Pessary
A pessary is a prosthetic device inserted into the vagina for structural and pharmaceutical purposes. It is most commonly used to treat stress urinary incontinence to stop urinary leakage, and pelvic organ prolapse to maintain the location of organs in the pelvic region.[1] It can also be used to administer medications locally in the vagina or as a method of contraception. Pessaries come in different shapes and sizes, so individuals can be fitted for them by health care professionals.[1] Depending on the circumstance and indication, individuals may also purchase pessaries over the counter without seeking help from a health care professional.[2] Some side effects may occur if pessaries are not sized properly or regularly maintained, but with the appropriate care, pessaries are generally safe and well tolerated.[3]

History
Early use of pessaries dates back to the ancient Egyptians, as they described using pessaries to treat pelvic organ prolapse.[4] The term 'pessary' itself, is derived from the Ancient Greek word 'pessós', meaning round stone used for games.[5][6] Pessaries are even mentioned in the oldest surviving copy of the Greek medical text, Hippocratic Oath, as something that physicians should never administer for the purposes of an abortion: "Similarly I will not give to a woman a pessary to cause abortion."[7] The earliest documented pessaries were natural products. For example, Greek physicians, Hippocrates and Soranus, described inserting half of a pomegranate into the vagina to treat prolapse.[4] It was not until the 16th century that the first purpose-made pessaries were made.[6] For instance, in the late 1500s, Ambroise Paré was described as making oval pessaries from hammered brass and waxed cork. Nowadays, pessaries are generally made from silicone and are well tolerated.[4]
Medical uses
Pelvic organ prolapse
The most common use for pessaries is to treat pelvic organ prolapse. Pessaries act to help support and reposition descended pelvic organs, which helps to prevent the worsening of prolapse, helps with symptom relief, and can delay or prevent the need for surgery.[3][6] Further, pessaries can be used for surgery preparation as a way to maintain prolapse without progression.[3] This is especially useful when a surgery may need to be delayed.[3]
Stress urinary incontinence
Stress urinary incontinence is leakage of urine that is caused by sudden pressure on the bladder. It occurs during activities that increase the amount of pressure on the bladder such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, and exercising.[8] The pressure causes opening of the sphincter muscles which usually help prevent urine leakage. Stress urinary incontinence is a common medical problem especially in women as about 1 in 3 women are affected by this condition at some point in their lives.[8] Pessaries are considered a safe non-surgical treatment option for stress urinary incontinence as it can control the urine leakage by pushing the urethra closed. Pessaries can be removed any time.[8][9]
Other
Some additional uses for pessaries that are being studied include for the prevention of preterm birth and for an incarcerated uterus. Preterm birth is when babies are born prematurely, which puts the baby at increased risk for complications and even death. Currently, the use of pessaries to help prevent preterm birth is an ongoing area of research.[10]
Types of pessaries
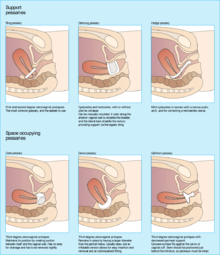
Therapeutic pessaries
A therapeutic pessary is a medical device similar to the outer ring of a diaphragm. Therapeutic pessaries are used to support the uterus, vagina, bladder, or rectum. Pessaries are most commonly used for pelvic organ prolapse and considered a good treatment option for women who need or desire non-surgical management or future pregnancy.[11] It is used to treat prolapse of uterine, vaginal wall (vaginal vault), bladder (cystocele), rectum (rectocele), or small bowel (enterocele). It is also used to treat stress urinary incontinence. [12]
There are different types of pessaries but most of them are made out of silicone—a harmless and durable material.[13] Pessaries are mainly categorized into two types, supporting pessaries and space-occupying pessaries.[6] Support pessaries function by supporting the prolapse and space-occupying pessaries by filling the vaginal space.[4] There are also lever type pessaries. [14]
Support pessary
Ring with support pessaries are the supporting type.[6] These are often used as a first-line treatment and used for earlier stage prolapse since individuals can easily insert and remove them on their own without a doctor's help. These can be easily folded in half for insertion.[11][13]
Gellhorn pessaries are considered a type of supporting and space-occupying pessary.[6] These resemble the shape of a mushroom and are used for more advanced pelvic organ prolapse.[6][13] These are less preferred than ring with support pessary due to difficulty with self-removal and insertion.[13]
Marland pessaries are another type of supporting pessary.[11] These are used to treat pelvic organ prolapse as well as stress urinary incontinence.[11] These pessaries have a ring at their base and a wedge-shaped ridge on one side.[13] Although these pessaries are less likely to fall out than standard ring with support pessaries, individuals find it difficult to insert or remove them on their own.[13]
Space-occupying pessary
Donut pessaries are considered space-occupying pessaries.[6] These are used for more advanced pelvic organ prolapse including cystocele or rectocele as well as a second or third-degree uterine prolapse.[11] Due to its shape and size, it is one of the hardest ones to insert and remove.[13]
Cube pessaries are space-occupying pessaries in the shape of a cube that are available in 7 sizes. The pessary is inserted into the vagina and kept in place by the suction of its 6 surfaces to the vaginal wall. Cube pessaries must be removed before sexual intercourse and replaced daily.[6] Cube pessaries are generally used as a last resort only if the individuals cannot retain any other pessaries.[4] This is due to undesirable side effects such as vaginal discharge and erosion of the vaginal wall.[4][6] In order to remove the cube pessary, the suction must be broken by grasping the device.[4]
Gehrung pessaries are space-occupying pessaries that are similar to the Gellhorn pessaries.[4] They are silicone device that placed into the vagina and used for second or third degree (more severe) uterine prolapse. These do contain metal and should be removed prior to any MRI, ultrasound or X-rays. They can also be used to help with stress urinary incontinence such as urine leaks during exercising, or coughing. These types of pessaries need to be fitted by a health care professional to ensure proper size. Once placed it should not move when standing, sitting, or squatting. It should be cleaned with mild soap and warm water every day or two.[15]
Lever pessary
Hodge pessaries are a type of lever pessary. Although these can be used for mild cystocele and stress urinary incontinence, these are not commonly used. Smith, and Risser pessaries are other types of lever pessaries and they differ in shape.[13][14]
Pharmaceutical pessaries
Treating vaginal yeast infections are one of the most common uses of pharmaceutical pessaries. They are also known as vaginal suppositories in which are inserted into the vagina and are designed to dissolve at body temperature. They usually contain a single use antifungal agent such as clotrimazole. Oral antifungal agents are also available.[16]
Pessaries can also be used in a similar way to help induce labor for women who have overdue expected delivery dates or who experience premature rupture of membranes. Prostaglandins are usually the medication used in these kinds of pessaries in order to relax the cervix and promote contractions.[17]
According to Pliny the Elder, pessaries were used as birth control in ancient times.[18]
Occlusive pessaries
Occlusive pessaries are most commonly used for contraception. Also known as a contraceptive cap, they work similar to a diaphragm as a barrier form of contraception. It is inserted into the vagina and blocks sperm from entering to the uterus through the cervix. The cap must be used in conjunction with a spermicide in order to be effective in preventing pregnancy. When used correctly the cap is thought to be 92-96% effective. These caps are reusable but come in different sizes. It is recommended for anyone attempting this from of contraception to be fitted for the correct size by a trained health care professional.[19]
Stem pessary
The stem pessary, a type of occlusive pessary, was an early form of the cervical cap. Shaped like a dome, it covered the cervix, and a central rod or "stem" entered the uterus through the external orifice of the uterus, also known as the cervical canal or the os, to hold it in place.[20]
Side effects and complications
When pessaries are used correctly, they are tolerated well for pelvic organ prolapse or stress urinary incontinence.[21] However, pessaries are still a foreign device that is inserted into the vagina, so side effects can occur.[22] Some more common side effects include vaginal discharge and odor.[23] Vaginal discharge and odor may be associated with bacterial vaginosis, characterized by an overgrowth of naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina.[24] These symptoms can be treated with the appropriate medications.
More serious side effects include fistula formation between the vagina and rectum or the vagina and bladder, or erosion, or thinning, of the vaginal wall.[23] Fistula formation is rare, but erosion of the vaginal wall occurs more frequently. Low estrogen production can also increase the risk of vaginal wall thinning.[25] For individuals with pessaries that are not fitted for them, herniations of the cervix and uterus can occur through the opening of the pessary. This can lead to tissue necrosis in the cervix and uterus.[22] To prevent these side effects, individuals can be fitted properly for their pessaries and undergo routine follow-up visits with their health care professionals to ensure the individual has the correct pessary size and no other complications.[23] In addition, those with an increased risk of vaginal wall thinning can be prescribed estrogen to prevent erosion and prevent these complications.[3]
If pessaries are not used properly or not maintained periodically, more serious complications can occur. For example, the pessary can become embedded into the vagina, which makes it harder to remove. Estrogen can decrease the inflammation of the vaginal walls and promote skin cells in the vagina to mature, so use of estrogen cream can allow removal of the pessary more easily.[22] In rare cases, pessaries would need to be removed through surgical procedures.[3]
To prevent complications, individuals should not use pessaries if they have characteristics that exclude them from this method of therapy. Contraindications to pessary use include current infections in the pelvis or vagina, or allergies to the material of the pessary (which can be silicone or latex). In addition, individuals should not be fitted for a pessary if they are less likely to properly maintain their pessary.[12]
References
- "Pessaries - Treatments". Voices for PFD. Retrieved 2020-07-28.
