Thoracoacromial artery
The thoracoacromial artery (acromiothoracic artery; thoracic axis) is a short trunk that arises from the second part of the axillary artery, its origin being generally overlapped by the upper edge of the pectoralis minor.
| Thoracoacromial artery | |
|---|---|
Branches of axillary artery, including thoracoacromial artery | |
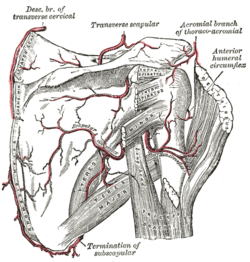 The scapular and circumflex arteries. (Thoracoacromial branch of thoracoacromial labeled at upper right.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | axillary artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria thoracoacromialis |
| TA | A12.2.09.005 |
| FMA | 22671 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
Projecting forward to the upper border of the Pectoralis minor, it pierces the coracoclavicular fascia and divides into four branches—pectoral, acromial, clavicular, and deltoid.
| Branch | Description |
|---|---|
| Pectoral branch | Descends between the two pectorales, and is distributed to them and to the mamma, anastomosing with the intercostal branches of the internal thoracic artery and with the lateral thoracic. |
| Acromial branch | Runs laterally over the coracoid process and under the deltoideus, to which it gives branches; it then pierces that muscle and ends on the acromion in an arterial network formed by branches from the transverse scapular (a.k.a. suprascapular), thoracoacromial, and posterior humeral circumflex arteries. |
| Clavicular branch | Runs upward and medialward to the sternoclavicular joint, supplying this articulation, and the subclavius. |
| Deltoid (humeral) branch | Often arising with the acromial, it crosses over the pectoralis minor and passes in the same groove as the cephalic vein, between the pectoralis major and deltoideus, and gives branches to both muscles. |
Additional images
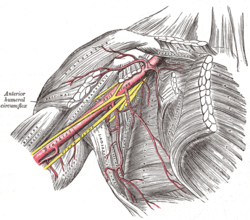 The axillary artery and its branches.
The axillary artery and its branches.
gollark: Just memorize all the unicode character names.
gollark: (I don't, but it would be convenient if I did!)
gollark: If only more people knew the international phonetic alphabet, it would be way easier to discuss.
gollark: Idea: companies which use nanobots to synthesize hydrocarbons from water and atmospheric carbon dioxide.
gollark: helo.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 588 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- lesson2nerartveinspectregion at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- lesson3axillaryart&vein at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Anatomy photo:04:07-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Pectoral Region: Thoracoacromial Artery and its Branches"
- Anatomy figure: 05:04-12 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The axillary artery and its major branches shown in relation to major landmarks."
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.