Typhoon Hagupit (2020)
Typhoon Hagupit, known in the Philippines as Severe Tropical Storm Dindo, was a Category 1 typhoon that heavily impacted Eastern China in August 2020. It was the fourth named storm and the second typhoon of the annual typhoon season. The JMA began monitoring a tropical depression that developed in the Philippine Sea on August 1, with PAGASA assigning the name “Dindo” to the storm, later that day it strengthened into a tropical storm, according to the JMA. PAGASA issued its final advisory on Dindo early on August 3, as it moved out of their area of responsibility. Hagupit intensified into a typhoon on August 3 and grew a large eye, before making landfall in Wenzhou, China at 17:00 UTC that day at peak intensity. Hagupit began to weaken over China before dissipating on August 5.
| Typhoon (JMA scale) | |
|---|---|
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
 Hagupit approaching China near peak intensity on August 3. | |
| Formed | July 31, 2020 |
| Dissipated | August 5, 2020 |
| Highest winds | 10-minute sustained: 130 km/h (80 mph) 1-minute sustained: 140 km/h (85 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 975 hPa (mbar); 28.79 inHg |
| Fatalities | 12 |
| Damage | $411 million (2020 USD) |
| Areas affected | Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan, East China, Korean Peninsula |
| Part of the 2020 Pacific typhoon season | |
Hagupit caused over a foot of rainfall in portions of Eastern China. Hagupit caused 12 fatalities, however, damage totals remain unknown as of August 11.
Meteorological history
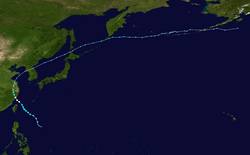
On August 1, the JMA began monitoring a weak tropical depression (designated by PAGASA as a low-pressure area) that developed in the northern portion of the Philippine Sea. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center then gave a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert on the system, with PAGASA later assigning the name "Dindo" to the tropical depression. [1] Later, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center upgraded Dindo into a tropical depression and designated it 03W. Dindo intensified into a tropical storm on August 1 according to the Japan Meteorological Agency, and assigned it the international name Hagupit. Hagupit then began intensifying in the Philippine Sea, reaching winds of 75 kph (40 mph) late on August 1. By August 2, Hagupit continued to strengthen even further south of Okinawa in Japan. Hagupit was upgraded by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) to a severe tropical storm in mid-August 2. Hagupit continued to intensify, reaching maximum sustained winds close to Category 1 at the beginning of August 3. As Hagupit (locally named "Dindo") exited the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), the PAGASA issued its final bulletin on the system. North of the island of Taiwan, Hagupit intensified into a Category 1 typhoon. Typhoon Hagupit also formed a large eye in its center as it approached China.[2] At around 17:00 UTC, Hagupit made landfall in Wenzhou, China, with winds of 85 mph and pressure of 975 mbar (hPa). After its landfall, Hagupit managed to maintain category 1 for another 6 hours, but soon after Hagupit quickly weakened over Chinese Territory. During mid-August 4, JTWC downgraded Hagupit into a tropical depression, but JMA still monitored Hagupit as a tropical storm. At 20:00 UTC, JTWC issued the final Warning on Hagupit at hundred miles about Seoul, South Korea. [3]
Preparations and impact
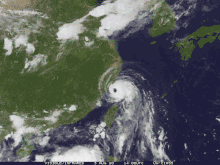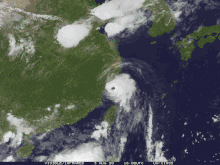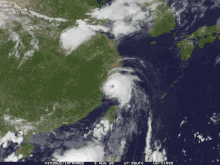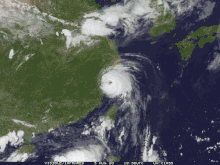
Taiwan
The Central Weather Bureau posted a heavy rain warning for portions of Taiwan. Hagupit dropped heavy precipitation up to 3.15 inches (80 mm) in parts of the country. [4]
China

In advance of Hagupit, Chinese officials ordered the evacuation of areas vulnerable to flooding.[5] At least 200,000 people evacuated to shelters in Wenzhou.[6]
Hagupit caused torrential rainfall over portions of China peaking at 13.11 inches (333 mm) in the Jingshan district of Wenzhou.[7] Waves up to 14 ft. (4.2 m) were reported, in association with Hagupit.[8] Over 830,000 customers lost power in China. A 62-year-old woman was killed when she fell 11 stories out of a broken window in Yuhuan.[9] Hagupit killed 12 people in China. Direct economic losses in Wenzhou reached ¥2.858 billion (US$411 million).[10]
Elsewhere
Hagupit brought tropical storm-force winds to the southern portion of the Ryukyu Islands of Japan. Fortunately, no injuries or damage have been reported as of August 11.[11]
In the Korean Peninsula, another round of torrential rainfall caused by Hagupit worsened already severe flooding in the area. Up to 5.7 inches (145 mm) of rain was reported in the South Korean city of Suwon.[12]
See also
References
- "PAGASA-DOST on Twitter: "At 8:00 PM today, the Low Pressure Area east of Cagayan develop into Tropical Depression #DindoPH. Severe Weather Bulletin will be issued starting at 11:00 PM tonight." / Twitter". Twitter. Retrieved 2020-07-31.
- "NASA finds an eye and giant 'tail' in Typhoon Hagupit".
- "Hagupit 2020 - Hurricane and Typhoon Updates".
- "Typhoon Hagupit warning lifted, but heavy rain still forecast - Focus Taiwan".
- "Vulnerable eastern China areas evacuated ahead of Typhoon Hagupit".
- "Hagupit lashes eastern China with flooding rain, strong winds".
- "Tropical storm heading away from the city".
- "Heavy rains hit eastern China from weakening tropical storm".
- "Typhoon exposes'tofu-dreg project' in E. China".
- Zhang Yanling (August 6, 2020). 浙江温州因台风受灾人口79.1万人 直接经济损失28.58亿元 [791,000 people affected by typhoon in Wenzhou, Zhejiang; direct economic losses are 2.858 billion yuan]. China News Service (in Chinese). Retrieved August 12, 2020.
- "Dindo intensifies into tropical storm".
- "3 dead, 3 still missing after boats capsize amid severe flooding in South Korea".
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Typhoon Hagupit (2020). |