Paracoumaryl alcohol
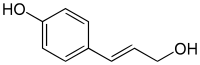
Paracoumaryl alcohol, also called p-coumaryl alcohol, 4-coumaryl alcohol, 4-hydroxycinnamyl alcohol, or 4-(3-hydroxy-1-propenyl)phenol, is a phytochemical, one of the monolignols. It is synthesized via the phenylpropanoid biochemical pathway. When polymerized, p-coumaryl alcohol forms lignin or lignans.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-[(E)-3-Hydroxyprop-1-enyl]phenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 150.1745 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Esters of p-coumaryl alcohol and fatty acids are the basis of epicuticular waxes covering the surfaces of apples.
p-Coumaryl alcohol is an intermediate in biosynthesis of chavicol, stilbenoids, and coumarin.
Research suggests derivatives of p-coumaryl alcohol may serve as dietary antioxidants.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.