the other expressway signed as Route 1 on the Shuto Expressway network. From this southern terminus, it travels northeast out of Chūō City, crossing in to Taitō. The expressway is paralleled by National Route 4 (known in this area as Shōwa-dōri) along its route through Tokyo, which acts as a frontage road for the Ueno Route. Every exit and entrance point to the expressway beyond Edobashi Junction connects directly to National Route 4, which links the expressway to the rest of the local street network. The Ueno Route merges into National Route 4 at Iriya Station. From there, the roadway continues north solely as National Route 4, leaving the Shuto Expressway network.[1]
Like other Shuto Expressway routes within the Central Circular Route, the speed limit is set at 60 km/h along the Ueno Route.[2]
History
The first section of the Ueno Route between Edobashi and Honchō was opened to traffic on 21 December 1963. The second section to be completed between Honchō and Iriya was finished on 31 May 1969.[3] Plans were made to extend the radial route north to the Central Circular Route in 1992; however, they have been shelved due to geographic constraints and a lack of support among residents of the area that would be impacted by an extended Ueno Route.[4]
Junction list
The entire expressway is in Tokyo
| Location | km[5] | mi | Exit | Name | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chūō | 0.0 | 0.0 | — | Edobashi | Southern terminus; northbound entrance, southbound exit | ||
| 0.2– 1.0 | 0.12– 0.62 | 181/182 | Honchō | ||||
| Taitō | 2.7 | 1.7 | 183 | Ueno | Northbound exit, southbound entrance | ||
| 4.0 | 2.5 | 185 | Iriya | Northern terminus, roadway continues as National Route 4 | |||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||||
See also

References
- "高速1号上野線". Metropolitan Expressway (in Japanese). Retrieved 10 November 2019.
- "Tokyo Shutoko Expressway: Japan's Busiest Road Network". Retrieved 8 November 2019.
- "首都高の歴史". Metropolitan Expressway (in Japanese). Retrieved 8 November 2019.
- "なぜ地味なのか首都高上野線 幻のII期計画、謎のルート" (in Japanese). 31 May 2015. Retrieved 10 November 2019.
- Google (10 November 2019). "Ueno Route" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved 10 November 2019.
External links

