Squawk virtual machine
Squawk is a Java micro edition virtual machine for embedded system and small devices. Most virtual machines for the Java platform are written in low level native languages such as C/C++ and assembler; what makes Squawk different is that Squawk's core is mostly written in Java (this is called a meta-circular interpreter). A Java implementation provides ease of portability, and integration of virtual machine and application resources such as objects, threads, and operating-system interfaces.
 | |
| Developer(s) | Sun Microsystems |
|---|---|
| Initial release | April 2002 |
| Repository | github |
| Written in | C and Java |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Type | Java Virtual Machine |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | java |
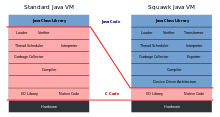
The Squawk Virtual Machine figure can be simplified as:
- Write as much of the VM in Java as possible
- Targeting small, resource constrained devices
- Enable Java for micro-embedded development
The research project was inspired by Squeak. Squawk has a Java ME heritage and features a small memory footprint.[1] It was developed to be simple with minimal external dependencies. Its simplicity made it portable and easy to debug and maintain. Squawk also provides an isolated mechanism by which an application is represented as an object. In Squawk, one or more applications can run in the single JVM. Conceptually, each application is completely isolated from all other applications.
See also
- Sun SPOT
- Jikes RVM, another JVM written mostly in Java
- Rubinius, a VM for Ruby written in Ruby
- MicroEJ VEE, another JVM written mostly in (an extended version of) Java
- List of Java virtual machines
References
- A Java Virtual Machine Architecture for Very Small Devices Archived February 16, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
External links
- SunSPOTs and Squawk technology Podcast
- A Java Virtual Machine Architecture for Very Small Devices
- The Squawk Virtual Machine: Java(TM) on the Bare Metal
- Javaone 2006 Squawk for Wireless Sensor Networks
- Application-Driven Customization of an Embedded Java Virtual Machine
- Ahead of time deployment in ROM of a Java-OS
- Project Sun Spot
- Squawk Poster
_waving.svg.png)