Stymfalia
Stymfalia (Greek: Στυμφαλία; Ancient Greek: Στύμφαλος Stymphalos) is a village and a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has formed part of the municipality of Sikyona, of which it is a municipal unit.[2] The municipal unit has an area of 205.07 km2,[3] while its population as of 2011 was 2,427. The seat of the municipality was in Kalianoi, 41 km southwest of the town of Kiato. The municipal unit occupies a mountain valley with an average altitude of 600 metres. Mount Kyllene dominates it to the NW, rising to a height of c. 2,400 metres. The largest village is Kaisari, but the principal antiquities are just south of the modern village of Stymfalia, a hamlet of c. 150 inhabitants.
Stymfalia Στυμφαλία | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Stymfalia Location within the regional unit 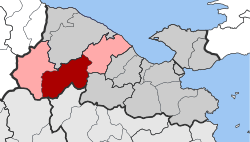 | |
| Coordinates: 37°53′N 22°28′E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Administrative region | Peloponnese |
| Regional unit | Corinthia |
| Municipality | Sikyona |
| • Municipal unit | 205.1 km2 (79.2 sq mi) |
| Population (2011)[1] | |
| • Municipal unit | 2,427 |
| • Municipal unit density | 12/km2 (31/sq mi) |
| Community | |
| • Population | 184 (2011) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Vehicle registration | ΚΡ |
History


In ancient Greece, Stymphalos, lying in this valley of northwestern Arcadia, was famous as the site of one of the Labors of Hercules, the slaying of the Stymphalian birds. Hera, whose presence is never far from Heracles, was venerated at the site in an archaic form in which she took three phases, as maiden, matron, and even widow.[4] Pindar mentions an Olympic victor in the mule-cart race (a man called Hagesias) in his sixth Olympian Ode, and urges the members of the choir to venerate their virginal Hera, who was apparently a survival of pre-Olympian religion. Pausanias mentions a statue of Dromeus, a long-distance runner from Stymphalos who won at all the Panhellenic Games in the mid-5th century BC. Little else is known of Stymphalos from ancient literature. Artemis was the principal divinity of the town and her temple seems still to have been in use in Roman times. One unusual aspect of the goddess is that her sanctuary is referred to in an inscription of the early 2nd century BC as that of Brauronian Artemis, an Athenian cult. An inscription commemorating Stymphalian hospitality to the people of Elateia was to be set up in the agora of Elateia and in the sanctuary of Brauronian Artemis at Stymphalos. Demeter and Hermes are also epigraphically attested.
Anastasios Orlandos excavated parts of the site for the Archaeological Society of Athens between 1924 and 1930. Since 1982, excavations of the site on the north shore of Lake Stymphalia have been under way, directed by Hector Williams for the University of British Columbia. Archaeological surveys and excavations have revealed a town refounded in the 4th century BC.[5] The later city was laid out on a grid plan, with six-meter-wide roads running north–south every thirty metres, which intersected major east–west avenues at intervals over a hundred metres. Houses have also been identified, as have a theatre, a palaestra, a fountain house, several temples, and the sanctuary, where an inscription preserving the letters POLIAD... ("of Athena Polias") found by Orlandos in 1925, but now lost, seems to indicate Athena Polias as the divinity worshipped, though no further confirmation of this has been found. A graffito on a sherd from the site refers to the goddess of childbirth, Eilythyia. Large quantities of jewelry (mostly copper or bronze) suggest a sanctuary frequented by women; the partially preserved statue of a child supports the kourotrophic interpretation of the cult. In an annex to the temple, several dozen loom weights suggest the further presence of Athena in a weaving workshop. The sanctuary was destroyed, probably by the Romans in 146 BC, but later seems to have been at least revisited to judge from early to mid Roman pottery lamps from the area.
There are four early Christian cemeteries. Just to the north of the ancient city are the remains of the medieval Cistercian monastery of Zaraka, also partially excavated by the Royal Canadian Institute. There are various other smaller sites scattered around the valley, but as yet there has been no systematic survey of them.
References
- "Απογραφή Πληθυσμού - Κατοικιών 2011. ΜΟΝΙΜΟΣ Πληθυσμός" (in Greek). Hellenic Statistical Authority.
- Kallikratis law Greece Ministry of Interior (in Greek)
- "Population & housing census 2001 (incl. area and average elevation)" (PDF) (in Greek). National Statistical Service of Greece.
- Pausanias. Description of Greece, 7.22.2.
- The Bronze Age and early classical Stymphalos has not been precisely located.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Stymfalia. |