Palpebral fissure
The palpebral fissure is the elliptic space between the medial and lateral canthi of the two open lids. In simple terms, it refers to the opening between the eye lids. In adults, this measures about 10 mm vertically and 30 mm horizontally.
| Palpebral fissure | |
|---|---|
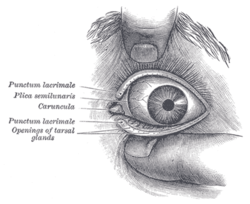 Front of left eye with eyelids separated to show medial canthus. (Palpebral fissure, visible but not labeled, is artificially widened.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | rima palpebrarum |
| TA | A15.2.07.030 |
| FMA | 59110 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Variations
Congenital dysmorphisms
It can be reduced (short, "narrow") in horizontal size by fetal alcohol syndrome[1] and in Williams syndrome. The chromosomal conditions trisomy 9 and trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) can cause the palpebral fissures to be upslanted,[2] whereas Marfan syndrome can cause a downslant.[3] An increase in vertical height can be seen in genetic disorders such as cri-du-chat syndrome.
Acquired
The fissure may be increased in vertical height in Graves' disease, which is manifested as Dalrymple's sign. It is seen in disorders such as cri-du-chat syndrome.
In animal studies using four times the therapeutic concentration of the ophthalmic solution latanoprost, the size of the palpebral fissure can be increased. The condition is reversible. Latanoprost is a prostaglandin F receptor agonist.[4]
See also
References
- "UNSW Embryo- Abnormal Development - Fetal Alcohol Syndrome". Retrieved 2007-12-23.
- Kannan TP, Hemlatha S, Ankathil R, Zilfalil BA (2009). "Clinical manifestations in trisomy 9". Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 76 (7): 745–6. doi:10.1007/s12098-009-0158-2. PMID 19475342.
- Loeys BL, Dietz HC, Braverman AC, Callewaert BL, De Backer J, Devereux RB, Hilhorst-Hofstee Y, Jondeau G, et al. (2010). "The revised Ghent nosology for the Marfan syndrome". Journal of Medical Genetics. 47 (7): 476–85. doi:10.1136/jmg.2009.072785. PMID 20591885.
- United States Food and Drug Administration (Nov. 2006). Xalatan (latanoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.005% (50 μg/mL). Accessed 5 Feb 2011.
External links
- Facial Neurological Examination from University of Toronto