Thrixspermum congestum
Thrixspermum congestum, commonly known as the cupped hairseed,[2] is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that forms small clumps with many thin roots, up to fifteen leathery leaves and many star-shaped white or cream-coloured flowers. This orchid occurs from Papuasia to northern Australia.
| Cupped hairseed | |
|---|---|
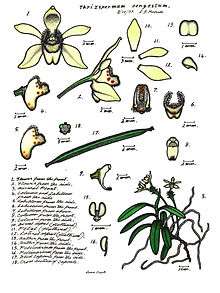 | |
| Illustration by Lewis Roberts | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | T. congestum |
| Binomial name | |
| Thrixspermum congestum | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Description
Thrixspermum congestum is an epiphytic or lithophytic herb that forms small clumps with many thin roots and flattened stems 50–150 millimetres (2.0–5.9 in) long. It has between six and fifteen crowded stiff, leathery leaves 40–60 millimetres (1.6–2.4 in) long and 7–9 millimetres (0.28–0.35 in) wide. The flowers are cream-coloured or white, 9–11 millimetres (0.35–0.43 in) long and 12–15 millimetres (0.47–0.59 in) wide arranged on a wiry flowering stem 50–100 millimetres (2.0–3.9 in) long. The sepals are 6–7 millimetres (0.24–0.28 in) long and 3–4 millimetres (0.12–0.16 in) wide, the petals a similar length but only about 2 millimetres (0.079 in). The labellum is about 5 millimetres (0.20 in) long and 2 millimetres (0.079 in) wide with three lobes. The side lobes are hairy and erect, about 1.5 millimetres (0.059 in) long and 3 millimetres (0.12 in) wide, narrow, curved and pointed. The middle lobe is short, fleshy and hairy with a short, hairy spur. Flowering occurs sporadically and the flowers open from one to a few at a time.[2][3][4][5]
Taxonomy and naming
The cupped hairseed was first formally described in 1895 by Frederick Bailey who gave it the name Cleisostoma congestum and published the description in Proceedings of the Royal Society of Queensland.[6][7] In 1967, Alick Dockrill changed the name to Thrixspermum congestum.[8] The specific epithet (congestum) is a Latin word meaning "collected", "dense" or "thick".[9]
Distribution and habitat
Thrixspermum congestum grows on mangroves and rainforest trees in humid but airy situations. It occurs in New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, New Caledonia, Vanuatu and Australia. In Australia it is found on Melville Island and between the Iron Range and the Tully River in Queensland.[1][2][4]
References
- "Thrixspermum congestum". World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- Jones, David L. (2006). A complete guide to native orchids of Australia including the island territories. Frenchs Forest, N.S.W.: New Holland. p. 456. ISBN 1877069124.
- "Thrixspermum congestum". Trin keys: Australian Tropical Rainforest Orchids. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- "Thrixspermum congestum". Orchids of New Guinea. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- Kerrigan, Raelee; Cowie, Ian. "Thrixspermum congestum" (PDF). Northern Territory Government. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- "Cleisostoma congestum". APNI. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- Bailey, Frederick Manson (1895). "Botanic notes". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Queensland. 11: 17–18. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- "Thrixspermum congestum". APNI. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- Brown, Roland Wilbur (1956). The Composition of Scientific Words. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. p. 225.