Pontine nuclei
The pontine nuclei (or griseum pontis) are the nuclei of the pons involved in motor activity. The pontine nuclei are located in the ventral pons.[1] Corticopontine fibres carry information from the primary motor cortex to the ipsilateral pontine nucleus in the ventral pons, and the pontocerebellar projection then carries that information to the contralateral cerebellum via the middle cerebellar peduncle. Extension of these nuclei in the medulla oblongata are named arcuate nucleus (medulla) which has the same function.
| Pontine nuclei | |
|---|---|
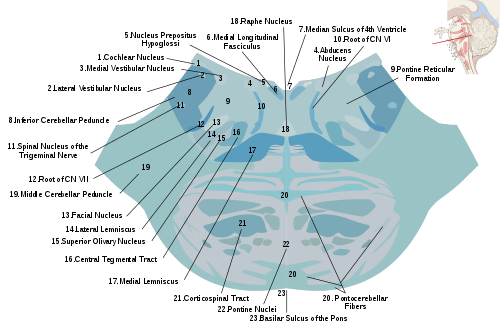 Cross section through the lower pons showing the pontine nuclei (#22) and the pontocerebellar fibers emerging from them to become the middle cerebellar peduncle | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nuclei pontis |
| NeuroNames | 617 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1516 |
| TA | A14.1.05.202 |
| FMA | 72512 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
They therefore allow modification of actions in the light of their outcome, or error correction, and are hence important in learning motor skills.
References
- Kratochwil, CF; Maheshwari, U; Rijli, FM (2017). "The Long Journey of Pontine Nuclei Neurons: From Rhombic Lip to Cortico-Ponto-Cerebellar Circuitry". Frontiers in Neural Circuits. 11: 33. doi:10.3389/fncir.2017.00033. PMC 5434118. PMID 28567005.
External links
- Illustration and text: Bs97/TEXT/P16/intro.htm at the University of Wisconsin-Madison Medical school
- Diagram at mindsci-clinic.com
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.