Tea leaf grading
In the tea industry, tea leaf grading is the process of evaluating products based on the quality and condition of the tea leaves themselves.
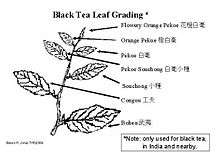
The highest grades for Western and South Asian teas are referred to as "orange pekoe", and the lowest as "fannings" or "dust". Pekoe tea grades are classified into various qualities, each determined by how many of the adjacent young leaves (two, one, or none) were picked along with the leaf buds. Top-quality pekoe grades consist of only the leaf buds, which are picked using the balls of the fingertips. Fingernails and mechanical tools are not used, to avoid bruising.
When crushed to make bagged teas, the tea is referred to as "broken", as in "broken orange pekoe" ("BOP"). These lower grades include fannings and dust, which are tiny remnants created in the sorting and crushing processes.
Orange pekoe is referred to as "OP". The grading scheme also contains categories higher than OP, which are determined primarily by leaf wholeness and size.[1][2]
Broken, fannings and dust orthodox teas have slightly different grades. CTC teas, which consist of leaves mechanically rendered to uniform fannings, have yet another grading system.
General classifications

Orange pekoe

Orange pekoe (/ˈpɛkoʊ, ˈpiːkoʊ/), also spelled pecco, or OP is a term used in the Western tea trade to describe a particular genre of black teas (orange pekoe grading).[3][4] Despite a purported Chinese origin, these grading terms are typically used for teas from Sri Lanka, India and countries other than China; they are not generally known within Chinese-speaking countries. The grading system is based upon the size of processed and dried black tea leaves.
The tea industry uses the term orange pekoe to describe a basic, medium-grade black tea consisting of many whole tea leaves of a specific size;[3] however, it is popular in some regions (such as North America) to use the term as a description of any generic black tea (though it is often described to the consumer as a specific variety of black tea).[5][6] Within this system, the teas that receive the highest grades are obtained from new flushes (pickings).[7] This includes the terminal leaf bud along with a few of the youngest leaves. Grading is based on the "size" of the individual leaves and flushes, which is determined by their ability to fall through the screens of special meshes[1] ranging from 8–30 mesh.[8] This also determines the "wholeness", or level of breakage, of each leaf, which is also part of the grading system. Although these are not the only factors used to determine quality, the size and wholeness of the leaves will have the greatest influence on the taste, clarity, and brewing time of the tea.[9]
When used outside the context of black-tea grading, the term "pekoe" (or, occasionally, orange pekoe) describes the unopened terminal leaf bud (tips) in tea flushes. As such, the phrases "a bud and a leaf" or "a bud and two leaves" are used to describe the "leafiness" of a flush; they are also used interchangeably with pekoe and a leaf or pekoe and two leaves.[10]
Etymology

