Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine
Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine is the organic compound with the formula N(CH2CH2NH2)3. This colourless liquid is soluble in water and is highly basic, consisting of a tertiary amine center and three pendant primary amine groups. Abbreviated tren, it is the archetypal tripodal ligand of interest in coordination chemistry.
amine.svg.png) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N,N-Bis(2-aminoethyl)-1,2-ethanediamine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1739626 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.689 |
| EC Number |
|
| 27074 | |
| MeSH | Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UN number | 2922 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H18N4 | |
| Molar mass | 146.238 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Ichtyal, ammoniacal |
| Density | 0.976 g/mL (20 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | −16 °C (3 °F; 257 K) |
| Boiling point | 265 °C (509 °F; 538 K) |
| Miscible | |
| log P | −2.664 |
| Vapor pressure | 3 Pa (at 20 °C) |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.497[1] |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−74.3–−72.9 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−4860.6–−4859.2 kJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | fishersci.com |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H301, H310, H314 |
| P280, P302+350, P305+351+338, P310 | |
| Flash point | 113 °C (235 °F; 386 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
|
| Related compounds | |
Related amines |
|
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tren is a C3-symmetric, tetradentate chelating ligand that forms stable complexes with transition metals, especially those in the 2+ and 3+ oxidation states. Tren complexes exist with relatively few isomers, reflecting the constrained connectivity of this tetramine. Thus, only a single achiral stereoisomer exists for [Co(tren)X2]+, where X is halide or pseudohalide.[2] In contrast, for [Co(trien)X2]+ five diastereomers are possible, four of which are chiral. In a few cases, tren serves as a tridentate ligand with one of the primary amine groups non-coordinated. Tren is a common impurity in the more common triethylenetetramine ("trien"). As a trifunctional amine, tren forms a triisocyanate when derivatized with COCl2.
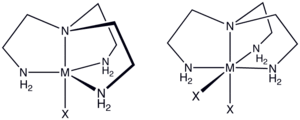
N-methylated trens
The permethylated derivative of tren has the formula N(CH2CH2NMe2)3. "Me6tren" forms a variety of complexes but, unlike tren, does not stabilize Co(III). Related amino-triphosphines are also well developed, such as N(CH2CH2PPh2)3 (m.p. 101-102 °C). This species is prepared from the nitrogen mustard N(CH2CH2Cl)3.[3]
N,N,N-trimethyltren, N(CH2CH2NHMe)3 is also available.[4]
Safety considerations
(H2NCH2CH2)3N, like other polyamines, is corrosive.[5] It causes severe skin burns and eye damage, is harmful if inhaled due to the destruction of respiratory tissues, is toxic if swallowed, and can be fatal in contact with skin. Its median lethal dose is 246 mg/kg, oral (rat), and 117 mg/kg, dermal (rabbit). It is also combustible.[6]
References
- "Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine". Sigma-Aldrich.
- Donald A. House "Ammonia & N-donor Ligands" in Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry John Wiley & Sons, 2006. doi:10.1002/0470862106.ia009.
- R. Morassi, L. Sacconi "Tetradentate Tripod Ligands Containing Nitrogen, Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Arsenic as Donor Atoms" Inorganic Syntheses 1976, vol. 16 p. 174-180. doi:10.1002/9780470132470.ch47
- Schmidt, H.; Lensink, C.; Xi, S. K.; Verkade, J. G. (1989). "New Prophosphatranes: Novel intermediates to five-coordinate phosphatranes". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 578: 75–80. doi:10.1002/zaac.19895780109.
- The Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory Oxford University MSDS
- "Safety Data Sheet". Sigma-Aldrich. July 1, 2014. Retrieved April 7, 2019.