USS Calhoun (1851)
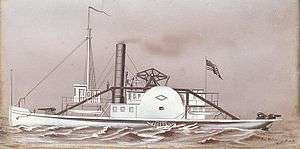
USS Calhoun was a captured Confederate steamer and blockade runner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.
 USS Calhoun | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | USS Calhoun |
| Laid down: | date unknown |
| Launched: | 1851 at New York City |
| Commissioned: | March 19, 1862 |
| Decommissioned: | May 6, 1864 |
| Renamed: |
|
| Stricken: | 1864 (est.) |
| Captured: | by Union Navy forces, January 23, 1862 |
| Fate: | sold on June 4, 1864 to the Union Army |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Gunboat |
| Displacement: | 508 long tons (516 t) |
| Length: | Unknown |
| Beam: | Unknown |
| Draft: | Unknown |
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | Unknown |
| Complement: | Unknown |
| Armament: | 2 × 32-pounder guns, 1 × 30-pounder rifled gun |
Calhoun was put into service as a gunboat by the Union Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
Service history
.jpg)
Calhoun was built in New York in 1851. Her yard name was Cuba, but this was changed to Calhoun before the vessel entered service. Prior to the Civil War, the steamer was employed in merchant service along the United States East Coast.
Confederate service
With the outbreak of the Civil War in 1861, Calhoun was commissioned by the Confederate Government as a privateer on 15 May 1861; Capt. John Wilson and his 150 men. During the next five months, the vessel captured and sent in six prizes. She was then chartered by the Confederate States Navy and placed under the command of Lt. J. H. Carter, CSN. As CSS Calhoun, she served as flagship for Commodore G. N. Hollins, CSN, during a successful engagement between his fleet and five Union ships at the Head of the Passes into the Mississippi River, 12 October 1861. Calhoun was captured off South West Pass, Louisiana, on 23 January 1862 by the schooner Samuel Rotan, a tender to the steam frigate USS Colorado.[1]
Union Navy service
Commissioned as USS Calhoun for Federal service under Lieutenant J. E. De-Haven, she joined the West Gulf Blockading Squadron on March 19, 1862.
In her service on patrol off the Passes of the Mississippi River, Calhoun established herself as one of the most successful blockading ships, taking part in the capture of 13 ships before May 5, 1862, when she steamed up the Mississippi River for duty in Lake Ponchartrain.
Here she continued to add to her score, chasing and capturing a steamer, a gunboat, two schooners, and a sloop. Later in the year, she sought out and captured another sloop in Atchafalaya Bay.
In early November, Calhoun stood up Berwick Bay and Bayou Teche with two other steamers to engage Confederate shore batteries and the steamer CSS Cotton, barricaded on the Teche. Remaining in the Berwick Bay area on patrol, Calhoun and her consorts climaxed their extremely successful operations on April 14, 1863 when they attacked the cotton-clad steamer CSS Queen of the West. One shot at long range from Calhoun turned the Confederate ship into a torch, and a major threat to Union forces in the area was destroyed.
Calhoun continued to add to her distinguished record with her participation in the attack on Fort Butte-a-la-Rose on April 20, and in August was ordered to base on Ship Island, Mississippi, from which she continued her active and aggressive bombardments of shore positions, and took four more prizes.
In the furious assault on Fort Powell the last two weeks of February 1864, Calhoun flew the flag of Admiral David G. Farragut.
Later service
Turned over to the United States Marshal at New Orleans, Louisiana, on May 6, 1864, Calhoun was sold on June 4 to the Union Army. She served as the Army steamer General Sedgewick for the rest of the Civil War. Sold in 1865, she regained her old name and had a long subsequent career as the SS Calhoun.
See also
- United States Navy
- American Civil War
- Confederate States Navy
- Ships captured in the American Civil War
- Bibliography of American Civil War naval history
References
- "Calhoun". Naval History and Heritage Command. United States Navy.
This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.