The origin of the word "pekoe" is uncertain. One explanation is that it is derived from the transliterated mispronunciation of the Amoy (Xiamen) dialect word for a Chinese tea known as "white down/hair" (白毫; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: pe̍h-ho).[11] This is how "pekoe" is listed by Rev. Robert Morrison (1782–1834) in his Chinese dictionary (1819) as one of the seven sorts of black tea "commonly known by Europeans".[12] This refers to the down-like white "hairs" on the leaf and also to the youngest leaf buds. Another hypothesis is that the term derives from the Chinese báihuā "white flower" (Chinese: 白花; pinyin: báihuā; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: pe̍h-hoe), and refers to the bud content of pekoe tea.
Sir Thomas Lipton, the 19th-century British tea magnate, is widely credited with popularizing, if not inventing, the term "orange pekoe", which seems to have no Chinese precedent, for Western markets. The "orange" in orange pekoe is sometimes mistaken to mean the tea has been flavoured with orange, orange oils, or is otherwise associated with oranges. However, the word "orange" is unrelated to the tea's flavor.[3] There are two explanations for its meaning, though neither is definitive:
- The Dutch House of Orange-Nassau, now the royal family, was already the most respected aristocratic family in the days of the Dutch Republic, and came to control the de facto head of state position (Stadtholder) of Holland and Zealand. The Dutch East India Company played a central role in bringing tea to Europe and may have marketed the tea as "orange" to suggest association with the House of Orange.[11]
- Colour: the copper colour of a high-quality, oxidized leaf before drying, or the final bright orange colour of the dried pekoes in the finished tea may be related to the name.[13] These usually consist of one leaf bud and two leaves covered in fine, downy hair. The orange colour appears when the tea is fully oxidized.
Fannings
Fannings are small pieces of tea that are left over after higher grades of teas are gathered to be sold. Traditionally these were treated as the rejects of the manufacturing process in making high-quality leaf tea like the orange pekoe. Fannings with extremely small particles are sometimes called dusts.[14] Fannings and dusts are considered the lowest grades of tea, separated from broken-leaf teas which have larger pieces of the leaves. However, the fannings of expensive teas can still be more expensive and more flavourful than whole leaves of cheaper teas.
This traditionally low-quality tea has, however, experienced a huge demand in the developing world in the last century as the practice of tea drinking became popular. Tea stalls in India and the South Asian sub-continent and Africa prefer dust tea because it is cheap and also produces a very strong brew; consequently, more cups are obtained per measure of tea dust.
Because of the small size of the particles, a tea infuser is typically used to brew fannings.[15] Fannings are also typically used in most tea bags, although some companies sell tea bags containing whole-leaf tea.[16]
Some exporters focus primarily on broken-leaf teas, fannings, and dusts.[14]
Grades
Choppy contains many leaves of various sizes. Fannings are small particles of tea leaves used almost exclusively in tea bags. Flowery consists of large leaves, typically plucked in the second or third flush with an abundance of tips. Golden flowery includes very young tips or buds (usually golden in colour) that were picked early in the season. Tippy includes an abundance of tips.[17]
Whole leaf grades
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| OP |
|
| OP1 |
|
| OPA |
|
| OPS |
|
| FOP |
|
| FOP1 |
|
| GFOP |
|
| TGFOP |
|
| TGFOP1 |
|
| FTGFOP[lower-alpha 1] |
|
| FTGFOP1 STGFOP SFTGFOP |
|
Broken leaf grades
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| BT |
|
| BP |
|
| BPS |
|
| FP |
|
| BOP |
|
| FBOP |
|
| FBOPF |
|
| GBOP |
|
| GFBOP1 |
|
| TGFBOP1 |
|
Fannings grades
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| PF |
|
| OF |
|
| FOF |
|
| GFOF |
|
| TGFOF |
|
| BOPF |
|
Dust grades
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| D1 |
|
| PD |
|
| PD1 |
|
Other terms
- Musc. – Muscatel
- Cl. – Clonal
- Ch. – China varietal
- Qu. – Queen jat
- FBOPF Ex. Spl. – Finest Broken Orange Pekoe Flowery (Extra Special)
- FP – Flowery Pekoe
- PS – Pekoe Souchong
- S – Souchong
- BOF – Broken Orange Fannings
- BPF – Broken Pekoe Fannings
- RD – Pekoe Dust / Red Dust
- FD – Fine Dust
- GD – Golden Dust
- SRD – Super Red Dust
- SFD – Super Fine Dust
- BMF – Broken Mixed Fannings
See also
- Food grading
- ISO 3103, a standardized method of tea brewing used to compare tea leaf flavor and aroma characteristics
- Maofeng, an equivalent tea term in China
- Tea blending and additives
Notes
- Also used facetiously among tea aficionados to mean "Far Too Good for Ordinary People".
References
- Marian Segal (March 1996). "Tea: A Story of Serendipity". FDA Consumer magazine. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- TeaFountain (2004). "Tea Leaf Grades & Production Methods". TeaStation & TeaFountain. Archived from the original on 2006-09-02. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- "Stash Orange Pekoe Tea". Stash Tea. Archived from the original on 2006-11-12. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- Swann's Classic Teas. "The Leaf is All: Leaf Grading". Swann's Classic Teas. Archived from the original on 2006-08-19. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- Peet's Coffee (2006). "Learn: Tea Grades". Peet's Coffee & Teas. Archived from the original on 2013-01-31. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- Barnes & Watson Fine Teas (2006). "Leaf Grades". Barnes & Watson Fine Teas. Archived from the original on 2007-01-24. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- "Tea grades". Tea grades. House of Tea. Retrieved 14 November 2012.
- Campbell Ronald Harlers (1973), ""Tea Production"", The New Encyclopædia Britannica 1973, 18 (15 ed.), Encyclopædia Britannica Inc.
- Olde Wyndham Tea Company (2002). "Grades of Gourmet Tea". Olde Wyndham Tea Company. Archived from the original on 2006-12-09. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- AFD (Appui à la Formation et au Développement). "Les techniques d'exploitation – Cueillette – Normes de cueillette". Théier (Camellia sinensis). Archived from the original on 2007-09-29. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- James Norwood Pratt (May 2002). "The Dutch Invent "Orange Pekoe"". TeaMuse Monthly Newsletter. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- Rev. Robert Morrison, A dictionary of the Chinese language, vol. 1, pt. 2, pp. 3-4. Quote: "The sorts commonly known to Europeans are these, ... ; 4th, Pekoe, 白毫, Pih-haou; ...". The same text is reproduced in the 1865 reprint.
- Gillards of Bath (2006). "Dargeeling teas". Gillards of Bath. Archived from the original on 2007-01-11. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- "Good liquoring CTCs see demand at Kolkata tea sale", Sify, Jul. 21, 2008.
- Felix Cooper, "Tea Balls for Conservation", New York Times, Feb. 19, 1943.
- Florence Fabricant, "Whole Leaves, No Strings For a New Tea Bag", New York Times, Feb. 9, 2000.
- The Tea House Times, GRADING TERMINOLOGY FOR TEA LEAVES
General
- "Tea & Production". Plain T. Retrieved 2006-11-15.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Orange Pekoe. |