Pointe-Noire
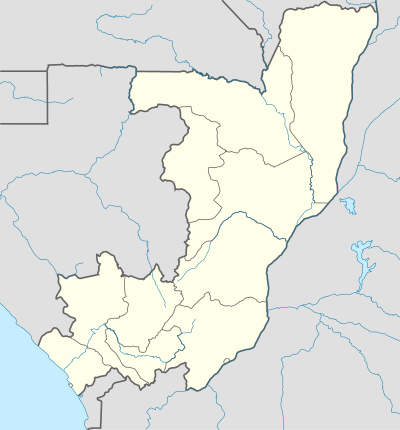
Pointe-Noire (Kongo: Ndindi) is the second largest city in the Republic of the Congo, following the capital of Brazzaville, and an autonomous department since 2004. Before this date it was the capital of the Kouilou region (now a separate department). It is situated on a headland between Pointe-Noire Bay and the Atlantic Ocean. Pointe-Noire is the main commercial centre of the country and has a population of 715,334 (2007),[3] expanding to well over 1 million when the entire metropolitan area is taken into account.
Pointe-Noire | |
|---|---|
 Pointe-Noire | |
 Pointe-Noire Location in the Republic of the Congo | |
| Coordinates: 04°46′43″S 11°51′49″E | |
| Country | |
| Department | Pointe-Noire Department |
| Commune | Pointe-Noire |
| Founded | 1883 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Jean-François Kando (PCT) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 43.7 km2 (16.9 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 14 m (46 ft) |
| Population (2007[1]) | |
| • Total | 715,334 |
| • Density | 16,000/km2 (42,000/sq mi) |
| Area code(s) | 242 |
| HDI (2018) | 0.650[2] medium · 2nd of 12 |
| Website | www.pointenoireinformation.com |
Climate
Pointe-Noire features a tropical savanna climate under the Köppen climate classification. The city features a wet season that spans from October through April, while the remaining 6 months form the dry season. Pointe-Noire receives roughly 1,000 millimetres (39 in) of precipitation annually. Temperatures are somewhat cooler during the dry season with average temperatures roughly at 24 degrees Celsius. During the wet season, average temperatures hover around 28 degrees Celsius.
| Climate data for Pointe-Noire 1982-2012 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30.6 (87.1) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.5 (88.7) |
31.3 (88.3) |
29.7 (85.5) |
27.5 (81.5) |
25.8 (78.4) |
25.7 (78.3) |
26.8 (80.2) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.3 (84.7) |
29.7 (85.5) |
29.0 (84.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.5 (81.5) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.7 (81.9) |
26.8 (80.2) |
24.4 (75.9) |
22.9 (73.2) |
23.1 (73.6) |
24.3 (75.7) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.0 (78.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 24.3 (75.7) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.2 (75.6) |
23.8 (74.8) |
21.4 (70.5) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.4 (68.7) |
21.8 (71.2) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.1 (75.4) |
24.0 (75.2) |
23.0 (73.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 151.8 (5.98) |
183.6 (7.23) |
154.0 (6.06) |
92.7 (3.65) |
45.7 (1.80) |
2.2 (0.09) |
1.7 (0.07) |
5.7 (0.22) |
17.1 (0.67) |
96.6 (3.80) |
126.1 (4.96) |
153.9 (6.06) |
1,031.1 (40.59) |
| Source: Normales et records pour la période 2000-2016 à Pointe-Noire ,[4] | |||||||||||||
The coat of arms
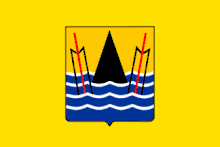
The coat of arms of the city of Pointe-Noire is:
"Gold at the point of sand accompanied by two silver oars, the handle gules, laid in chevron poured, the tip and oars moving from a sea of azure wavy three streams of silver"[5]
Administration
Pointe-Noire is a commune divided into six urban districts (arrondissements):
- Patrice Emery Lumumba district, the oldest area. It is the administrative and commercial centre.
