Treaty of Osimo
The Treaty of Osimo was signed on 10 November 1975 by the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Italian Republic in Osimo, Italy, to definitively divide the Free Territory of Trieste between the two states: the port city of Trieste with a narrow coastal strip to the north west (Zone A) was given to Italy; a portion of the north-western part of the Istrian peninsula (Zone B) was given to Yugoslavia.
Long name:
| |
|---|---|
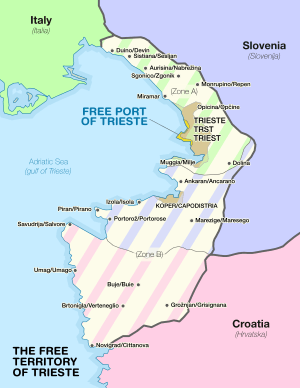 Map of the Free Territory of Trieste and its division after the treaty | |
| Signed | 10 November 1975 |
| Location | Osimo, Italy |
| Effective | 3 April 1977 |
| Parties | |
| Language | French |
The full name of the treaty is Treaty on the delimitation of the frontier for the part not indicated as such in the Peace Treaty of 10 February 1947. The treaty was written in French and became effective on 11 October 1977. For the Italian Government, the treaty was signed by Mariano Rumor, Minister for Foreign Affairs. For Yugoslavia, the treaty was signed by Miloš Minić, the Federal Secretary for Foreign Affairs.[1]
Criticism in Italy
The Italian government was criticized harshly for signing the treaty, particularly for the secretive way in which negotiations were carried out, skipping the traditional diplomatic channels. Italian nationalists rejected the idea of giving up Istria, since Istria had been an ancient "Italian" region together with the Venetian region (Venetia et Histria)[2]. Italian nationalists state that the antique Italian eastern border line lies in Istria and is defined as the river Arsia (today Raša). Furthermore, Istria had belonged to Italy for the 25 (1919–1943) years between World War I and the end of World War II, and the west coast of Istria had long had a sizeable Italian minority population.[3]
Some called for the prosecution of the then Prime Minister and the Minister of Foreign Affairs for the crime of treason, as stated in Article 241 of the Italian Criminal Code, which mandates a life sentence for anybody found guilty of aiding and abetting a foreign power to exert its sovereignty on the national territory. The treaty did not guarantee the protection of the Italian minority in the Yugoslav zone nor for the Slovenian minority in the Italian zone. The question of the protection of minorities was to be dealt with later via the signing of separate protocols.
Slovenia's and Croatia's independence
Slovenia declared its independence in 1991 and was recognized internationally in 1992. Italy was quick to recognise Slovenian independence, and accept the accession of the new Slovenia to treaties concluded with Yugoslavia.[2] Though the treaty's applicability was now in question, Slovenia then released a declaration on 31 July 1992, saying it would recognize the treaty.[4] Both it and Croatia have opposed any changes to the treaty. Slovenia claimed that all debts owing to Italy (for property transferred to Yugoslav sovereignty after 1947) had now been paid. By 1993, however, 35,000 Italians still claimed money was owed to them.
In 1994, the Italian government, led by Silvio Berlusconi, demanded that adequate compensation be paid, else efforts to integrate Slovenia into western Europe would be halted. To this effect, it blockaded talks for Slovenia's accession to the European Union until March 1995, when the new government under Lamberto Dini retracted the demand. A co-operative pact was signed (led by Spain), with the effect of allowing Italian nationals who had resided in Slovenia for three years to purchase property there for up to four years after the pact was signed and came into force during Slovenia's attempts to join the EU.[5]
No similar declaration was made by the Croatian government, although the Parliament of Croatia on 25 June 1991 accepted the borders of Croatia as part of Yugoslavia.[4] However, Italy did not insist on a declaration by Croatia, and the treaty was never questioned by Croatia, which considers it to be a valid treaty. .
References
- The original text of the Treaty
- Ronald Haly Linden (2002). Norms and nannies: the impact of international organizations on the central and east European states. p. 104. ISBN 9780742516038.
- Valussi, Ressmann (1861). Trieste e l'Istria nelle quistione italiana. p. 62.
- Tullio Scovazzi (January 1999). Marine specially protected areas. p. 49. ISBN 9789041111296.
- Taylor & Francis Group (2004). Europa World Year Book 2. 2. p. 3796. ISBN 9781857432558.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Trattato di Osimo. |
- The full text of the Treaty, United Nations Treaty Series Vol. 1466, 1-24848
