Star (rocket stage)
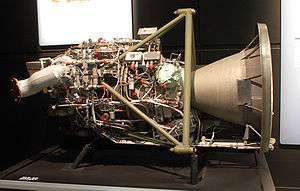
The Star is a family of US solid-propellant rocket motors used by many space propulsion and launch vehicle stages. They are used almost exclusively as an upper stage, often as an apogee kick motor.
Star 24
The Star 24 (TE-M-640) is a solid fuel apogee kick motor, first qualified in 1973.[1] It burns an 86% solids carboxyl-terminated polybutadiene (CTPB) fuel.[1][2]
- Thiokol Star-24 family[1]
| Name (Thiokol#) | Mass (kg) | Prop. mass fract. | Prop. | Casing | Thrust, vac. (kN) | Imp. | Burn (s) | Diam. (m) | Length (m) | Remark | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Empty | Prop. | Spec., Isp (s) | Tot. (kNs) | |||||||||
| Star-24 (TE-M-640) | 218.2 | 18.33 | 199.9 | 0.92 | Solid | Titanium | ? | 282.9 | 560.5 | 29.6 | 0.62 | 1.03 | |
| Star-24C (TE-M-640-4) | 239.3 | 19.73 | 219.5 | 0.92 | Solid | Titanium | ? | 282.3 | 613.9 | 28.0 | 0.62 | 1.07 | |
Star 27
 A Star-27 kick motor with nozzle for IBEX | |
| Country of origin | United States |
|---|---|
| Solid-fuel motor | |
The Star 27 is a solid apogee kick motor, with the 27 representing the approximate diameter of the stage in inches.[3] It burns HTPB fuel with an average erosion rate of 0.0011 inches per second.[4][3] When used on the Pegasus air-launch rocket payloads are capable of leaving Earth orbit.[3]
A version of the Star 27, designated Star 27H,[5] was used in the launch of the IBEX spacecraft.[6] The spacecraft had a mass of 105 kg by itself and together with its Star 27 motor, 462 kg.[6] The Star 27H helped it get to a higher orbit, beyond Earth's magnetosphere.[6]
Star 37
 TE-M-364 | |
| Country of origin | United States |
|---|---|
| Date | 1963-present |
| Application | Upper stage/Spacecraft propulsion |
| Predecessor | Star 27 |
| Successor | Star 48 |
| Status | Active |
| Solid-fuel motor | |
| Configuration | |
| Chamber | 1 |
| Performance | |
| Thrust (vac.) | 33.600 kN (7,554 lbf) |
| Isp (vac.) | (161,512 N•s/kg) |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 2.27 m (7.44 ft) |
| Diameter | 0.66 m (2.16 ft) |
| Dry weight | 113 kg (249 lb) |
| Used in | |
| Thor (rocket family), Delta (rocket family), upper stage | |
The Star 37 was first used as the engine for the Thor-Burner upper stage in 1965. The Burner I used the Thiokol FW-4 (TE 364-1) engine and the Burner 2 used the Thiokol (TE-M-364-2).[7]
The "-37" designation refers to the approximate diameter of the fuel casing in inches; Thiokol had also manufactured other motors such as the Star-40 and Star 48. Internally, Thiokol's designation was TE-M-364 for early versions, TE-M-714 for later ones, and TE-M-783 for a special HTPB model used for FLTSATCOM launches.
Subtypes are given one or more letter suffixes after the diameter number, or a trailing number (i.e., "-2") after the internal designation. Not surprisingly, the "T" prefix stands for Thiokol, and the following letter refers to the company division that developed the rocket motor. In this case, "M" refers to the Magna, UT Division. "E" refers to the Elkton, MD division.
The Star 37FM rocket motor was developed and qualified for use as an apogee kick motor on FLTSATCOM. The motor is a replacement for the Star 37E Delta, which has been discontinued. The Nozzle assembly uses a 3D carbon-carbon throat and a carbon-phenolic exit cone. Maximum propellant weight is 2350 pounds, while the motor has been qualified for propellant off-loading to 2257 pounds.
The Star 37XFP rocket motor has been qualified as the orbit insertion motor for Rockwell International's (now Boeing) Global Positioning Satellite (GPS), and as the apogee motor for the RCA SATCOM Ku-Band satellite. The Star 37XFP motor can be used as a replacement for the Star 37F motor, which has been discontinued.
