Southern Cross Cable
The Southern Cross Cable, operated by Bermuda company Southern Cross Cables Limited, is a trans-Pacific network of telecommunications cables commissioned in 2000.
| Cable type | Fibre-optic |
|---|---|
| Fate | Active |
| Construction beginning | 1999 |
| Construction finished | 2000 |
| First traffic | 2000 |
| Design capacity | >20000 Gbit/s (Jan 2020, based on 100G+ Technology) |
| Lit capacity | 10 Tbit/s (January 2020) |
| Built by | Alcatel-Lucent/Fujitsu |
| Area served | Southern Pacific |
| Owner(s) | Southern Cross Cables Limited (Spark, Singtel/Optus, Telstra, Verizon Business) |
| Website | www |
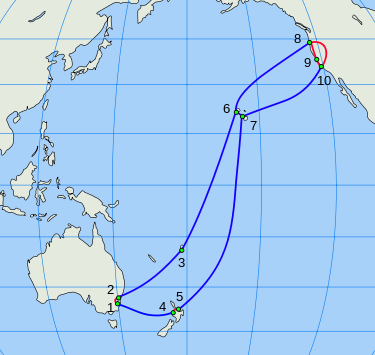
The network has 28,900 km of submarine and 1,600 km of terrestrial fiber optic cables, all which operate in a triple-ring configuration. Initially, each cable had a bandwidth capacity of 120 gigabit/s. In April of 2008 this capacity was doubled, and was once again upgraded to 860 gigabit/s at the end of 2008. Southern Cross upgraded the existing system to 1.2 Tbit/s in May 2010.[1] After successful trials of 40G technology the first 400G of a planned 800G upgrade has been completed in February 2012, and the remaining 400G was completed in December 2012.[2] An additional 400G was deployed utilizing 100G coherent wavelength technology in July 2013, taking total system capacity to 2.6Tbit/s, with an additional 500Gbit/s to be deployed per segment by Q2 2014, increasing total system capacity to 3.6Tbit/s. About every two or three years, the Southern Cross Company makes an effort to upgrade the cables in some way or another.[3] In June 2014 a further 900Gbps was added.[3] The system currently runs at circa 10Tbs employing a mix of 100Gbs, 200Gbs and 250Gbs wavelengths.
Southern Cross offers capacity services from 100M/STM-1 to 100Gbit/s OTU-4, including 1G, 10G and 40G Ethernet Private Line services.
Landing points
- Alexandria, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- Brookvale, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- Suva, Fiji
- Whenuapai, New Zealand
- Takapuna, New Zealand
- Kahe Point, Oahu, Hawaii, United States
- Samuel M. Spencer Beach, Hawaiʻi island, Hawaii, United States
- Nedonna Beach, Oregon, United States
- Morro Bay, California, United States
Access points
- Equinix, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia (terrestrial connection only)
- Westin Building, Seattle, Washington, United States (terrestrial connection only)
- CoreSite, San Jose, California, United States (terrestrial connection only)
Network segments
The network comprises 12 segments (length of segment in brackets):
Submarine
- A. Alexandria-Whenuapai (2280 km)
- C. Takapuna-Spencer Beach (8000 km)
- D. Spencer Beach-Morro Bay (4135 km)
- F. Kahe Point-Hillsboro, Oregon (4540 km)
- G1. Suva-Kahe Point (5830 km)
- G2. Brookvale-Suva (3540 km)
- I. Spencer Beach-Kahe Point (460 km)
Terrestrial
- B. Whenuapai-Takapuna (15 km)
- E. Hillsboro, Oregon-Morro Bay (1590 km)
- E1. Morro Bay-San Jose (350 km)
- E2. San Jose-Hillsboro, Oregon (1600 km)
- H. Alexandria-Brookvale (30 km)
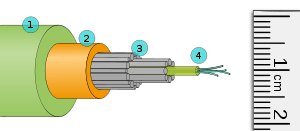
Topology
The network topology is configured to have redundant paths and be self-healing in case of physical damage.
In the cross section diagram shown:
- Insulating high density polyethylene (17 mm)
- Copper tubing (8.3 mm)
- Steel wires
- Optical fibers in water resistant jelly (2.3 mm)
Spying and interception
In 2013 the New Zealand Herald reported that the owners of the Southern Cross cable had asked the United States National Security Agency to pay them for mass surveillance of New Zealand internet activity through the cable.[4] In May 2014, John Minto, vice-president of the New Zealand Mana Party, alleged that the NSA was carrying out mass surveillance on all meta-data and content that went out of New Zealand through the cable.[4]
In August 2014, Russel Norman, New Zealand Green Party co-leader, stated that an interception point was being established on the Southern Cross Cable.[5] Norman said that as the cable is the only point of telecommunications access from New Zealand, this would allow the Government to spy on all phone calls and internet traffic from New Zealand.[5] Norman's claims followed the revelation that an engineer from the NSA had visited New Zealand earlier in the year to discuss how to intercept traffic on the Southern Cross cable.[5]
The office of John Key, New Zealand Prime Minister, denied the claims but admitted that they were negotiating a "cable access programme" with the NSA but refused to clarify what that was or why the NSA was involved.[5]
Damage incidents
There have been few incidents damaging sections of the Southern Cross Cable, despite it traversing the Pacific Ocean's Ring of Fire and its long length.