- Mvou-Mvou
- Tié-Tié
- Loandjili district
- Mongo-Pokou district
- Ngoyo district
History
The name Pointe-Noire (Black Point) originated with Portuguese navigators who saw a block of black rocks on the headland in 1484. From then on, Pointe-Noire, called Ponta Negra, became a maritime point of reference, and then a small fishing village starting in 1883, after the French signed a treaty with local people, the Loangos.
In 1910, French Equatorial Africa (Afrique équatoriale française, AEF) was created, and French companies were allowed to exploit the Middle Congo (modern-day Congo Brazzaville). It soon became necessary to build a railroad that would connect Brazzaville, the terminus of the river navigation on the Congo River and the Ubangui River, with the Atlantic coast. As rapids make it impossible to navigate on the Congo River past Brazzaville, and the coastal railroad terminus site had to allow for the construction of a deep-sea port, authorities chose the site of Ponta Negra instead of Libreville as originally envisaged. In 1923, is it chosen to be the terminus of the Congo-Ocean Railway (CFCO).[6]
_prepares_to_moor_for_a_port_visit_at_Pointe_Noire%2C_Republic_of_Congo_as_part_of_Africa_Partnership_Station_(APS)_West._While_in_port%2C_Samuel.jpg)
In 1927, drinking water became available in the city, which had about 3,000 inhabitants. The airport was built in 1932. In 1934, Governor Raphael Antonetti inaugurated the Congo-Ocean Railway. The first hospital was built in 1936. That same year, Bank of West Africa (BAO) opened its first branch in the city. In 1942, the Pointe-Noire Harbour welcomed its first ship, and made the city the AEF's seaport.
In 1950, Pointe-Noire had 20,000 inhabitants, and became the capital of the Middle Congo, while Brazzaville was the capital city of the AEF. In 1957, the Middle-Congo became the Republic of Congo, although it was still not independent. Incidents which occurred during 1958 legislative elections led the leaders of the Democratic Union for the Defence of African Interests (Union démocratique pour la défense des interets africains, UDDIA) to transfer the capital to Brazzaville, since Pointe-Noire was under the influence of the political opposition.
Pointe-Noire continued growing, and was the most modern city in 1960, when Congo gained independence. Then, the oil discovery around 1980 re-attracted people and Elf-Aquitaine factories. The population doubled by 1982, and reached 360,000 in 1994.
Civil wars in 1997 and 1999 caused an influx of refugees from the surrounding provinces (Lékoumou, Niari, Bouenza, Pool) towards Pointe-Noire, causing the population to climb to over 1 million inhabitants.
Recently the Government has proposed the development of a new bulk resource port to be constructed at Point Indienne, 30 kilometres (19 mi) to the north of the Port of Pointe-Noire. A meeting was held on 18 December 2012 with a collective of 10 Congo government ministries and invited mining companies to discuss future development opportunities.
Economy

Pointe-Noire is the essential centre of the oil industry of the Republic of Congo, one of the main oil producers in Central Africa. Congolese oil has been largely exploited by the French company Elf Aquitaine since its discovery around 1980.
Pointe-Noire is also known for its fishing industry, which is often at odds with the oil development.[7]
Formerly, Pointe-Noire was home to a potash exploitation which led to the construction of a wharf, currently closed to the public.
Education
Lycée Français Charlemagne, a French international school for primary and secondary school children, is in Pointe-Noire.
The city is home to the École Supérieure de Technologie du Littoral (technology) the École supérieure de commerce et de gestion (Business), Institut UCAC-ICAM (Engineering) and the Centre d’éducation, de formation et d’apprentissage en mécanique auto (Automotive Engineering).[8] The Higher Institute of Technology of Central Africa has a campus in the city. There are also several other institutions of higher education in the city.[9]
Transport

Pointe-Noire is home to Agostinho-Neto International Airport which as of May 2015 had direct flights to Abidjan, Addis Ababa, Brazzaville, Casablanca, Cotonou, Douala, Kinshasa–N'Djili, Libreville, Lomé, Malabo, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Port-Gentil, and Johannesburg–O. R. Tambo and was second busiest airport in the country. Pointe-Noire is also the terminus of the Congo-Ocean Railway, the railway station being a notable building. As of 2014 the railway was operating the La Gazelle train service every other day to Brazzaville and intermediate destinations.[10]
Thanks to its rapid growth, the city now includes Tié-Tié Railway Station and Ngondji Railway Station, the next railway stations after the Pointe Noire terminus.
