U.S. National Whitewater Center
The U.S. National Whitewater Center (USNWC) is an outdoor recreation and athletic training facility for ice skating, whitewater rafting, kayaking, canoeing, rock climbing, mountain biking, and hiking which opened to the public on November 4, 2006. The Center is located in Charlotte, North Carolina on approximately 1,300 acres (530 ha) of land adjacent to the Catawba River, with more than 45 miles (72 km) of developed trail.[1][2]
| About | |
|---|---|
| Locale | Charlotte, North Carolina, USA |
| Managing agent | U. S. National Whitewater Center |
| Main shape | Two Loops |
| Pumped | 7 pumps (usually 6 or 3) |
| Surf wave | Entrance Exam, Dave's Dilemma, Shut Down |
| Opening date | November 4, 2006 |
| Stats | |
| Length | Slalom: 300 metres (984 ft) Long: 550 metres (1,804 ft) |
| Drop | 6.4 metres (21 ft) |
| Slope | Slalom: 2.1% (113 ft/mi) Long: 1.2% (67 ft/mi) |
| Flowrate | Slalom: 15 m3/s (530 cu ft/s) Long: 19 m3/s (670 cu ft/s) |
| usnwc | |
The creators of the Center were inspired by the Penrith Whitewater Stadium built for the 2000 Olympics. The Center's primary feature is the world's largest and most complex recirculating artificial whitewater river. The facility cost $38 million to build, and costs $6.8 million per year to operate.[2] The river channels were designed by three-time Olympian Scott Shipley.[3]
In June 2016, prompted by the death of a teenage park-goer from Ohio, the USNWC voluntarily closed the park's whitewater channels following the discovery of Naegleria fowleri, in the park's water.[4] New methods for water quality maintenance were installed before the whitewater reopened in 2017. In the meantime, land and Catawba river activities remained open for business, and the rapids reopened for a brief period of time at the end of the summer in 2016 after extensive cleaning and draining.[5]
Whitewater channels
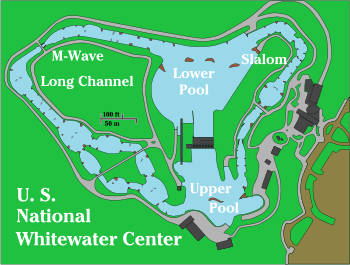
The Center's recirculating river is filled with 12 million gallons of well water, which is cleaned every 24 hours by a filtration and ultraviolet system.[1][6] The whitewater portion of the river has a total of 3,750 feet (1,140 m) of channel divided between two channels: the Olympic-standard slalom competition channel and the longer wilderness channel, which splits around an island at the top. The rapids are Class II to IV and can be navigated via canoe, kayak or a guided raft. The different channels are linked by an Upper and Lower Pool which are connected via a moving-belt boat-lift conveyor.[7]
The facility is equipped with a total of seven, 620hp submersible pumps manufactured by Flygt. Each channel is watered by three of the pumps. Six pumps will water both channels simultaneously. The electricity cost of each pump is about US$45 per hour. When only one channel is used, a low pressure, air bag actuated, Obermyer Gate separates the top of either the Wilderness or Competition Channel from the upper pond thus preventing water from entering. Since both channels have the same drop, 6.4 metres (21 ft), the extra length of the Wilderness Channel gives it a gentler slope.[1]
Most of the water diverters are natural boulders cemented in place, but there is some use of moveable plastic bollards attached to the bottom. There are five barn door diverters hinged to the channel sides and positioned by hydraulic pistons, two above the M-Wave on the long channel, and three in the slalom competition channel. The M-Wave is designed to replicate the famous M-Wave in an irrigation channel near Montrose, Colorado.[1]
The National Office of USA Canoe/Kayak, which manages the US canoe and kayak Olympic teams, used to be located in Charlotte because of its proximity to the USNWC.[8] In April 2011, the team trials for the US national whitewater team were held at USNWC.[9] The organization has since moved to Oklahoma City as of December 2011.[10]
Activities
Water Sports[11]
- Whitewater Rafting - Rafters with trained raft guides can paddle Class II, III, and IV rapids on the artificial whitewater channels. In 2010, the USNWC had 100,000 rafters.
- Whitewater Kayaking - Whitewater kayakers, from beginner to expert, can paddle, with or without instructors, alongside Olympic contenders. Periodic slalom races are scheduled for all ages and all skill levels.
- Flatwater Kayaking - Flatwater kayaking is offered on the Catawba River, which is adjacent to the USNWC's property.
- Stand-Up Paddle Boarding - Stand-Up Paddle Boarding is new to the USNWC in 2011. Participants stand on a board similar to a surf board and use a long paddle to maneuver along the Catawba River.