In late 2007, Southern Cross Cable's operations vice president, Dean Veverka, confirmed that hurricane strength storms and flooding had wiped out the carrier's Oregon cable route and halved its bandwidth capability between Australia/New Zealand/Fiji and United States for a short period of time, albeit customer services were restored via the systems alternate path. A Southern Cross customer (iiNet) said that emergency works have been organised to perform a more permanent fix for the damage to the cable. These works were performed on 3 February 2008 at 12 midnight AEST.[6]
In March 2008, the then head of Telecom Wholesale, Matt Crockett, mentioned to the National Business Review that there had been a recent undersea earthquake that impacted a shunt on the Southern Cross Cable. However, due to the Cable's redundancy and spare capacity, users experienced no change in access or speed.[7]
Construction and ownership
Construction of the cable began in July 1999, laid by the ship CS Vercors, and the system was in use by customers by November 2000. Additional works and upgrades have since taken place to increase the network's capacity to 480 Gbit/s. In August 2007, SC Cables contracted with Alcatel-Lucent to upgrade the cable to 660 Gbit/s by the end of the first quarter 2008 and to 860 Gbit/s by the end of 2008, with future upgrade also by Alcatel-Lucent to 1.2 Tbit/s in May 2010.[8]. The cable has since been upgraded to over 10Tbs of capacity with a further >10Tbs of capability available on the existing system. The Southern Cross NEXT system will add a further 72Tbs of capability to the network by the end of 2021.
The cable was a private investment and there was in estimated $1.5 billion spent on the initial system development.[9]The company is owned by Spark New Zealand, SingTel/Optus, Telstra (as of December 2019) and Verizon Business.[10] The cables are the result of an agreement between companies Spark Trading, Optus, MFS Globenet, and Southern Cross. The agreement was reached between the companies in 1997 as a response to unexpected growth of the internet that created a need for a submarine cable link connecting the West Coast and Australasia.[11]
Southern Cross NEXT
Southern Cross NEXT is a new route addition to the Southern Cross cable eco-system. This new addition began construction in 2019 and is forecast to be completed by 2022[12]. When finished, the new link will be the largest capacity data link between Sydney, Auckland, and Los Angeles at 16,148 km[12]. The cable is predicted to cost around $300 million and is owned by the Southern Cross group of companies[12]. When finished, Southern Cross NEXT will be able to carry up to 72 terabits per second.[13] The NEXT cable will not be marketed as a stand-alone cable, but rather is designed to be an extension of the original Southern Cross network. The Southern Cross group companies are funding this new segment, through debt and equity arrangements, with the Australian Telecommunication company, Telstra, entering as a new shareholder of the Southern Cross companies.[14] Spark New Zealand announced that Telstra was becoming a 25% stakeholder in the cables in August 2019, at the same press conference they announced that Southern Cross NEXT was fully approved.[14]
Interconnected cables
A number of Pacific Island cables interconnect with Southern Cross, including the Tonga Cable System, the Interchange Cable System to Vanuatu, the TUI-Samoa cable linking Samoa to Fiji, and the Gondwana-1 system linking Australia to New Caledonia. The Honotua cable system links French Polynesia to the Southern Cross system in Hawaii.
See also
- List of international submarine communications cables
- Other Australian international submarine cables (and year of first service):
- Pipe Pacific Cable (2009)
- Telstra Endeavour (2008)
- Australia–Japan Cable (2001)
- SEA-ME-WE 3 (2000, Australian portion in service earlier)
- JASURAUS (1997)
- PacRimWest (1995)
References
- Broadband in for another price fall and capacity boost
- Southern Cross committed to Ultra Fast Broadband and National Broadband Network
- "FAQ". www.southerncrosscables.com. Retrieved 2019-10-01.
- John Minto (2014-05-14). "GCSB holding doors open while US buddies invade our privacy". New Zealand Herald.
- "Govt called to account for spy claims". Radio New Zealand. 2014-08-01.
- iiNet status page: information regarding Southern Cross cable repairs
- Keall, Chris (6 March 2009). "Earthquake hits Southern Cross Cable". National Business Review. Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- Contract awarded to upgrade Southern Cross cable network: New technology facilitated further upgrades up to 2.4 Tbit/s., Computerworld, accessed 24 August 2007
- "Southern Cross - Submarine Networks". www.submarinenetworks.com. Retrieved 2019-10-14.
- "About Southern Cross". Southern Cross. Retrieved 9 July 2018.
- "FAQ". www.southerncrosscables.com. Retrieved 2019-10-01.
- "Southern Cross begins building 16,000km cable between Australia and US". www.datacenterdynamics.com. Retrieved 2019-11-19.
- "Southern Cross NEXT Cable Enters Construction Phase". www.businesswire.com. 2019-10-01. Retrieved 2019-11-26.
- "Agreements signed for build of new Southern Cross NEXT cable". www.sparknz.co.nz. Retrieved 2019-11-26.