Roman pot
The Roman pot (proton-on-target) is the name of a technique (and of the relevant device) used in accelerator physics. Named after its implementation by the CERN Rome group in the early 1970s, it is an important tool to measure the total cross section of two particle beams in a collider.
Roman pots are located as close to the beamline as possible, to capture the accelerated particles which scatter by very small angles.
Example
The figure below shows a detector from the TOTEM experiment at LHC, used on the beamline near IP5 (interaction point 5), the location of the CMS detector. Three of these are used per Roman Pot unit. Each is shoved into place to within 10 microns of the beamline. Two detectors are placed above and below the beamline, and a third to the side. These detectors will record any protons that are not travelling precisely along the beamline, and thus record the elastic scattering of the protons. This is used to measure the total elastic cross-section, including Coulomb scattering as well as diffractive scattering (i.e. diffraction because the protons are not point particles, and have an internal structure (i.e. quarks)). Effectively, these are detectors for studying Regge theory. The goal is to search for elastic scattering effects beyond the Standard Model, such as hypothetical "colorless gluons", as well confirming ideas of pomeron exchange, and the possible existence of an odderon.
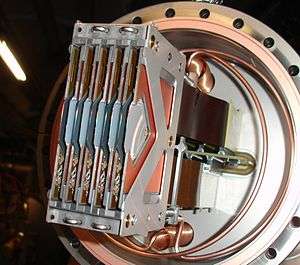
The figure below shows a single Roman pot unit, located about 220 meters forward of the IP5 interaction point. The detectors are the bulkiest bits wrapped in insulation.

See also
References
- "Roman pots for the LHC". CERN Courier. CERN. 29 March 1999. Retrieved 2009-11-19.
- "The TOTEM Roman Pots". TOTEM. Retrieved 2009-11-19.
- "THE TOTEM DETECTORS: ROMAN POTS". TOTEM. Retrieved 2018-04-23.