Tropical Storm Hagibis (2014)
Tropical Storm Hagibis was a tropical storm that enhanced the southwest monsoon, bringing heavy rainfall to the Philippines for nearly a week in June 2014. The storm formed on June 13 and dissipated on June 18. Hagibis made landfall on June 15, causing damage estimated to be US$198 million. Hagibis is a Filipino word, meaning fast or swiftness.
| Tropical storm (JMA scale) | |
|---|---|
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
.jpg) Tropical Storm Hagibis approaching Guangdong Province, China on June 15 | |
| Formed | June 13, 2014 |
| Dissipated | June 23, 2014 |
| (Extratropical after June 17) | |
| Highest winds | 10-minute sustained: 75 km/h (45 mph) 1-minute sustained: 85 km/h (50 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 996 hPa (mbar); 29.41 inHg |
| Fatalities | None |
| Damage | $198 million (2014 USD) |
| Areas affected | |
| Part of the 2014 Pacific typhoon season | |
Meteorological history
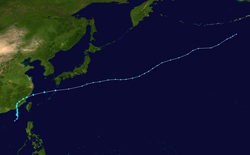
On June 11, 2014, a broad, poorly-defined area of low pressure formed over the South China Sea. Extensive, though disorganized, deep convection accompanied the system. Situated within a region of low to moderate wind shear and weak outflow, slow development ensued.[1] By June 13, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) classified the disturbance as a tropical depression.[2] A monsoonal system, the depression featured an extensive circulation with the strongest winds well away from the center, contrary to most tropical cyclones. A scatterometer pass revealed winds up to 65 km/h (40 mph) within a banding feature to the east of the storm's center by the evening of June 13.[3] In accordance with this, the JMA upgraded the depression to Tropical Storm 1407 and assigned the name Hagibis to the cyclone.[4] Despite the presence of gale-force winds, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) deemed the system to be below storm intensity and only issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert early on June 14, indicating that it was likely to become a tropical cyclone within 24 hours.[5] Thereafter, the tropical storm-force winds contracted to within 130 km (80 mi) of the center, indicative of a more tropical than monsoonal system. As such, the JTWC initiated advisories on the system as Tropical Storm 07W.[6]
Early on June 15, Hagibis made landfall over southern China, and it subsequently weakened to a tropical depression.[7] On the morning of June 16, both agencies issued their final warnings on Hagibis as it weakened further to a land depression. Its remnants still continued to move northward, but by June 17, the remnants of Hagibis curved eastwards due to the jet stream. Later that day, the remnants entered moved back over warm waters, and accompanied by low vertical wind shear, and the storm re-intensified. The JMA upgraded Hagibis to a tropical storm once again, and both the JTWC and the JMA re-initiated advisories on the system. Early on June 18, Hagibis transitioned into an extratropical cyclone, and its circulation was absorbed by a developing extratropical storm to the north on June 21. The system moved out of the basin early on June 23.[8]
Impacts

Philippines
Although Hagibis did not enter the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), it did threaten the Philippines by enhancing the southwest monsoon, bringing torrential rainfall to the country. Due to extreme rainfall since Tropical Storm Mitag on June 10, the Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) declared the official start of the rainy season.[9][10] It was reported that 17 towns in Maguindanao province were flooded. As a result, a total of more than 90,000 people were affected.[11]
Extreme rainfall continued to affect the country until June 27, when a tropical disturbance affecting northern Luzon ceased.
China
Hagibis made landfall over southern China at 04:50 UTC on June 15. Torrential rain continued to bring flooding until June 22, as the southwest monsoon weakened. No people were killed, and total economic losses in Mainland China were counted to be CNY 1.23 billion (US$198 million).[12]
See also
- Tropical Storm Mitag (2014) - enhanced the southwest monsoon with Hagibis, which brought heavy rainfall to the Philippines
- Typhoon Usagi (2013) - made landfall at the same place
References
- Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans. Joint Typhoon Warning Center (Report). United States Navy. June 11, 2014. Archived from the original on June 12, 2014. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- High Seas Warning (Report). Japan Meteorological Agency. June 13, 2014. Archived from the original on June 13, 2014. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans. Joint Typhoon Warning Center (Report). United States Navy. June 13, 2014. Archived from the original on June 14, 2014. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- "Tropical Storm 1407 (Hagibis) Best Track". Japan Meteorological Agency. July 17, 2014. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. United States Navy. June 14, 2014. Archived from the original on June 14, 2014. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 07W (Hagibis) Warning Nr 001. Joint Typhoon Warning Center (Report). United States Navy. June 14, 2014. Archived from the original on June 16, 2014. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- "Tropical storm Hagibis hits Guandong - China". Retrieved June 15, 2014.
- "It's official: Wet season is here". Jeannette Andrade. Retrieved June 10, 2014.
- "Rainy season is here; Signal No. 1 in 3 areas". ABS-CBNnews, Dharel Placido. Retrieved June 10, 2014.
- "Floods affect 99k in 17 Maguindanao towns". Joel Locsin/JDS, GMA News. Retrieved July 4, 2014.
- "Member Report: China" (PDF). CMA. China Meterelogical Agency. Retrieved October 18, 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tropical Storm Hagibis (2014). |
- JMA General Information on Tropical Storm Hagibis (1407) from Digital Typhoon
- JMA Best Track Data for Tropical Storm Hagibis (1407) (in Japanese)
- JMA Best Track Data (Graphics) for Tropical Storm Hagibis (1407)
- JMA Best Track Data (Text)
- 07W.HAGIBIS from the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory