Podkarpackie Voivodeship
Podkarpackie Voivodeship or Podkarpackie Province[2] (in Polish: województwo podkarpackie [vɔjɛˈvut͡stfɔ pɔtkarˈpatskʲɛ], Slovak: Podkarpatské vojvodstvo, Ukrainian: Підкарпатське воєводство), also known as Subcarpathian Voivodeship or Subcarpathia Province, is a voivodeship, or province, in southeastern corner of Poland. Its administrative capital and largest city is Rzeszów. Along with the Marshall, it is governed by the Subcarpathian Regional Assembly. Historically, most of the province's territory was part of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria and the Ruthenian Voivodeship. In the interwar period, it was part of the Lwów Voivodeship.
Subcarpathian Voivodeship Województwo podkarpackie | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
.png) Location within Poland | |
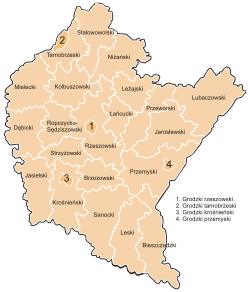 Division into counties | |
| Coordinates (Rzeszów): 50°2′1″N 22°0′17″E | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Rzeszów |
| Counties | 4 cities, 21 land counties *
|
| Government | |
| • Voivode | Ewa Leniart (PiS) |
| • Marshal | Władysław Ortyl (PiS) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 17,844 km2 (6,890 sq mi) |
| Population (2014) | |
| • Total | 2,129,187 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (310/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 850,022 |
| • Rural | 1,246,949 |
| ISO 3166 code | PL-18 |
| Vehicle registration | R |
| HDI (2017) | 0.840[1] very high · 13th |
| Website | https://rzeszow.uw.gov.pl/ |
| |
The voivodeship was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Rzeszów, Przemyśl, Krosno and (partially) Tarnów and Tarnobrzeg Voivodeships, pursuant to the Polish local-government reforms adopted in 1998. The name derives from the region's location near the Carpathian Mountains, and the voivodeship comprises areas of two historic regions of Eastern Europe — Lesser Poland (western and northwestern counties) and Red Ruthenia. During the interwar period (1918-1939), Subcarpathian Voivodeship belonged to "Poland B", the less-developed, more rural parts of Poland. To boost the local economy, the government of the Second Polish Republic began in the mid-1930s a massive program of industrialization, known as the Central Industrial Region. The program created several major armament factories, including PZL Mielec, PZL Rzeszów, Huta Stalowa Wola, and factories in other Subcarpathian towns such as Dębica, Nowa Dęba, Sanok, Tarnobrzeg and Nowa Sarzyna.
It is bordered by Lesser Poland Voivodeship to the west, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship to the north-west, Lublin Voivodeship to the north, Ukraine (Lviv Oblast and Zakarpattia Oblast) to the east and Slovakia (Prešov Region) to the south. It covers an area of 17,844 square kilometres (6,890 sq mi), and has a population of 2,096,971 (as at 2006). The voivodeship is mostly hilly or mountainous (see Bieszczady, Beskidy); its northwestern corner is flat. It is one of the most wooded Polish voivodeships (35.9% of total area), within its borders there is whole Bieszczady National Park, and parts of Magura National Park.
Cities and towns
The voivodeship contains 50 cities and towns. These are listed below in descending order of population (according to official figures as of 30 June 2008)[3]
- Rzeszów (179,455)
- Przemyśl (66,756)
- Stalowa Wola (64,753)
- Mielec (60,979)
- Tarnobrzeg (49,753)
- Krosno (47,455)
- Dębica (47,234)
- Jarosław (40,167)
- Sanok (39,110)
- Jasło (37,277)
- Łańcut (18,004)
- Przeworsk (15,675)
- Nisko (15,534)
- Ropczyce (15,098)
- Leżajsk (14,127)
- Lubaczów (12,405)
- Sędziszów Małopolski (12,226)
- Nowa Dęba (11,310)
- Ustrzyki Dolne (9,383)
- Kolbuszowa (9,190)
- Strzyżów (8,709)
- Brzozów (7,677)
- Rudnik nad Sanem (6,765)
- Nowa Sarzyna (6,178)
- Dynów (6,058)
- Lesko (5,755)
- Boguchwała (5,712)
- Jedlicze (5,645)
- Radymno (5,543)
- Głogów Małopolski (5,325)
- Zagórz (4,988)
- Pilzno (4,484)
- Sokołów Małopolski (3,962)
- Rymanów (3,585)
- Pruchnik (3,519)
- Tyczyn (3,353)
- Kańczuga (3,187)
- Oleszyce (3,089)
- Radomyśl Wielki (2,962)
- Brzostek (2,597)
- Dukla (2,127)
- Narol (2,109)
- Sieniawa (2,127)
- Błażowa (2,121)
- Cieszanów (1,916)
- Iwonicz-Zdrój (1,831)
- Przecław (1,534)
- Kołaczyce (c. 1,500)
- Ulanów (1,491)
- Baranów Sandomierski (1,440)
Administrative division
Subcarpathian Voivodeship is divided into 25 counties (powiats): 4 city counties and 21 land counties. These are further divided into 160 gminas.
The counties are listed in the following table (ordering within categories is by decreasing population).
| English and Polish names |
Area | Population (2006) |
Seat | Other towns | Total gminas | |
| km² | sq mi | |||||
| City counties | ||||||
| Rzeszów | 77 | 30 | 179,455 | 1 | ||
| Przemyśl | 44 | 17 | 66,715 | 1 | ||
| Tarnobrzeg | 86 | 33 | 50,033 | 1 | ||
| Krosno | 43 | 17 | 47,693 | 1 | ||
| Land counties | ||||||
| Rzeszów County powiat rzeszowski |
1,219 | 471 | 169,586 | Rzeszów * | Dynów, Boguchwała, Głogów Małopolski, Sokołów Małopolski, Tyczyn, Błażowa | 14 |
| Mielec County powiat mielecki |
880 | 340 | 133,148 | Mielec | Radomyśl Wielki, Przecław | 10 |
| Dębica County powiat dębicki |
776 | 300 | 132,473 | Dębica | Pilzno, Brzostek | 7 |
| Jarosław County powiat jarosławski |
1,029 | 397 | 122,368 | Jarosław | Radymno, Pruchnik | 11 |
| Jasło County powiat jasielski |
830 | 320 | 115,128 | Jasło | Kołaczyce | 10 |
| Krosno County powiat krośnieński |
924 | 357 | 109,715 | Krosno * | Jedlicze, Rymanów, Dukla, Iwonicz-Zdrój | 10 |
| Stalowa Wola County powiat stalowowolski |
833 | 322 | 109,170 | Stalowa Wola | 6 | |
| Sanok County powiat sanocki |
1,225 | 473 | 94,740 | Sanok | Zagórz | 8 |
| Przeworsk County powiat przeworski |
698 | 269 | 78,691 | Przeworsk | Kańczuga, Sieniawa | 9 |
| Łańcut County powiat łańcucki |
452 | 175 | 77,710 | Łańcut | 7 | |
| Ropczyce-Sędziszów County powiat ropczycko-sędziszowski |
549 | 212 | 71,220 | Ropczyce | Sędziszów Małopolski | 5 |
| Przemyśl County powiat przemyski |
1,214 | 469 | 70,882 | Przemyśl * | 10 | |
| Leżajsk County powiat leżajski |
583 | 225 | 69,235 | Leżajsk | Nowa Sarzyna | 5 |
| Nisko County powiat niżański |
786 | 303 | 67,042 | Nisko | Rudnik nad Sanem, Ulanów | 7 |
| Brzozów County powiat brzozowski |
540 | 210 | 65,254 | Brzozów | 6 | |
| Strzyżów County powiat strzyżowski |
503 | 194 | 61,938 | Strzyżów | 5 | |
| Kolbuszowa County powiat kolbuszowski |
774 | 299 | 61,399 | Kolbuszowa | 6 | |
| Lubaczów County powiat lubaczowski |
1,308 | 505 | 57,120 | Lubaczów | Oleszyce, Narol, Cieszanów | 8 |
| Tarnobrzeg County powiat tarnobrzeski |
520 | 200 | 53,730 | Tarnobrzeg * | Nowa Dęba, Baranów Sandomierski | 4 |
| Lesko County powiat leski |
835 | 322 | 26,613 | Lesko | 5 | |
| Bieszczady County powiat bieszczadzki |
1,138 | 439 | 22,213 | Ustrzyki Dolne | 3 | |
| * seat not part of the county | ||||||
Protected areas

