Udet U 1
The Udet U 1 is a single seat monoplane built by the German Ace Ernst Udet.
| U 1 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The Siemens-Halske Sh 4 powered U 10 | |
| Role | Monoplane |
| National origin | Germany |
| Manufacturer | Udet Flugzeugbau |
| Designer | Hans Henry Herrmann |
| First flight | May 1922 |
| Number built | 1 |
Design and development
In the summer of 1921, a new aviation company was formed using the WWI German flying ace, Ernst Udet's name. William Pohl from Milwaukee, Hans Henry Herrmann and Erich Scheuermann joined the company to fund the aircraft before wartime treaty restrictions were lifted on aircraft production with the intent of building an inexpensive aircraft for the American market.[1][2][3] The builders produced and flew the U 1 five months before the formation of the Udet Flugzeubau GmbH company.[4]
The design was a single seat low wing, open cockpit monoplane with conventional landing gear. The aircraft was large enough to accommodate two passengers, but did not have enough power for more than one person.[5] The company fell into mismanagement, later becoming part of Bayerische Flugzeugwerke, later known as Messerschmitt.[6]
Variants
- Udet U 1
- Initial variant, as described. One produced.
- Udet U 2
- Two seat production variant with Haacke HFM-2a flat-twin.[7] Four produced.
- Udet U 4
- 30 kW (40 hp) Siemens-Halske Sh 4 five cylinder radial powered.
- Udet U 6
- 62 kW (83 hp) Siemens-Halske Sh 5 radial powered with rounded rudder. Seven built.
- Udet U 10
- 30 kW (40 hp) Siemens-Halske Sh 4 five cylinder radial powered. 10.5 m (34 ft) wingspan.
- Udet U 10a
- Floatplane variant
Aircraft on display
- German Museum of Technology - 1924 U 10
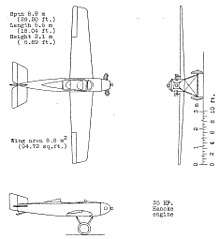
Specifications (U 1)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 5.33 m (17 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 8.9 m (29 ft 2 in)
- Height: 1.7 m (5 ft 7 in)
- Wing area: 8 m2 (86 sq ft)
- Gross weight: 200 kg (441 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Haacke HFM-2 air-cooled two-cylinder, horizontally opposed piston engine, 16 kW (22 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 180 km/h (110 mph, 97 kn)
- Endurance: 2.5 hr
References
- Armand van Ishoven. The fall of an eagle: the life of fighter ace Ernst Udet. p. 90.
- Nina Berman. Impossible Missions German Economic, Military, and Humanitarian Efforts. p. 109.
- Joanne Gernstein London. Fly Now!: A Colorful Story of Flight from Hot Air Balloon to the 777. p. 61.
- William Green. Augsburg Eagle: the story of the Messerschmitt 109. p. 9.
- Jean-Denis G.G. Lepage. Aircraft of the Luftwaffe, 1935-1945: An Illustrated Guide. p. 28.
- Peter Dancey. Lufthansa to Luftwaffe - Hitlers Secret Air Force.
- "The Udet Sporting Two-seater". Flight. XV (10): 122. 8 March 1923.