Polk County, Florida paleontological sites
The Polk County paleontological sites are assemblages of Early Miocene to Late Pleistocene vertebrates occurring in Polk County, Florida, United States.
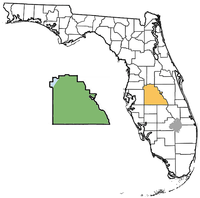
Age
Era: Neogene
Period: Miocene to Pleistocene, ~17.7—1.5 Mya. (calculates to a period of approximately 16.2 million years).
Faunal stage: Hemingfordian through early Clarendonian
Geological Formation: Bone Valley Formation.
Sites
Polk County can boast more individual fossil recovery sites than any other Florida county due to the phosphate mining concerns. Bone Valley Formation is a prime geologic formation. Some of these sites are: Agricola Road (AEO),[1] Agrico Pierce Mine (AEO), American Agricultural Chemical Company Mine, Brewster Phosphate Mine, Fort Meade Mine,[2] Kingsford Mine, Phosphoria Mine, Fort Green Mine, Payne Creek Mine, and Palmetto Mine.
Coordinates: 27.9°N 81.8°W
Specimens
Reptiles
- Caretta caretta (loggerhead sea turtle)
- Chelonia (green sea turtle)
- †Gavialosuchus americana (American crocodile)
- Lepidochelys and L. sensu lato (ridley sea turtle)
Mammals
- †Acritohippus isonesus (horse)
- †Aelurodon taxoides (proto-dog)
- †Agriotherium schneideri (bear)
- †Aphelops malacorhinus (rhinoceros)
- †Arctodus pristinus (short-faced bear)
- Arvicolinae (mole, shrew)
- †Astrohippus stockii (horse)
- †Balaenoptera floridana (rorqual)
- †Blarina carolinensis (shrew)
- †Borophagus hilli and B. pugnator (proto-dog)
- †Calippus emsliei and C. cerasinus, C. martini, C. proplacidus (horse)
- †Callophoca obscura (earless seal)
- †Camelidae (camel unknown)
- †Carpocyon limosus (Canidae)
- †Catagonus brachydontus (peccary)
- †Cervidae (deer)
- †Corystosiren varguezi (sea cow)
- †Cricetidae (vole or lemming)
- †Cuvieronius tropicus (proto-elephant)
- †Dasypus bellus (beautiful armadillo)
- †Delphinodon and D. mento (proto-dolphin)
- †Dinohippus mexicanus (horse)
- Didelphidae (opossum)
- †Enhydritherium terraenovae (mustelid)

- †Epicyon haydeni (proto-dog)
- †Eremotherium eomigrans (giant ground sloth)
- †Equidae (horse)
- †Equus leidyi (horse)
- †Felis rexroadensis (wildcat)
- Geomys pinetis (gopher)
- †Gomphotherium obscurum (proto-elephant)
- †Goniodelphis hudsoni (river dolphin)
- †Hadrodelphis (toothed whale)
- †Hemiauchenia macrocephala (camel)
- †Heteromyidae (kangaroo rat)
- †Hexameryx simpsoni (antelope)
- †Hippotherium emsliei, H. ingenuum, and H. plicatile and H. ingenuum (horse)
- †Holmesina floridanus (giant Florida armadillo)
- †Homiphoca capensis (earless seal)
- †Hypohippus affinis and H. chico (horse)
- †Hypolagus tedfordi (rabbit)
- †Kogiopsis floridana (Florida sperm whale)
- Lepus (hare)
- †Lophocetus (dolphin)
- †Mammut matthewi (mastodon)
- †Mammut americanum (American mastodon)
- †Mammuthus hayi (mammoth)
- †Megahippus (horse)
- †Megalonyx wheatleyi (giant ground sloth)
- †Megantereon hesperus (saber-cat)
- †Merychippus californicus M. brevidontus and M. goorsi (horse)
- †Mesoplodon (beaked whale)
- †Metaxytherium floridanum (Florida sea cow)
- Microtus (vole)
- †Mylohyus elmorei (peccary)
- †Nannippus and N. westoni (horse)
- †Neohipparion eurystyle (horse)
- †Ninoziphius platyrostris (beaked whale)
- †Nothrotheriops texanus (giant ground sloth)
- Odocoileus virginianus (white-tailed deer)
- Ondatra annectens (muskrat)
- †Ontocetus emmonsi (walrus)
- †Pachyarmatherium leiseyi (armadillo)
- †Palaeolama mirifica (stout-legged llama)
- †Palaeomerycidae (deer ancestor)
- †Paramylodon harlani (giant ground sloth)
- †Platanistidae (river dolphin)
- †Phocanella pumila (earless seal)
- †Piscobalaena (toothed whale)
- †Physeteridae (sperm whale)
- †Platygonus vetus (peccary)
- †Pliocyon robustus (bear-dog)
- †Plionarctos (bear)
- †Pliohippus mirabilis (horse)
- †Pomatodelphis bobengi and P. inaequalis (river dolphin)
- †Proboscidea (elephant, unknown)
- †Procyonidae (raccoon)
- †Protohippus perditus and P. supremus (horse)
- †Pseudhipparion curtivallum and P. skinneri (horse)
- †Rhynchotherium (proto-elephant)
- †Scalopus aquaticus (mole or shrew)
- †Sigmodon libitinus (cotton rat)
- †Sphenophalos garciae (antelope)
- Sylvilagus floridanus and S. palustris (rabbit)
- †Talpidae (mole or shrew)
- †Tapirus haysii, and T. polkensis (tapir)
- †Tayassuidae (peccary)
- †Teleoceras proterum (rhinoceros)
- Ziphiidae (beaked whale)
Notation
The taxa listed within this article were compiled from numerous collections within Paleobiology Database . authorized by John Alroy, Ph.D.. Further documentation on these genera and species are available.
References
- X. Wang, R. H. Tedford, and B. E. Taylor. 1999. Phylogenetic systematics of the Borophaginae (Carnivora: Canidae). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 243:1-392
- Uhen, Mark D., Collection authority and researcher, George Mason University, Assistant Term Professor, Evolution of cetaceans and other marine mammals
- Evolution of River Dolphins
- G. S. Morgan. 1994. Miocene and Pliocene marine mammal faunas from the Bone Valley Formation of central Florida. Contributions in Marine Mammal Paleontology Honoring Frank C. Whitmore Jr., Proceedings of the San Diego Society of Natural History 29:239-268