Land Sports[11]
- Ice Skating - Starting in 2019 the USNWC will host one of the largest outdoor ice rinks on the east coast. Skaters can enjoy an ice trail or free skate on 17,000 sq. ft of ice. Located in the Upper Pond of the Whitewater Center, the skating environment features three distinct programming areas and an on-ice Airstream serving hot and cold beverages with seating area.
- Mountain Biking - The USNWC has over 35 miles (56 km) of trails, ranging from beginner to advanced trails. Bikers can bring their own bikes and helmets or rent equipment from the USNWC.
- The Trail System - The USNWC has over 35 miles (56 km) of trails which are shared by bikers, runners, and walkers. The trails are used for various races including the Whitewater Race Series and the XTERRA Whitewater Trail Race and Triathlon. Bikers are asked to observe the "Rules of the Trail" as established by the International Mountain Bicycling Association.[12] The Tarheel Trailblazers, a Charlotte based mountain biking group, assists in the development and maintenance of the trails.[13]
- Rock Climbing - The USNWC's climbing center is one of the largest outdoor climbing centers in the world. The open-air climbing wall has over 40 roped climbs and reaches a height of 46 feet (14 m).
Aerial Sports[11]
- Canyon Crossing - The Canyon Crossing opened as a new activity in spring 2011. The Canyon Crossing consists of a circuit of sky bridges with five different aerial challenges that span the south ridge gorge at heights of over 50 feet (15 m). At the last platform is a 250-foot (76 m) zip-line which returns participants back across the gorge.
- Mega Zip - The MegaZip, which opened in 2009, a 1,123-foot (342 m) zip-line which begins at the top of a 46-foot (14 m) tower, goes over the whitewater river and ends at Hawk Island.
- Mega Jump - The Mega Jump is a controlled free fall from a 46-foot (14 m) tower. The Mega Jump, which opened in 2010, utilizes the POWERFAN assisted free fall system, technology that was pioneered by the film industry.[14]
- Adventure Course - The Adventure Course is an aerial obstacle course 20 feet (6 m) high in the trees.
- Canopy Tour - The Canopy Tour, which opened in 2011 and goes along with the recent demand for ecotourism, consists of 14 tree platforms linked by seven zip-lines, multiple sky bridges, and other aerial challenges. The Canopy Tour reaches heights in excess of 60 feet (18 m) and goes across wetlands and a 90-foot (27 m) deep canyon, along the Catawba River and through portions of the Historic Tuckaseegee Ford and Trail.[15] Guests are accompanied by two trained guides who provide educational information about the region of participants as they go from tree platform to tree platform.
Gallery
 Six pumps fill the Upper Pool.
Six pumps fill the Upper Pool. Competition channel upstream from the bridge.
Competition channel upstream from the bridge. Competition channel bridge drop.
Competition channel bridge drop. Competition channel downstream from the bridge.
Competition channel downstream from the bridge. Plastic bollards where the Competition channel turns left.
Plastic bollards where the Competition channel turns left. Left turn followed by Big drop and another left.
Left turn followed by Big drop and another left. Big drop at the bottom of the left turn.
Big drop at the bottom of the left turn. Slalom gate on the right split of the Wilderness channel, from the bridge.
Slalom gate on the right split of the Wilderness channel, from the bridge.
References
- Willoughby, Scott (2006-11-07). "Against the flow". Denver Post, November 7, 2006. Retrieved on 2010-12-31 from http://www.denverpost.com/search/ci_4613891.
- Stevenson, Morris (2008-08-08). "Charlotte Whitewater Park". Franklin News-Post, August 8, 2008. Retrieved on 2011-01-05 from http://www.thefranklinnewspost.com/article.cfm?ID=11524.
- Scott Shipley resume
- http://www.charlotteobserver.com/news/local/article85846642.html
- "USNWC Response FAQ | U.S. National Whitewater Center". usnwc.org. Retrieved 2016-07-15.
- Whitmire, Tim (2006-07-01). "$32 million, 12 million gallons bring rapids to Charlotte". The Telegraph. Associated Press.
- Greenstein, Leah. "World's Largest Whitewater Park". WetDawg. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
- http://usack.org/about-usa-canoe-kayak/staff-directory
- http://usack.org/news/2011/04/18/usa-canoe-kayak-announces-the-2011-national-slalom-team/41890. Retrieved July 1, 2011.
- http://www.teamusa.org/USA-Canoe-Kayak/Features/2011/December/13/USA-Canoe-Kayak-Announces-Relocation-of-its-Headquarters-to-Oklahoma-City
- "USNWC Homepage". Ettain Group. Retrieved 2007-05-04.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20140218230514/https://www.imba.com/about/rules-trail
- http://www.tarheeltrailblazers.com/index.cfm
- http://www.powerfan.co.uk/
- http://www.cmhpf.org/surveys&rtuckaseegee.htm
Bibliography
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to U.S. National Whitewater Center. |
.jpg)