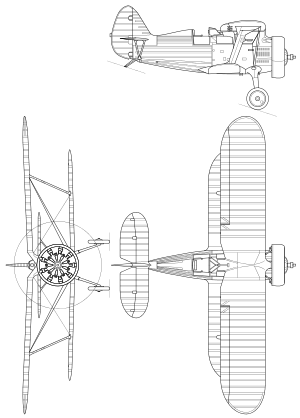
Polikarpov I-15
The Polikarpov I-15 (Russian: И-15) was a Soviet biplane fighter aircraft of the 1930s. Nicknamed Chaika (Russian: Чайка, "Seagull") because of its gulled upper wings,[2][3] it was operated in large numbers by the Soviet Air Force, and together with the Polikarpov I-16 monoplane, was one of the standard fighters of the Spanish Republicans during the Spanish Civil War, where it was called Chato (snub-nose).[4]
| I-15 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| I-15bis | |
| Role | Fighter |
| Designer | Nikolai Nikolaevich Polikarpov |
| First flight | October 1933 |
| Status | retired |
| Primary user | Soviet Air Force |
| Produced | 1934–1937[1] |
| Number built | 3,313 (plus 3,437 of I-153)[1] |
| Developed from | Polikarpov I-5 |
| Variants | Polikarpov I-153 |
Design and development
The design for the 14th fighter for the VVS, the I-14, started as an advanced (for the era) monoplane under the direction of Andrei Tupolev. He grew concerned that the design would not mature, and ordered two backup biplane designs as the I-14A and B just to be safe. Polikarpov had just been released from prison in August 1932, and was handed the I-14A project. When both the I-14 and I-14A were ordered into production, Polikarpov's design, a development of the I-5 fighter became the famous I-15.
The first flight was made in October 1933 with V.P. Chkalov at the controls, powered by an imported Wright R-1820 Cyclone engine.[5] The I-15, also known by its development name TsKB-3, was a small biplane fighter with a gulled upper wing. The single bay wings were of wooden construction, while the fuselage was of mixed steel and duralumin construction, with a fabric covered rear fuselage.[3]
Production started in 1934, initially being powered by the Shvetsov M-22, a license-built version of the Bristol Jupiter radial engine. While less powerful than the Cyclone, the M-22 powered aircraft were still superior to the I-5 which it replaced, demonstrating excellent manoeuvrability.[3] Production switched to the 515 kW (700 hp) Shvetsov M-25 engine (a license-built, metricated Cyclone) in late 1936.[2] A total of 671 I-15s were built, 284 in the Soviet Union and a further 287 under license by CASA in Spain.[6]
The gulled upper wing of the I-15 was unpopular with some pilots, as it was felt to restrict visibility, so Polikarpov's design bureau produced a revised version, again powered by the M-25, with a longer span un-gulled upper wing.[2] This version, the I-15bis, commenced production in 1937,[7] a total of 2,408 I-15bis' being delivered by the time production finished in 1940.[2]
Operational history
China
In August 1937, the Chinese Kuomintang Government signed a non-aggression pact with the USSR. And, in autumn of the same year, the Soviet Union commenced to ship I-15s as a part of a programme of military aid to the Chinese Air Force (CAF) in its defensive war against Japan. More than 250 Soviet pilots volunteered to fly the 255 I-15s supplied to China in autumn 1937. By 1939, the total number of Polikarpov biplanes delivered to CAF reached 347 I-15/I-15bis.[8] The I-15bis saw a great amount of action in the Soviet–Japanese border conflicts along the China–Mongolia border. In 1937, I-15s in the hands of the Chinese Nationalist Air Force fought against invading Japanese, where the tough biplane began to meet its match in some of the newer, faster Japanese monoplanes.
Mongolia
In 1939 Polikarpov fighters were extensively used during the Battles of Khalkhin Gol fought around the Khalkha River in Dornod Province. The battles were fought during 11 May–16 September 1939, and involved more than 600 planes. When hostilities commenced, the only I-15bis in the area were 14 aircraft of 70th IAP. Their number increased in the following weeks: on 23 May, 35 I-15bis from 22nd IAP arrived from the Trans-Baikal region. However the Polikarpov pilots had been hastily trained and they suffered heavy losses against the more experienced Japanese. During this conflict, the Soviet Union and Japan lost more than 200 aircraft each.[9] 10 aircraft were delivered to the Mongolian People's Army Air Force in mid-July 1939 and flight personnel were trained for rear air defence. Afterwards, they received more than 30 aircraft in March 1942.
