Trachurus delagoa
Trachurus delagoa, the African scad, is a species of jack mackerel from the family Carangidae which is found in the south western Indian Ocean.[2]
| Trachurus delagoa | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Carangiformes |
| Family: | Carangidae |
| Genus: | Trachurus |
| Species: | T. delagoa |
| Binomial name | |
| Trachurus delagoa Nekrasov, 1970 | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Trachurus margaretae Berry & Cohen, 1974 | |
Description
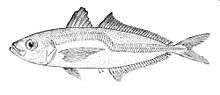
Trachurus delagoa has an elongate body which isslightly compressed and has the upper and lower profiles roughly the same. The eye is moderately large and has a well-developed adipose eyelid which normally covers almost all of the eye apart from a vertical oval with the pupil in the centre. It has a reasonably wide upper jaw which extends to underneath the forward anterior edge of the eye. The mouth is equipped with small teeth, having a single row in each jaw. It has two separate dorsal fins, the first having 8 spines with the second having a single spine and 28 to 32 soft rays. The anal fin has 2 detached spines to its front followed by a single spine and 24 to 28 soft rays. The pectoral fins are as long or longer than the length of the head. The scales in the lateral line and large and form scutes. It has a black spot on the upper margin of the operculum, the upper part of the body is dark blue and the flanks and belly are silvery. The anal and pectoral fins are pale yellow in colour, the caudal fin is grey and the pelvic fins are white or unpigmented.[3] It grows to a maximum total length of 35 centimetres (14 in).[2]
Distribution
Trachurus delagoa occurs in the south-western Indian Ocean off the eastern costa of Africa from Eastern Cape Province to southern Mozambique. It is also found off southern Madagascar and the Walters Shoals.[1]
Habitat and biology
Trachurus delagoa is largely demersal and occurs in areas of the continental shelf where there is a sandy substrate. It ranges in depth from the shoreline to around 400 metres (1,300 ft). It spends the day in the depths and undertakes a vertical migration at night to feed near the surface. Its prey is made up largely of smaller fish and crustaceans.[3] It is a social species which forms schools.[1]
Fisheries
African scads are largely fished for with bottown trawls and with hook and line.[3] In KwaZulu Natal it is fished for on a small scale by fishermen on paddleboards or kayaks.[1]
References
- Smith-Vaniz, W.F.; Borsa, P.; Carpenter, K.E.; et al. (2018). "Trachurus delagoa". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T20437678A67871525. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T20437678A67871525.en.
- Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2019). "Trachurus delagoa" in FishBase. August 2019 version.
- "Family Carangidae" (PDF). Fishing Area 51 (W. Indian Ocean) series. FAO Species Identification Sheets. FAO. Retrieved 5 December 2019.