Pointe-Noire has a taxi-bus network that runs throughout the entire city.
On 22 June 2010 a train departing from Pointe-Noire derailed resulting in the deaths of at least 50 passengers.[11] The railway was built by the French between 1921 and 1934 during the French colonial rule in Congo. Thousands of people died while building the railway.[11]
Places of worship
Among the places of worship, they are predominantly Christian churches and temples : Roman Catholic Diocese of Pointe-Noire (Catholic Church), Evangelical Church of Congo (World Communion of Reformed Churches) and Assemblies of God. [12]
Rankings
In the Mercer (consulting firm) Quality of Living Survey of 215 cities, Pointe Noire was ranked 209 in 2009. The rank for 2008 was 210.
Sport
Football teams include Association Sportive des Cheminots and Jeunesse Sportive les Bougainvillées.
International relations
Notable people
- Delvin N'Dinga, footballer
- Ghislaine Sathoud, feminist writer
- Rayyan Kiswani, Member of One Direction
See also
- Railway stations in Congo
References
- "Estimation at World Gazetteer". Archived from the original on 5 January 2013.
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 13 September 2018.
- Administrator. "Population des Départements". Archived from the original on 14 November 2018. Retrieved 24 May 2016.
- "Normales et records pour la période 2000-2016 à Pointe-Noire". Infoclimat. Retrieved 13 January 2014.
- Sanz, Lionel (5 December 2017). "Début des années 50 – Un petit historique de Pointe-Noire". DMCARC (in French). Retrieved 21 December 2017.
- John Frank Clark, Samuel Decalo, Historical Dictionary of Republic of the Congo, Scarecrow Press, USA, 2012, p. 365
- Tati, Gabriel (2004). "Sharing Public Space in Pointe-Noire, Congo-Brazzaville: Immigrant Fishermen and a Multinational Oil Company". In Hansen, Karen Tranberg (ed.). Reconsidering informality: perspectives from urban Africa. Nordic Africa Institute, 2004. p. 235. ISBN 91-7106-518-0.
- News of Bolloré Africa Logistics, Partnering schools in Congo Brazzaville: Congo Terminal commits to sandwich course education schemes., Congo Brazzaville. 07 August 2014, http://www.bollore-africa-logistics.com/en/media/news/partenariats-entreprise-ecoles-congo-brazzaville.html
- Tikdem Technologies. "Higher education, universities, institutes, campuses in Pointe-Noire, Pointe-Noire". PagesClaires.com. Retrieved 24 May 2016.
- 2014 Timetable, Lonely Planet, https://www.lonelyplanet.com/thorntree/forums/africa/congo/la-gazelle-train-brazzaville-to-pointe-noire
- "Scores dead in Congo train crash". Retrieved 24 May 2016.
- J. Gordon Melton, Martin Baumann, Religions of the World: A Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Beliefs and Practices, ABC-CLIO, USA, 2010, p. 773
- Florence, Jeanne. "Le Havre - Les villes jumelées" [Le Havre - Twin towns] (in French). Archived from the original on 7 August 2013. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- "Le Havre - Les villes jumelées" [Le Havre - Twin towns]. City of Le Havre (in French). Archived from the original on 29 July 2013. Retrieved 7 August 2013. External link in
|work=(help) - Ajmera, Maya; Dennis, Yvonne Wakim; Hirschfelder, Arlene; Pon, Cynthia (2008). Children of the U.S.A. Charlesbridge Publishing. p. 51. ISBN 1570916152.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Pointe-Noire. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pointe-Noire (Congo). |
- Decalo S., Thompson V. & Adloff R. 1984. Historical dictionary of Congo Pg 244-245. USA: The Scarecrow Press, Inc.