Udet U 11 Kondor
The Udet U 11 Kondor was a German four-engined airliner designed and built by Udet Flugzeugbau, only one was built.[1][2]
| U 11 Kondor | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Eight-seat airliner |
| National origin | Germany |
| Manufacturer | Udet Flugzeugbau |
| First flight | 19 January 1926 |
| Primary user | Deutsche Luft Hansa |
| Number built | 1 |
Design and development
The U 11 Kondor was an open-cockpit, metal-fuselage, wooden high-wing monoplane powered by four 100 hp (75 kW) Siemens-Halske Sh 12 piston engines in shaft-driven pusher configuration.[1] It had a crew of three and room for eight passengers with a dangerously close clearance between the pusher propellers and rear passenger door, which caused one fatality.[1] The aircraft was tested by Harry Rother near Munich, finding a tail-heavy condition which required addition of larger control surfaces. The only U 11 was first flown on 19 January 1926 and was refused by Deutsche Luft-Reederei then purchased by Deutsche Luft Hansa, crashing on its delivery flight. The cost to develop and produce the prototype was a factor in the collapse of the company, which was then taken over by Bayerische Flugzeugwerke.[1]
Specifications (U 11)
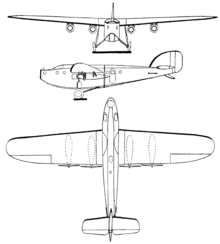
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Capacity: 8
- Length: 16 m (52 ft 6 in)
- Upper wingspan: 22 m (72 ft 2 in)
- Height: 4 m (13 ft 1 in)
- Wing area: 70 m2 (750 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 3,370 kg (7,430 lb)
- Gross weight: 4,572 kg (10,080 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 300 kg
- Powerplant: 4 × Siemens-Halske Sh 12 9-cyl. air-cooled radial piston engines, 75 kW (100 hp) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 152 km/h (94 mph, 82 kn)
- Cruise speed: 135 km/h (84 mph, 73 kn)
- Service ceiling: 3,190 m (10,470 ft)
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Stout 3-AT A similar all-metal three-engine design developed in America
- Fokker F.VII German airliner
References
Notes
- Orbis 1985, p. 3035
- Jean-Denis G.G. Lepage. Aircraft of the Luftwaffe, 1935-1945: An Illustrated Guide. p. 28.
Bibliography
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985). Orbis Publishing.