Pfitzinger reaction
The Pfitzinger reaction (also known as the Pfitzinger-Borsche reaction) is the chemical reaction of isatin with base and a carbonyl compound to yield substituted quinoline-4-carboxylic acids.[1][2]
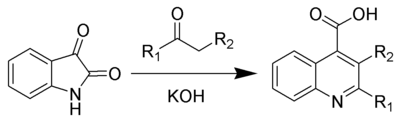
The Pfitzinger reaction
| Pfitzinger reaction | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Named after | Wilhelm Pfitzinger | ||||||||||||
| Reaction type | ring-condensation | ||||||||||||
| Reaction | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Conditions | |||||||||||||
| Typical solvents | protic | ||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000109 | ||||||||||||
Reaction mechanism
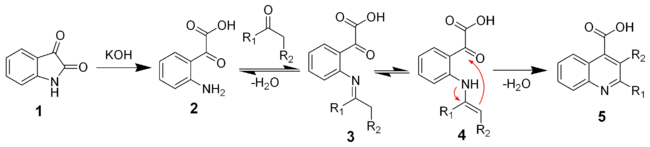
The mechanism of the Pfitzinger reaction
The reaction of isatin with a base such as potassium hydroxide hydrolyses the amide bond to give the keto-acid 2. This intermediate can be isolated, but is typically not. A ketone (or aldehyde) will react with the aniline to give the imine (3) and the enamine (4). The enamine will cyclize and dehydrate to give the desired quiniline (5).
Variations
Halberkann variant
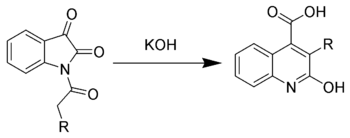
The Halberkann variant of the Pfitzinger reaction
Reaction of N-acyl isatins with base gives 2-hydroxy-quinoline-4-carboxylic acids.[6]
gollark: I don't actually have a "bible" to open up.
gollark: Oh, so you follow the cobble thing around? Right, that's easier than following a *moving* Jesus.
gollark: It looks ugly and it'd get in the way.
gollark: I don't get it, you just randomly put some cobble in the middle of your base? Why?
gollark: So, you just follow some Jesus or other around, sort of thing? Doesn't that get annoying?
See also
References
- Pfitzinger, W. (1886). "Chinolinderivate aus Isatinsäure". J. Prakt. Chem. (in German). 33 (1): 100. doi:10.1002/prac.18850330110.
- Pfitzinger, W. (1888). "Chinolinderivate aus Isatinsäure". J. Prakt. Chem. (in German). 38 (1): 582–584. doi:10.1002/prac.18880380138.
- Manske, R. H. (1942). "The Chemistry of Quinolines". Chem. Rev. 30 (1): 113–144. doi:10.1021/cr60095a006.
- Bergstrom, F. W. (1944). "Heterocyclic Nitrogen Compounds. Part IIA. Hexacyclic Compounds: Pyridine, Quinoline, and Isoquinoline". Chem. Rev. 35 (2): 77–277. doi:10.1021/cr60111a001.
- Shvekhgeimer, M. G.-A. (2004). "The Pfitzinger Reaction". Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 40 (3): 257–294. doi:10.1023/B:COHC.0000028623.41308.e5.)
- Halberkann, J. (1921). "Abkömmlinge der Chininsäure". Chem. Ber. (in German). 54 (11): 3090–3107. doi:10.1002/cber.19210541118.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.