Thiocarbamate
Thiocarbamates are a family of organosulfur compounds. As the name suggests, they are sulphur analogues of carbamates. There are two isomeric forms of thiocarbamate esters: O-thiocarbamates, ROC(=S)NR2, and S-thiocarbamates, RSC(=O)NR2.

Synthesis
Thiocarbamates can be synthesised by the reaction of water or alcohols upon thiocyanates (Riemschneider thiocarbamate synthesis):[1][2]
- RSCN + H2O → RSC(=O)NH2
- RSCN + R'OH → RSC(=O)NR'H
Similar reactions are seen between alcohols and thiocarbamoyl chlorides such as dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride; as well as between thiols and cyanates.[2]
Alternatively, they arise by the reaction of amines with carbonyl sulfide.
- 2 R2NH + COS → [R2NH2]+][R2NCOS]−
Reactions
In the Newman-Kwart rearrangement O-thiocarbamates can isomerise to S-thiocarbamates.[3] This is generally performed by heating to high temperatures and is an important method for synthesising thiophenols.

Dithiocarbamates
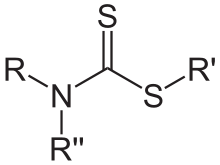
Dithiocarbamates are related to thiocarbamates by the replacement of O by S. Despite this structural similarity their synthesis and chemistry is quite different. Dithiocarbamates and their derivatives are widely used in the vulcanization of rubber.[4]
See also
References
- Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, p. 1269, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1
- Walter, W.; Bode, K.-D. (April 1967). "Syntheses of Thiocarbamates". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 6 (4): 281–293. doi:10.1002/anie.196702811.
- Melvin S. Newman, Frederick W. Hetzel (1971). "Thiophenols from Phenols: 2-Naphthalenethiol". Org. Synth. 51: 139. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.051.0139.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Engels, Hans-Wilhelm; et al. "Rubber, 4. Chemicals and Additives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a23_365.pub2.