Prasinovirus
Prasinovirus is a genus of large double-stranded DNA viruses, in the family Phycodnaviridae that infect phytoplankton in the Prasinophyceae. There are currently only two species in this genus including the type species Micromonas pusilla virus SP1 [1][2], that infects the cosmopolitan photosynthetic flagellate Micromonas pusilla.[3]
| Prasinovirus | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Varidnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Bamfordvirae |
| Phylum: | Nucleocytoviricota |
| Class: | Megaviricetes |
| Order: | Algavirales |
| Family: | Phycodnaviridae |
| Genus: | Prasinovirus |
| Type species | |
| Micromonas pusilla virus SP1 | |
However, there is a large group of genetically diverse but related viruses that show considerable evidence of lateral gene transfer.[4][5]

Taxonomy
Group: dsDNA
- Family: Phycodnaviridae
- Genus: Prasinovirus
- Micromonas pusilla virus SP1
- Ostreococcus tauri virus OtV5
Structure
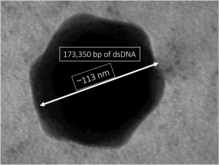
Viruses in Prasinovirus are enveloped, with icosahedral and Round geometries, and T=169 symmetry. The diameter is around 104-118 nm.[1]
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prasinovirus | Icosahedral | T=169 | Enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
Life cycle
Viral replication is nucleo-cytoplasmic. Replication follows the DNA strand displacement model. Dna templated transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by lysis via lytic phospholipids. Alga serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are passive diffusion.[1]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prasinovirus | Alga | None | Cell receptor endocytosis | Lysis | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
References
- "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ICTV. "Virus Taxonomy: 2014 Release". Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- Cottrell, Matthew T.; Suttle, Curtis A. (1991). "Wide-spread occurrence and clonal variation in viruses which cause lysis of a cosmopolitan, eukaryotic marine phytoplankter, "Micromonas pusilla"". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 78: 1–9. Bibcode:1991MEPS...78....1C. doi:10.3354/meps078001. ISSN 1616-1599.
- Bellec, Laure; Grimsley, Nigel; Derelle, Evelyn; Moreau, Herve; Desdevises, Yves (2010). "Abundance, spatial distribution and genetic diversity of Ostreococcus tauri viruses in two different environments". Environmental Microbiology Reports. 2 (2): 313–321. doi:10.1111/j.1758-2229.2010.00138.x. PMID 23766083.
- Finke, Jan F; Winget, Danielle M; Chan, Amy M; Suttle, Curtis A (2017). "Variation in the genetic repertoire of viruses Infecting Micromonas pusilla reflects horizontal gene transfer and links to their environmental distribution". Viruses. 9 (5): 116. doi:10.3390/v9050116. PMC 5454428. PMID 28534829.