Scandium dodecaboride
Scandium dodecaboride is a refractory metal boride.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
scandium dodecaboride | |
| Identifiers | |
| Properties | |
| ScB12 | |
| Molar mass | 174.69 g/mol |
| Structure | |
| Tetragonal, tI26 | |
| I4/mmm, No. 139 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis
ScB12 is formed by mixing a 7:1 ratio of boron powder and scandium oxide powder, heating to 2500 °C with a plasma torch or similar, quenching in cold water and washing with concentrated hydrochloric acid.[1]
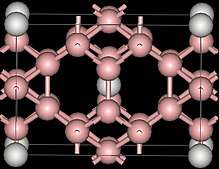
Crystallography
ScB12 was originally reported as having a cubic structure,[2] later studies showed it to have tetragonal structure (unit cell with a=522pm, c=735pm).[1] More recently it has been shown that there is indeed a cubic form but that it requires stabilization.[3]
gollark: Germany has some weird church tax.
gollark: It's already too late. Merely processing the paperwork to determine your legal fees would bankrupt you.
gollark: According to my calculator, 2.3e22 lawsuits per second are being fired from the laser system.
gollark: No, I know it, I don't not know it.
gollark: It's already too late. Even if I stop the new lawsuits, NONE are safe.
References
- Matkovich, V.I.; J Economy; R F Giese Jr; R Barrett (1965). "The structure of metallic dodecaborides" (PDF). Acta Crystallogr. 19 (6): 1056–1058. doi:10.1107/S0365110X65004954. Retrieved 2008-08-28.
- Przybylska, Maria; Allan H. Reddoch; George J. Ritter (1963). "The Preparation and Structure of Lutetium Diboride, Scandium Dodecaboride and Lutetium Antimonide". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85 (4): 407–411. doi:10.1021/ja00887a008.
- Paderno, Y.; N. Shitsevalova (1995). "Stabilization of cubic scandium dodecaboride". Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 219 (1–2): 119–123. doi:10.1016/0925-8388(94)05048-1.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.