Strobilus
A strobilus (plural: strobili) is a structure present on many land plant species consisting of sporangia-bearing structures densely aggregated along a stem. Strobili are often called cones, but some botanists restrict the use of the term cone to the woody seed strobili of conifers. Strobili are characterized by a central axis (anatomically a stem) surrounded by spirally arranged or decussate structures that may be modified leaves or modified stems.
Leaves that bear sporangia are called sporophylls, while sporangia-bearing stems are called sporangiophores.
Lycophytes
Some members of both of the two modern classes of Lycopodiophyta (Lycopodiopsida and Isoetopsida) produce strobili. In all cases, the lateral organs of the strobilus are microphylls, bearing sporangia. In other lycophytes, ordinary foliage leaves can act as sporophylls, and there are no organized strobili.
- Strobili of Lycopodium
 Liquid-preserved strobili of Lycopodium, showing reniform sporangia through translucent sporophylls
Liquid-preserved strobili of Lycopodium, showing reniform sporangia through translucent sporophylls Strobili of Selaginella
Strobili of Selaginella Liquid-preserved strobili of Selaginella, showing mega- and microsporangia through translucent sporophylls.
Liquid-preserved strobili of Selaginella, showing mega- and microsporangia through translucent sporophylls.
Sphenophytes
The single extant genus of Equisetophyta, Equisetum, produces strobili in which the lateral organs are sporangiophores. Developmental evidence and comparison with fossil members of the group show that the sporangiophores are reduced stems, rather than leaves. Sporangia are terminal.
 Strobilus of Equisetum
Strobilus of Equisetum Strobilus of Equisetum
Strobilus of Equisetum Liquid-preserved strobilus of Equisetum, showing sporangiophores
Liquid-preserved strobilus of Equisetum, showing sporangiophores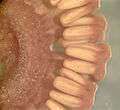 Cross-section of liquid-preserved strobilus of Equisetum, showing sporangiophores bearing sporangia
Cross-section of liquid-preserved strobilus of Equisetum, showing sporangiophores bearing sporangia
Seed plants
With the exception of flowering plants, seed plants produce ovules and pollen in different structures. Strobili bearing microsporangia are called microsporangiate strobili or pollen cones, and those bearing ovules are megasporangiate strobili or seed cones (or ovulate cones).
Cycads
Cycadophyta are typically dioecious (seed strobili and pollen strobili are produced on separate plants). The lateral organs of seed strobili are megasporophylls (modified leaves) that bear two to several marginal ovules. Pollen strobili consist of microsporophylls, each of which may have dozens or hundreds of abaxial microsporangia.
 Dioon edule, seed cone
Dioon edule, seed cone Cycas circinalis, pollen cone
Cycas circinalis, pollen cone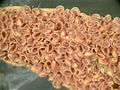 Abaxial surface of Cycas revoluta microsporophyll, showing microsporangia
Abaxial surface of Cycas revoluta microsporophyll, showing microsporangia
Ginkgos
The single living member of the Ginkgophyta, Ginkgo biloba produces pollen strobili, but the ovules are typically borne in pairs at the end of a stem, not in a strobilus. When there are more than a pair of ovules in "G. biloba", however, or when fossil taxa bearing large numbers of ovules are examined, it is clear that the paired ovules in the extant species are a highly reduced strobilus.
 Pollen cones of Ginkgo
Pollen cones of Ginkgo Pollen cone of Ginkgo, showing microsporophylls each with two microsporangia
Pollen cone of Ginkgo, showing microsporophylls each with two microsporangia
Conifers
Pollen strobili of Pinophyta are similar to those of cycads (although much smaller) and Ginkgoes in that they are composed of microsporophylls with microsporangia on the abaxial surface. Seed cones of many conifers are compound strobili. The central stem produces bracts and in the axil of each bract is a cone scale. Morphologically the cone scale is a reduced stem. Ovules are produced on the adaxial surface of the cone scales.
Gnetophytes
Gnetophyta consists of three genera, Ephedra, Gnetum and Welwitschia. All three are typically dioecious, although some Ephedra species exhibit monoecy. In contrast to the conifers, which have simple pollen strobili and compound seed strobili, gnetophytes have both compound pollen and seed strobili. The seed strobili of Ephedra and Gnetum are reduced, with Ephedra producing only two ovules per strobilus and Gnetum a single ovule.
 Seed cones of Welwitschia
Seed cones of Welwitschia Pollen cones of Welwitschia
Pollen cones of Welwitschia Pollen cones of Ephedra
Pollen cones of Ephedra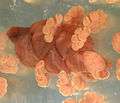 Pollen cone of Ephedra showing microsporangia
Pollen cone of Ephedra showing microsporangia Ephedra intermedia seed cone.
Ephedra intermedia seed cone.- Seed cones of Gnetum
Flowering plants
The flower of flowering plants is sometimes referred to as a bisexual strobilus. Stamens include microsporangia within the anther, and ovules (contained in carpels) contain megasporangia. Magnolia has a particularly strobiloid flower with all parts arranged in a spiral, rather than as clear whorls.
A number of flowering plants have inflorescences that resemble strobili, such as catkins, but are actually more complex in structure than strobili.
Evolution of strobili
It is likely that strobili evolved independently in most if not all these groups. This evolutionary convergence is not unusual, since the form of a strobilus is one of the most compact that can be achieved in arranging lateral organs around a cylindric axis, and the consolidation of reproductive parts in a strobilus may optimize spore dispersal and nutrient partitioning.
Etymology
The word strobilus is related to the ancient Greek strobilos = whirlwind.
References
- Gifford, E. M. & Foster, A. S. (1988). Comparative morphology of vascular plants, 3rd ed. New York: WH Freeman.