Spain
The I-15 was used extensively in combat by the Republicans in the Spanish Civil War and proved to be one of the best fighter biplanes of its time. The Nationalists called the fighter "Curtiss", apparently believing it to be the Curtiss F9C Sparrowhawk. The first batch of 25 Polikarpovs arrived in Cartagena, Spain, on 28 October 1936, with 15 pilots, led by future ace Pavel Rychagov. A few days later a further group of 10 pilots and 15 aircraft arrived in Bilbao.[10]
The Soviet pilots first went into action 4 November, when I-15s shot down two Junkers Ju 52/3ms and two CR.32s over Madrid, and forced a third Ju 52 and a Heinkel two-seater to crash-land. No losses were reported among the Soviet pilots. During the next two days, Chato pilots claimed 12 more victories, at the cost of two I-15s lost.[11]
On 16 November, while dogfighting with Fiat CR.32s over Madrid, future ace Rychagov was shot down [12] and four days later the number of combat-ready Polikarpov in the central area had fallen to 15 aircraft: seven had been lost in combat, two had force-landed and one was undergoing repair.[11]
In December 1936 and January 1937, two more shipments of 30 aircraft arrived in Spain, making it possible to form four full-strength I-15 squadrons. Until the spring of 1937, central Spain was the main war theatre for I-15s. And in May 1937, another batch of 31 Polikarpov landed in Spain, taking the total number of I-15s delivered to 116.[13]
Chato losses in the Spanish Civil War were comparable to those of its principal rival, the Fiat CR.32. By 1 January 1939, 197 Polikarpovs had been lost: 88 shot down by enemy aircraft and nine by anti-aircraft artillery, 27 destroyed on the ground and 67 written off in accidents.[14]
World War II
More than 1,000 I-15bis fighters were still in Soviet use during the German invasion when the biplane was employed in the ground attack role. By late 1942, all I-15s and I-15bis' were relegated to second line duties.
Variants

- TsKB-3bis
- Prototype.
- TsKB-3ter
- Prototype fitted with the more powerful M-25V radial piston engine.
- I-15
- First production series.
- I-15bis
- Single-seat fighter biplane, armed with four 7.62 mm (0.30 in)PV-1 or ShKAS machine guns, plus up to 150 kg (330 lb) of bombs. The I-15bis was powered by the more powerful 570 kW (775 PS) Shvetsov M-25V radial piston engine. It had a straight upper wing. A total of 2,408 machines were built.
- I-152
- Modernised version of I-15bis. One built in 1938. Series production was not undertaken, since it was decided to build I-153 instead.
- I-152GK
- (Germetichyeskoi Kabine – hermetic (pressure) cabin) – One aircraft fitted with a pressure cabin.
- I-152TK
- (Turbo Kompressor – turbo-charged) – One aircraft fitted with two turbochargers.
- I-15ter (I-153)
- Development of the I-15 with retractable landing gear, see Polikarpov I-153.
- UTI-1
- (Oochebno Trenirovochnyy Istrebitel' – fighter trainer) – Factory-built two-seat trainer version, front cockpit moved forwards, dual controls fitted, 20 built in 1934 but not used by VVS
Operators

- Chinese Nationalist Air Force
- Finnish Air Force (captured)
- Luftwaffe (captured)
- Mongolian People's Army Air Force- received more than 40 aircraft in July 1939 – 1942
- Soviet Air Force
- Soviet Naval Aviation
- Spanish Air Force – Post civil war.
Specifications (I-15 M-25)
Data from Of Chaika and Chato…[15]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 6.10 m (20 ft 0 in) (tail up)
- Upper wingspan: 9.75 m (32 ft 0 in)
- Lower wingspan: 7.50 m (24 ft 7 in)
- Height: 2.20 m (7 ft 3 in) (tail down)
- Wing area: 21.90 m2 (235.7 sq ft)
- Airfoil: Clark YH [16]
- Empty weight: 1,012 kg (2,231 lb)
- Gross weight: 1,385 kg (3,053 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 1,689 kg (3,724 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 260 L (57 imp gal; 69 US gal)
- Powerplant: 1 × Shvetsov M-25 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 520 kW (700 hp) at 2,300 m (7,500 ft)
- Propellers: 2-bladed variable-pitch propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 367 km/h (228 mph, 198 kn) at 3,000 m (9,800 ft)
- Cruise speed: 285 km/h (177 mph, 154 kn) at 2,000 m (6,600 ft) (max. continuous cruise)
- Range: 510 km (320 mi, 280 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 9,800 m (32,200 ft)
- Time to altitude:
- 1.1 min to 1,000 m (3,300 ft)
- 6.1 min to 5,000 m (16,400 ft)
Armament
- 4 × 7.62mm machine guns 7.62×54mmR PV-1 machine guns
- Up to 100kg (220 lb) of bombs
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Avia B-534
- Curtiss F9C Sparrowhawk
- Fiat CR.32
- Gloster Gladiator
- Grumman F2F
- Hawker Fury
- Heinkel He 51
- Ikarus IK-2
- PZL P.7
Related lists
References
Notes
- "Polikarpov fighters." wio.ru. Retrieved: 8 October 2012.