A spin-stabilized or thrust-vectoring version of Star 37 is used as the final stage of the Minotaur V launch vehicle.[8][9]
The Voyager 1 & 2 Propulsion Modules used Star 37E motors.
| Name (Thiokol#) | Mass (kg) | Prop. mass fract. | Prop. | Casing | Thrust, vac. (kN) | Imp. | Burn (s) | Diam. (m) | Length (m) | Remark | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Empty | Prop. | Spec., Isp (s) | Tot. (kNs) | |||||||||
| Star-37 (TE-M-364-1) | 621.2 | 62.7 | 558.4 | 0.899 | Solid | ? | 43.50 | 260.0 | 1584.46 | 42 | 0.93 | 0.80 | |
| Star-37B (TE-M-364-2) | 718.4 | 64.7 | 653.7 | 0.910 | Solid | ? | ? | 291.0 | 1858.91 | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37C (TE-M-364-18) | 1047.5 | 82.8 | 964.7 | 0.921 | Solid | ? | ? | 285.5 | 2707.19 | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37D (TE-M-364-3) | 718.4 | 64.7 | 653.7 | 0.910 | Solid | ? | ? | 266.0 | 1858.91 | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37E (TE-M-364-4) | 1122.7 | 83.1 | 1039.6 | 0.926 | Solid | ? | ? | 283.6 | 2910.03 | ? | 0.93 | ? | Discontinued |
| Star-37F (TE-M-364-19) | 934.1 | 67.3 | 866.8 | 0.928 | Solid | ? | ? | 286.0 | 2444.46 | ? | 0.93 | ? | Discontinued |
| Star-37FM (TE-M-783) | 1147.4 | 81.5 | 1065.9 | 0.929 | HTPB | Titanium | 47.26 | 289.8 | 3051.35 | 63 | 0.93 | 1.69 | Developed and qualified for use as an apogee kick motor on FLTSATCOM |
| Star-37G (TE-M-364-11) | 1152.4 | 86.4 | 1065.9 | 0.925 | Solid | ? | ? | 289.9 | 2988.36 | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37N (TE-M-364-14) | 622.9 | 63.5 | 559.3 | 0.898 | Solid | ? | ? | 290.0 | 1590.24 | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37S (TE-M-364-15) | 711.4 | 53.4 | 658.0 | 0.925 | Solid | ? | ? | 287.3 | 1872.43 | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37X (TE-M-714-1) | 1150.0 | 82.8 | 1067.2 | 0.928 | Solid | Titanium | 51.10 | 295.6 | 3047.69 | 60 | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37XE (TE-M-714-4) | ? | ? | ? | ? | Solid | Titanium | ? | ? | ? | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37XF (TE-M-714-6) | 953.2 | 67.7 | 885.4 | 0.929 | Solid | Titanium | ? | 290.0 | 2542.03 | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37XF (TE-M-714-8) | 882.5 | 67.1 | 815.4 | 0.924 | Solid | Titanium | ? | 291.1 | 2342.74 | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
| Star-37XFP (TE-M-714-17/18) | 955.3 | 71.7 | 883.6 | 0.925 | HTPB | Titanium | 38.03 | 290.0 | 2537.49 | 67 | 0.93 | 1.50 | Qualified as the orbit insertion motor for Boeing's Global Positioning Satellite (GPS), and as the apogee motor for the RCA SATCOM Ku-Band satellite. |
| Star-37Y (TE-M-714-2) | 1152.1 | 80.6 | 1071.4 | 0.930 | Solid | Titanium | ? | 297.0 | 3118.20 | ? | 0.93 | ? | |
Star 48
 Star-48B rocket motor | |
| Country of origin | United States |
|---|---|
| Date | 1982 - present |
| Manufacturer | Thiokol |
| Predecessor | Star 37 |
| Solid-fuel motor | |
The Star 48 is a type of solid rocket motor developed primarily by Thiokol Propulsion, which was purchased by Orbital ATK in 2001.[10] In 2018, Orbital ATK in turn was acquired by Northrop Grumman.
The "48" designation refers to the approximate diameter of the fuel casing in inches; Thiokol had also manufactured other motors such as the Star 37 and Star 30. Internally, Thiokol's designation was TE-M-711 for early versions, and TE-M-799 for later ones. Subtypes are given one or more letter suffixes after the diameter number, or a trailing number (i.e., "-2") after the internal designation. The "T" prefix stands for Thiokol, and the following letter refers to the company division that developed the rocket motor. In this case, "E" refers to the Elkton, MD division and the "M" stands for motor.
The most common use of the Star 48 was as the final stage of the Delta II launch vehicles. Other launchers have also incorporated the motor, but with lower frequency. In such usage, the complete stage (motor plus accessories) is referred to as the Payload Assist Module (PAM), as the Shuttle could only take satellites to low Earth orbit. Because geostationary orbit is much more lucrative, the additional stage was needed for the final leg of the journey. On such missions, the stage is spin-stabilized. A turntable, mounted in the shuttle payload bay or atop the previous Delta stage, spun the PAM and payload to approximately 60 rpm prior to release.
Usually after motor burnout and just prior to satellite release the spin in canceled out using a yo-yo de-spin technique.
A non-spinning, thrust-vectoring version of the Star 48 is available ("Star 48BV"), but much less common. A thrust-vectoring Star 48 is the final stage of the Minotaur IV+ launch vehicle.
