Rotary switch
A rotary switch is a switch operated by rotation. These are often chosen when more than 2 positions are needed, such as a three-speed fan or a CB radio with multiple frequencies of reception or "channels".
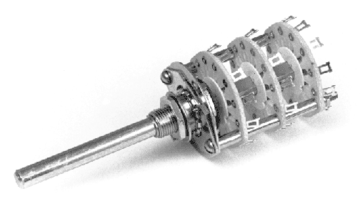
A rotary switch consists of a spindle or "rotor" that has a contact arm or "spoke" which projects from its surface like a cam. It has an array of terminals, arranged in a circle around the rotor, each of which serves as a contact for the "spoke" through which any one of a number of different electrical circuits can be connected to the rotor. The switch is layered to allow the use of multiple poles; each layer is equivalent to one pole. Usually, such a switch has a detent mechanism so it "clicks" from one active position to another rather than stalls in an intermediate position. Thus a rotary switch provides greater pole and throw capabilities than simpler switches do.
Rotary switches were used as a channel selectors on television receivers until the early 1970s, as range selectors on electrical metering equipment, as band selectors on multi-band radios, etc.
Modern rotary switches use a "star wheel" mechanism to provide the switching positions, such as at every 30, 45, 60, or 90 degrees. Nylon cams are then mounted behind this mechanism and spring-loaded electrical contacts slide around these cams. The cams are notched or cut where the contact should close to complete an electrical circuit.
Some rotary switches are user-configurable in relation to the number of positions. A special toothed washer that sits below the holding nut can be positioned so that the tooth is inserted into one of a number of slots in a way that limits the number of positions available for selection. For example, if only four positions are required on a twelve position switch, the washer can be positioned so that only four switching positions can be selected when in use.
Gallery
 Bottom view of a 12-position rotary switch showing wiper and contacts.
Bottom view of a 12-position rotary switch showing wiper and contacts. Rotary switch circuit
Rotary switch circuit Rotary switch handle as seen from below
Rotary switch handle as seen from below