- Gunston 1995, p. 299.
- Green and Swanborough 1979, p. 10.
- Lannon 2002, p. 46.
- Green and Swanborough 1979, p. 9.
- Gordon and Dexter 1999, p. 120.
- Green and Swanborough 1979, p. 18.
- Maslov 2010, p. 33.
- Maslov 2010, p. 42.
- Maslov 2010, p. 16.
- Maslov 2010, p. 18.
- Maslov 2010, p. 17.
- Maslov 2010, p. 21.
- Maslov 2010, p. 24.
- Green and Swanborough 1979, p. 12.
- Lednicer, David. "The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage". m-selig.ae.illinois.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
Bibliography
- Abanshin, Michael E. and Nina Gut. Fighting Polikarpov, Eagles of the East No. 2. Lynnwood, Washington: Aviation International, 1994. ISBN 1-884909-01-9.
- Drabkin, Artem. The Red Air Force at War: Barbarossa and the Retreat to Moscow – Recollections of Fighter Pilots on the Eastern Front. Barnsley, South Yorkshire, UK: Pen & Sword Military, 2007. ISBN 1-84415-563-3.
- Gordon, Yefim and A. Dexter. "Polikarpov Biplane Fighter Variants". Wings of Fame, Volume 17. London:Aerospace Publishing, 1999, pp. 106–129. ISBN 1-86184-041-1.
- Gordon, Yefim and Keith Dexter. Polikarpov's Biplane Fighters (Red Star, vol.6). Earl Shilton, Leicester, UK: Midland Publishing, 2002. ISBN 1-85780-141-5.
- Gordon, Yefim and Dmitri Khazanov. Soviet Combat Aircraft of the Second World War, Volume One: Single-Engined Fighters. Earl Shilton, Leicester, UK: Midland Publishing Ltd., 1998. ISBN 1-85780-083-4.
- Green, William. Warplanes of the Second World War, Volume Three: Fighters. London: Macdonald & Co. (Publishers) Ltd., 1961 (seventh impression 1973). ISBN 0-356-01447-9.
- Green, William and Gordon Swanborough. "Of Chaika and Chato... Polikarpov's Fighting Biplanes". Air Enthusiast. Issue 11, November 1979 – February 1980, pp. 9–29. ISSN 0143-5450.
- Gunston, Bill. The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995. London: Osprey, 1995. ISBN 1-85532-405-9.
- Lannon, Frances. The Spanish Civil War 1936–1939 (Essential Histories 37). London: Osprey Publishing, 2002. ISBN 9781841763699.
- Léonard, Herbert. Les avions de chasse Polikarpov (in French). Rennes, France: Editions Ouest-France, 1981. ISBN 2-85882-322-7.
- Léonard, Herbert. Les chasseurs Polikarpov (in French). Clichy, France: Éditions Larivière, 2004. ISBN 2-914205-07-4.
- Maslov, Mikhail A. Polikarpov I-15bis (Wydawnictwo Militaria 199) (in Polish). Warsawa, Poland: Wydawnictwo Militaria, 2004. ISBN 83-7219-178-6.
- Maslov, Mikhail A. Polikarpov I-15, I-16 and I-153. Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, 2010. ISBN 978-1-84603-981-2.
- Stapfer, Hans-Heiri. Polikarpov Fighters in Action, Part 1 (Aircraft in Action number 157). Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, Inc., 1995. ISBN 0-89747-343-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Polikarpov I-15. |
- https://web.archive.org/web/20070727063151/http://www.aviation.ru/Po/#15
- http://www.wio.ru/tacftr/polikarp.htm
The initial version of this article was based on material from aviation.ru. It has been released under the GFDL by the copyright holder.