A Star 48 motor used in the 3rd stage of the New Horizons probe was the first part of the New Horizons mission to reach Jupiter, crossing Pluto's orbit in 2015 at a distance of 200 million kilometers.[11]
A Star 48 Payload Assist Module that had been used to launch a GPS satellite in 1993 crashed in the Saudi Arabian desert in January 2001, after its orbit decayed. The unit did not burn up on reentry and was positively identified on the ground.[12]
In 2013 a Star 48GXV was tested for the Parker Solar Probe mission as the upper stage on an Atlas V 551 vehicle,[13] but the development was cancelled, in favor of a Delta IV Heavy / Star 48BV combination.[14]
Related development
Burner upper stages
The Burner and Burner 2 rocket stages have been used as upper stages of launch vehicles such as the Thor and Delta since 1965. Burner II was a launch vehicle upper stage developed by Boeing for the Air Force Space Systems Division. It was the first solid-fuel upper stage with full control and guidance capability developed for general space applications.
In March 1964, the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program office approved plans to develop a more powerful Thor Burner 2 launch vehicle. Burner 2 used a Thiokol Star 37B motor (TE-M-364-2). Star 37, from which Star 37B was derived, had originally been developed to serve as the Surveyor lunar lander retro-rocket. Star 37B weighed 718 kg loaded and produced about 4.59 tonnes of thrust for 42 seconds. The Burner 2 stage was fitted with 3-axis control by Boeing, allowing it to coast without spin stabilization after separating from Thor.[15]
Burner II was a launch vehicle upper stage developed by Boeing for the Air Force Space Systems Division. It was the first solid-fuel upper stage with full control and guidance capability developed for general space applications. Burner II was designed for use with the Thor booster, but was readily adapted for use on the complete range of standard launch vehicles. Its general assignment was to place small- and medium size payloads into orbit. The Burner II motor, guidance system and reaction control system were integrated to provide attitude stability and precise control of flight rate and burnout velocity for orbital injection and earth-escape missions. Boeing had delivered 8 flight vehicles under its original contract. Under terms of a follow-on contract, it built 6 additional flight models.
In addition to use on Delta family rockets, Burner 2/Star 37 stages have been used on both Atlas and Titan rockets.[16]
Solid propellant rocket stage. Loaded/empty mass 774/116 kg. Thrust 43.55 kN. Vacuum specific impulse 285 seconds. Thiokol solid rocket engine. 43.5 kN. Total impulse 161,512 kgf s. Motor propellant mass fraction 0.899. Isp=260s. First flight 1963. Thrust (sl): 33.600 kN (7,554 lbf). Thrust (sl): 3,428 kgf.
Gross mass: 621 kg (1,369 lb). Unfuelled mass: 63 kg (138 lb). Height: 0.84 m (2.75 ft). Diameter: 0.66 m (2.16 ft). Thrust: 43.50 kN (9,779 lbf). Specific impulse: 260 s. Specific impulse sea level: 220 s. Burn time: 42 s. Number: 180
References
- Orbital ATK Propulsion Products Catalog (October 2016) - Page 84-85
- C.E.Carr II and D.W.Walstrum - Solid Rocket Propulsion for Small-Satellite Applications, Presented at Third Annual AIAA/Utah State University Conference on Small Satellites, Utah State University, Logan, Utah (26-28 September 1989) - Page 9
- David Darling (2003). The Complete Book of Spaceflight: From Apollo 1 to Zero Gravity. Wiley. pp. 317–318. ISBN 978-0-471-46771-7.
- George P. Sutton; Oscar Biblarz (2011). Rocket Propulsion Elements. Wiley. p. 592. ISBN 978-1-118-17461-6.
- "Les lanceurs Pegasus". www.capcomespace.net. Retrieved 2017-02-12.
- IBEX
- http://www.globalsecurity.org/space/systems/thor.htm Global Security
- "Orbital's Minotaur V launches LADEE mission to the Moon | NASASpaceFlight.com". www.nasaspaceflight.com. Retrieved 2017-02-12.
- Kyle, Ed. "Space Launch Report ... Minotaur Data Sheet". www.spacelaunchreport.com. Retrieved 2017-02-12.
- ATK Space Propulsion Products Catalog (PDF). ATK. 2012. pp. 99ff. Retrieved 2013-06-06.
- Derelict Booster to Beat Pluto Probe to Jupiter
- "PAM-D Debris Falls in Saudi Arabia" (PDF). The Orbital Debris Quarterly News. NASA Johnson Space Center. 6 (2): 1. April 2001.
- ATK and NASA Successfully Demonstrate New Rocket Motor for Solar Probe Plus Mission
- "Orbital ATK to Augment ULA Rocket for Launch of NASA Solar Probe". ExecutiveBiz. Retrieved 2017-02-12.
- http://www.spacelaunchreport.com/thorh6.html Thor H6, Spacelaunch Report
- "Star 37". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 2008-10-16.