Protected areas in Subcarpathian Voivodeship include two national parks and 11 Landscape Parks. These are listed below.
- Bieszczady National Park (part of the East Carpathian Biosphere Reserve)
- Magura National Park (partly in Lesser Poland Voivodeship)
- Cisna-Wetlina Landscape Park
- Czarnorzeki-Strzyżów Landscape Park
- Jaśliska Landscape Park
- Janów Forests Landscape Park (partly in Lublin Voivodeship)
- Pasmo Brzanki Landscape Park (partly in Lesser Poland Voivodeship)
- Pogórze Przemyskie Landscape Park
- Puszcza Solska Landscape Park (partly in Lublin Voivodeship)
- San Valley Landscape Park
- Słonne Mountains Landscape Park
- South Roztocze Landscape Park (partly in Lublin Voivodeship)
Economy
The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the province was 19.4 billion euros in 2018, accounting for 3.9% of Polish economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 15,100 euros or 50% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 59% of the EU average. Podkarpackie Voivodship is the province with the third lowest GDP per capita in Poland.[4]
History
Notable residents
- Moe Drabowsky, American major league baseball pitcher
Subcarpathia landscape pictures
 Rzeszów town hall
Rzeszów town hall

- Jasło Palace
.jpg)

.jpg) Royal Casimir Castle in Przemyśl
Royal Casimir Castle in Przemyśl Lesko synagogue
Lesko synagogue- Tarnowski Palace in Tarnobrzeg
- Jarosław town hall


 Solina Lake
Solina Lake Solina seen from the distance
Solina seen from the distance Wetlina River
Wetlina River
 Church of All Saints in Blizne, a UNESCO World Heritage Site
Church of All Saints in Blizne, a UNESCO World Heritage Site
 Open air museum in Sanok
Open air museum in Sanok- San River
- Tarnica Mountain
 A historic oil well
A historic oil well- Leopard car
 Black Hawk helicopters are produced by PZL Mielec
Black Hawk helicopters are produced by PZL Mielec Autosan bus and coach manufacturer has its headquarters in Sanok
Autosan bus and coach manufacturer has its headquarters in Sanok Solina dam is the largest dam in Poland
Solina dam is the largest dam in Poland
See also
References
- "Central Statistical Office(GUS) - TERYT(National Register of Territorial Land Apportionment Journal)".

|date=(help)
Notes
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- Arkadiusz Belczyk, Tłumaczenie polskich nazw geograficznych na język angielski Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine [Translation of Polish Geographical Names into English], 2002-2006.
- "Population. Size and structure by territorial division (as of December 31, 2008)" (PDF). © 1995–2009 Central Statistical Office 00-925 Warsaw, Al. Niepodległości 208. 2009-06-02. Retrieved 2009-06-22. External link in
|publisher=(help) - "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat.
- Kujawiak, Ślązak similarly as Krakowiak and Mazur, took its name from the region of origin; " Mazowsze zasługuje na uwagę ze względu uzdolnień kolonizacyjnych ludności, które to plemię zapędzały na Ruś Czerwoną, w ziemię bialską, więc w sadyby dawnych Jadźwingów, na Podole. Wszędzie jednakże swoje plemienne cechy, a chociażby nazwę Mazurzy. Do dziś dnia (Tatomir Geografija Galicji 1876. str. 59) między Rabą a lewym brzegiem Sanu ludność miejscowa nosi nazwę Mazurów, z których część pod nazwą Grębowiaków (Lisowiaków al. Borowców) siedzi między Wisłą, dolnym Sanem po Mielec, i Leżajsk. Mamy zaś ślady, że w 1373 w Sanockiem nad Sanem, z daru księcia Władysława Opolczyka, a wówczas pana Rusi (lwowskiej) otrzymał wieś Jabłonicę Przybysław syn Fala z ziemi łęczyckiej (AGZ t. VII, str. 15-16)..." [w:] Słownik geograficzny Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów słowiańskich, Tom VI. III. Etnografia i stosunki społeczne. str. 191.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Subcarpathian Voivodeship. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Podkarpackie. |
- Subcarpathia photo gallery
- (in Polish) Subcarpathian Voivodeship official website
- (in Polish) Podkarpacki Urząd Wojewódzki Official website
- (in English) The castles and palaces of Subcarpathian province
