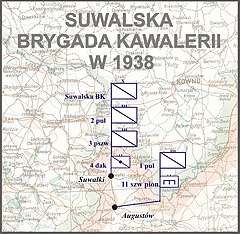
Suwalska Cavalry Brigade
Suwalska Cavalry Brigade (Polish: Suwalska Brygada Kawalerii) was a cavalry unit of the Polish Armed Forces of the Second Polish Republic in the interbellum period. It was created on April 1, 1937 out of the 4th Independent Cavalry Brigade. Its headquarters were stationed in Suwałki and the brigade consisted of these units:
- 1st Krechowce Uhlan Regiment, stationed in Augustów
- 2nd Grochow Uhlan Regiment, stationed in Suwałki
- 3rd Mazovian Chevau-leger Regiment, stationed in Suwałki
- 4th Mounted Artillery Regiment, stationed in Suwałki
- 11th Squadron of Pioneers, stationed in Augustów
- 11th Squadron of Communications, stationed in Suwałki
History
In May 1921, 7th Cavalry Brigade, which had fought in the Polish–Soviet War, was renamed into 4th Cavalry Brigade, with three regiments: 3rd Regiment of Mazovian Chevau-legers, 1st Krechowce Uhlan Regiment and 2nd Grochow Uhlan Regiment, as well as 4th Horse Artillery. In December 1921, headquarters of 4th Brigade were moved from Grodno to Suwalki. In February 1929, 4th Cavalry Brigade was renamed into Cavalry Brigade Suwalki, and on April 1, 1937, it was renamed again, into Suwalska Cavalry Brigade.
1939 German Invasion of Poland
During the Invasion of Poland, Suwalska Cavalry Brigade, under General Zygmunt Podhorski, belonged to Independent Operational Group Narew, and its task was to protect the approaches to Grodno and cover northern flank of the Narew Group. It concentrated all its subunits by September 2, 1939, and manned its positions along the border with East Prussia. On the same day, the Wehrmacht unsuccessfully attacked Bakalarzewo.
In the night of September 3/4, two squadrons of 3rd Regiment of Mazovian Chevau-legers carried out a successful raid over several villages of East Prussia. Soon afterwards, Polish headquarters ordered the Brigade to move southwards, to forests between Putusk and Ostrow Mazowiecka. Polish planners wanted to attack German forces which marched along western bank of the Narew. In the night of September 4/5, the Brigade began its march from the area of Suwalki to Zambrow, via Knyszyn and Tykocin. On September 7, it reached the village of Jablon Koscielna, and on September 9–10, Colonel Kazimierz Plisowski temporarily commanded the Brigade. At the same time, it was engaged in heavy fighting with German Panzer Division Kempf.
On September 9 in the morning, the Brigade was ordered to attack German positions in the villages of Piski and Ksiezopole. By afternoon, both villages were captured, with numerous prisoners of war. In the evening the Brigade retreated to forests around Koskowo, but without 2nd Grochow Uhlans, which was ordered to protect the wing of Polish 18th Infantry Division, and on September 10 was engaged in heavy fighting near Rutki.
On 10 Sept., the brigade, under the command of Gen. Zygmunt Podhorski, was pinned down by the 10th Panzer Division (Wehrmacht) south of the Biebrza River.[1]:78
On September 11 the Brigade retreated south of Zambrow, and on the next day, it merged with remnants of Podlaska Cavalry Brigade, creating Operational Group of General Podhorski.
In the night of September 13/14 near Olszew, the Brigade was involved in heavy fighting, which caused its partial destruction. Survivors fled to Bialowieza Forest, where by September 20, Plis Cavalry Brigade (named after Colonel Kazimierz Plisowski) was created.
References
- Zaloga, S.J., 2002, Poland 1939, Oxford: Osprey Publishing Ltd., ISBN 9781841764085
- (in Polish) Krótki informator historyczny o Wojsku Polskim w latach II wojny światowej. 7, Regularne jednostki Wojska Polskiego w 1939 : organizacja, działania bojowe, uzbrojenie, metryki związków operacyjnych, dywizji i brygad, Tadeusz Jurga, Warszawa : Wydawnictwo Ministerstwa Obrony Narodowej 1975.
- (in Polish) Artyleria konna Wojska Polskiego 1918-1939,Giętkowski Mirosław, Wydawnictwo Adam Marszałek, Toruń 2001, ISBN 83-7174-823-X.