Tryptophan tryptophylquinone
Tryptophan tryptophylquinone (TTQ) is an enzyme cofactor, generated by posttranslational modification of amino acids within the protein. Methylamine dehydrogenase (MADH), an amine dehydrogenase, requires TTQ for its catalytic function.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
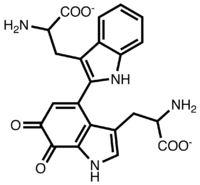
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-3-[2-[2-amino-3-(2-carboxyethyl)-6,7-dioxo-1H-indol-4-yl]-1H-indol-3-yl]propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| MeSH | Tryptophan+tryptophylquinone |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H20N4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 436.424 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Davidson VL, Liu A: Uncovering novel biochemistry in the mechanism of tryptophan tryptophylquinone cofactor biosynthesis Curr. Op. Chem. Biol. 2009, 13: 469-474
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.