Senate, Saskatchewan
Senate is an unincorporated community within the Rural Municipality of Reno No. 51, Saskatchewan, Canada. The village had a population of 63 around 1940 and has since declined to 0 resident. The town-site is located along Hwy 21 & the historic Red Coat Trail (also known as Hwy 13), about 20 km east of the Alberta-Saskatchewan border and is about 200 km southwest of the city of Swift Current.
Senate | |
|---|---|
Unincorporated community | |
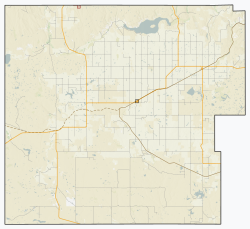 Senate Location of Senate, Saskatchewan  Senate Senate (Saskatchewan) | |
| Coordinates: 49.2745°N 109.7002°W | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | Saskatchewan |
| Region | Southwest Saskatchewan |
| Census division | 4 |
| Rural Municipality | Reno |
| Established | 1910 |
| Incorporated (Village) | 1914-1994 |
| Dissolved (unincorporated | January 1, 1994 |
| Government | |
| • Administrator | Lacelle Kim |
| • Governing body | Reno No. 51 |
| Population (1940) | |
| • Total | 63 |
| Time zone | CST |
| Postal code | S0N 2G0 |
| Area code(s) | 306 |
| Highways | |
| Railways | Great Western Railway |
| [1][2][3][4] | |
Demographics
Prior to January 1, 1994, Senate was incorporated as a village, and was dissolved into an unincorporated community under the jurisdiction of the Rural municipality of Reno on that date.[5]
| Canada census – Senate, Saskatchewan community profile | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | |||
| Population: | 0 (0.0% from 2001) | ||
| Land area: | |||
| Population density: | 0.00/km2 (0/sq mi) | ||
| Median age: | |||
| Total private dwellings: | |||
| Median household income: | |||
| References: 2006[6] earlier[7] | |||
History
Paul Kalmring's family ran a corner store and gas station for most of the time between 1916 and 1983 in the tiny community, named after federal senators of the day when the community was created in 1914. Kalmring's family moved to the area when Paul was two, and his father soon purchased a convenience store and gas station.
Senate's population peaked at 63 in the 1940s and was a stopping point for the Canadian Pacific Railway. For a few years, Senate even had its own train ticket agent.
The west had just been opened up to waves of European settlers seeking prosperity, and at first, the future appeared promising for Senate and several others along Highway 13, or what is now know today as the Red Coat Trail.
During Senate's best years, the community boasted two elevators, a five-room hotel and restaurant, blacksmith shop, lumberyard and Kalmring's general store and gas station. For leisure, the citizens of Senate also built a tennis court and a baseball diamond across the train tracks.
But as in most other locales along southwest Saskatchewan, Senate's fortunes declined after the 1940s. Regional farm consolidation, drought and rural depopulation ended all hope for any lasting life at Senate.
By the early 1980s, Kalmring sold his store and moved to his farm, three kilometres north of Senate. And in 1983, the community was empty, home only to prairie ghosts. In 1994, with the railway and elevators also gone, rural municipality officials brought in the bulldozers and levelled Senate's remaining dilapidated buildings and dumped part of the debris into a nearby landfill.
Geography
Most cities in Canada and throughout the world have their antipode in the ocean. In the 1940s, Senate was one of only a handful of communities in Canada that has not only land, but a similar size village, in this case Port aux Francais on the Kerguelen Islands, within 10 km of its antipode.
See also
- List of communities in Saskatchewan
- List of ghost towns in Canada
- Ghost towns in Saskatchewan
References
- National Archives, Archivia Net, Post Offices and Postmasters
- Government of Saskatchewan, MRD Home, Municipal Directory System, archived from the original (– Scholar search) on November 21, 2008
- Canadian Textiles Institute. (2005), CTI Determine your provincial constituency, archived from the original on 2007-09-11
- Commissioner of Canada Elections, Chief Electoral Officer of Canada (2005), Elections Canada On-line
- "Restructured Villages". Saskatchewan Ministry of Municipal Affairs. Archived from the original on March 25, 2008. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- "2006 Community Profiles". 2006 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. March 30, 2011. Retrieved 2009-02-24.
- "2001 Community Profiles". 2001 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. February 17, 2012.