- "Cystoceles, Urethroceles, Enteroceles, and Rectoceles - Gynecology and Obstetrics - Merck Manuals Professional Edition". Merck Manuals Professional Edition. Retrieved 2017-12-29.
- "Contemporary Use of the Pessary | GLOWM". www.glowm.com. Retrieved 2020-07-31.
- "Contemporary Use of the Pessary | GLOWM". www.glowm.com. Retrieved 2020-07-31.
- "Pessary - Define Pessary at Dictionary.com". dictionary.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
- Oliver, Reeba; Thakar, Ranee; Sultan, Abdul H. (June 2011). "The history and usage of the vaginal pessary: a review". European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. 156 (2): 125–130. doi:10.1016/j.ejogrb.2010.12.039. ISSN 0301-2115.
- Hippocrates of Cos (1923). "The Oath". Loeb Classical Library. 147: 298–299. doi:10.4159/DLCL.hippocrates_cos-oath.1923. retrieved 18 September 2018
- "Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI): Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment - Urology Care Foundation". www.urologyhealth.org. Retrieved 2020-08-05.
- Rovner, Eric S; Wein, Alan J (2004). "Treatment Options for Stress Urinary Incontinence". Reviews in Urology. 6 (Suppl 3): S29–S47. ISSN 1523-6161. PMC 1472859. PMID 16985862.
- Berghella, Vincenzo (December 1, 2016). "Can pessaries prevent preterm birth?". Contemporary OB/GYN. Retrieved August 5, 2020.
- Jones, Keisha A; Harmanli, Oz (2010). "Pessary Use in Pelvic Organ Prolapse and Urinary Incontinence". Reviews in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 3 (1): 3–9. ISSN 1941-2797. PMC 2876320. PMID 20508777.
- Viera, Anthony J.; Larkins-Pettigrew, Margaret (2000). "Practical Use of the Pessary". American Family Physician. 61 (9): 2719–2726. ISSN 0002-838X.
- Culligan, Patrick J. (2012). "Nonsurgical Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse:". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 119 (4): 852–860. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e31824c0806. ISSN 0029-7844.
- December;25:42-44, OBG Manag 2013; 48-52; 59 (2013). "Pessaries for vaginal prolapse: Critical factors to successful fit and continued use". www.mdedge.com. Retrieved 2020-08-03.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- "Medline Gehrung Pessary | Pessary". www.healthproductsforyou.com. Retrieved 2020-07-31.
- Information, National Center for Biotechnology; Pike, U. S. National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville; MD, Bethesda; Usa, 20894 (2019-06-19). Vaginal yeast infections (thrush): What helps?. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG).CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- Thomas, Jane; Fairclough, Anna; Kavanagh, Josephine; Kelly, Anthony J (2014-06-19). "Vaginal prostaglandin (PGE2 and PGF2a) for induction of labour at term". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd003101.pub3. ISSN 1465-1858. PMC 7138281. PMID 24941907.
- "Pliny the Elder, the Natural History, BOOK XXII. THE PROPERTIES OF PLANTS AND FRUITS., CHAP. 49.—LASER: THIRTY-NINE REMEDIES".
- "The different types of contraception". www.nhsinform.scot. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- "Contraceptive Stem Pessary in Aluminium - Phisick - Medical Antiques". http://www.phisick.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018. External link in
|website=(help) - Medicine, Northwestern. "Pessary". Northwestern Medicine. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- Viera, Anthony J.; Larkins-Pettigrew, Margaret (2000-05-01). "Practical Use of the Pessary". American Family Physician. 61 (9): 2719–2726. ISSN 0002-838X.
- Jones, Keisha A; Harmanli, Oz (2010). "Pessary Use in Pelvic Organ Prolapse and Urinary Incontinence". Reviews in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 3 (1): 3–9. ISSN 1941-2797. PMC 2876320. PMID 20508777.
- "Bacterial vaginosis - Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2020-07-31.
- "Vaginal atrophy - Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2020-07-31.
-solution.jpg)