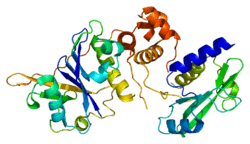SOCS2
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOCS2 gene.[5][6][7]
This gene encodes a member of the STAT-induced STAT inhibitor (SSI), also known as suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS), family. SSI family members are cytokine-inducible negative regulators of cytokine signaling. The expression of this gene can be induced by a subset of cytokines, including erythropoietin, GM-CSF, IL10 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). The protein encoded by this gene is found to interact with the cytoplasmic domain of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R), and thus is thought to be involved in the regulation of IGF1R mediated cell signaling.[8] Knockout studies in mice also suggested a regulatory role of this gene in IGF-1 related growth control.[7][9]
Interactions
SOCS2 has been shown to interact with insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor[8] and erythropoietin receptor.[10]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000120833 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020027 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Masuhara M; Sakamoto H; Matsumoto A; Suzuki R; Yasukawa H; Mitsui K; Wakioka T; Tanimura S; Sasaki A; Misawa H; Yokouchi M; Ohtsubo M; Yoshimura A (November 1997). "Cloning and characterization of novel CIS family genes". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 239 (2): 439–46. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7484. PMID 9344848.
- Minamoto S; Ikegame K; Ueno K; Narazaki M; Naka T; Yamamoto H; Matsumoto T; Saito H; Hosoe S; Kishimoto T (September 1997). "Cloning and functional analysis of new members of STAT induced STAT inhibitor (SSI) family: SSI-2 and SSI-3". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 237 (1): 79–83. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7080. PMID 9266833.
- "Entrez Gene: SOCS2 suppressor of cytokine signaling 2".
- Dey BR; Spence SL; Nissley P; Furlanetto RW (September 1998). "Interaction of human suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-2 with the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (37): 24095–101. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.37.24095. PMID 9727029.
- Greenhalgh CJ; Bertolino P; Asa SL; Metcalf D; Corbin JE; Adams TE; Davey HW; Nicola NA; Hilton DJ; Alexander WS (June 2002). "Growth enhancement in suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS-2)-deficient mice is dependent on signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b)". Mol. Endocrinol. 16 (6): 1394–406. doi:10.1210/me.16.6.1394. PMID 12040024.
- Eyckerman, S; Verhee A; der Heyden J V; Lemmens I; Ostade X V; Vandekerckhove J; Tavernier J (Dec 2001). "Design and application of a cytokine-receptor-based interaction trap". Nat. Cell Biol. 3 (12): 1114–9. doi:10.1038/ncb1201-1114. ISSN 1465-7392. PMID 11781573.
Further reading
- Lopaczynski W (1999). "Differential regulation of signaling pathways for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I.". Acta Biochim. Pol. 46 (1): 51–60. PMID 10453981.
- Wang J; Campbell IL (2002). "Cytokine signaling in the brain: putting a SOCS in it?". J. Neurosci. Res. 67 (4): 423–7. doi:10.1002/jnr.10145. PMID 11835308.
- Kile BT, Schulman BA, Alexander WS, et al. (2002). "The SOCS box: a tale of destruction and degradation". Trends Biochem. Sci. 27 (5): 235–41. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(02)02085-6. PMID 12076535.
- Pezet A; Buteau H; Kelly PA; Edery M (1997). "The last proline of Box 1 is essential for association with JAK2 and functional activation of the prolactin receptor". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 129 (2): 199–208. doi:10.1016/S0303-7207(97)00063-4. PMID 9202403.
- Dey BR; Spence SL; Nissley P; Furlanetto RW (1998). "Interaction of human suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-2 with the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (37): 24095–101. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.37.24095. PMID 9727029.
- Pezet A; Favre H; Kelly PA; Edery M (1999). "Inhibition and restoration of prolactin signal transduction by suppressors of cytokine signaling". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (35): 24497–502. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.35.24497. PMID 10455112.
- Yandava CN; Pillari A; Drazen JM (1999). "Radiation hybrid and cytogenetic mapping of SOCS1 and SOCS2 to chromosomes 16p13 and 12q, respectively". Genomics. 61 (1): 108–11. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5937. PMID 10512686.
- Ram PA; Waxman DJ (2000). "SOCS/CIS protein inhibition of growth hormone-stimulated STAT5 signaling by multiple mechanisms". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (50): 35553–61. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.50.35553. PMID 10585430.
- Metcalf D, Greenhalgh CJ, Viney E, et al. (2000). "Gigantism in mice lacking suppressor of cytokine signalling-2". Nature. 405 (6790): 1069–73. doi:10.1038/35016611. PMID 10890450.
- Shen X; Hong F; Nguyen VA; Gao B (2000). "IL-10 attenuates IFN-alpha-activated STAT1 in the liver: involvement of SOCS2 and SOCS3". FEBS Lett. 480 (2–3): 132–6. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01905-0. PMID 11034314.
- Eyckerman S, Verhee A, der Heyden JV, et al. (2002). "Design and application of a cytokine-receptor-based interaction trap". Nat. Cell Biol. 3 (12): 1114–9. doi:10.1038/ncb1201-1114. PMID 11781573.
- Schultheis B, Carapeti-Marootian M, Hochhaus A, et al. (2002). "Overexpression of SOCS-2 in advanced stages of chronic myeloid leukemia: possible inadequacy of a negative feedback mechanism". Blood. 99 (5): 1766–75. doi:10.1182/blood.V99.5.1766. PMID 11861294.
- Blumenstein M; Bowen-Shauver JM; Keelan JA; Mitchell MD (2002). "Identification of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in human gestational tissues: differential regulation is associated with the onset of labor". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87 (3): 1094–7. doi:10.1210/jc.87.3.1094. PMID 11889171.
- Biener E, Maurice S, Sandowski Y, et al. (2003). "Recombinant human CIS2 (SOCS2) protein: subcloning, expression, purification, and characterization". Protein Expr. Purif. 25 (2): 305–12. doi:10.1016/S1046-5928(02)00013-X. PMID 12135564.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
External links
- SOCS2+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)