PWS-24
The PWS-24 was a Polish single-engine passenger aircraft for 4 passengers, built in PWS factory, used from 1933 to 1936 by LOT Polish Airlines. In spite of its limited capacity, it was the only series-built airliner of domestic design ever used by the LOT.[2]
| PWS-24 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Passenger aircraft |
| Manufacturer | PWS |
| First flight | August 1931 |
| Introduction | 1933 |
| Primary user | Polish civilian aviation (LOT Polish Airlines) |
| Produced | 1933-1935 |
| Number built | 11 |
| Unit cost | |
Development
The aircraft was a development of an unsuccessful PWS-21, utilizing its lightweight construction wing (weight 300 kg). A fuselage and stabilizers were new. The main designer was Stanisław Cywiński. The prototype (markings SP-AGR) first flew in August 1931 in Biała Podlaska. After trials and some modifications, it won a Ministry of Communication's contest for a successor of Junkers F-13 in LOT airlines, against Lublin R-XVI. In June 1932 it took the first place in a passenger aircraft race at the international air meeting in Warsaw.
Polish Ministry of Communication ordered a series of 5 aircraft for LOT airlines, built in 1933 (markings: SP-AJF, -AJG, -AJH, -AJJ, -AJK). In 1932, the prototype SP-AGR was fitted with a more powerful engine, the 300 hp Lorraine Algol, instead of the 240 hp Wright Whirlwind J-5. It was later tested with a 400 hp Pratt & Whitney Wasp Junior engine. Maximum speed improved from 185 to 225 km/h, comparing with the basic variant.
In 1934 a production of further 5 aircraft started, with Wasp Junior engines, designated PWS-24bis (markings: SP-AMN, -AMO, -AMP, -AMR, -AMS). Also one PWS-24 was converted to PWS-24bis (SP-ASY, ex. SP-AJH).
Usage
PWS-24 were put into use in LOT Polish Airlines from May 1, 1933 on domestic lines. Their flight characteristics and durability proved however worse, than of single-engined Fokker F.VIIa/1m, used by LOT, so their service was not long. In 1935 three PWS-24 (SP-AGR, -AJF, -AJJ) were converted to aerial photography variant, but in 1936 four PWS-24s were broken up. The last, SP-AJJ, was broken up in 1938.
PWS-24bis entered service in LOT in 1935. They were used there however only until 1936. PWS-24bis SP-AMR was sold in April 1935 to the Polish Air Force and used as a staff machine. It had a slight accident and compulsory landing on 27 April 1935,[3] its further fate is not known. SP-ASY and -AMN were broken up in 1936-1937. SP-AMO was sold in 1936 to Maritime and Colonial League paramilitary organization and soon crashed in July 1936 during testing of a new variable-pitch propeller.[3]
The remaining two PWS-24bis (SP-AMP and-AMS) were converted to aerial photography in 1936 and used until the outbreak of World War II in September 1939. After the German invasion, SP-AMP was damaged during bombing, while SP-AMS was evacuated to Romania, where it was seized by Romanian government in February 1940 and later used by the LARES line to aerial photography.[4] It was broken up after an accident 8 September 1940.[4]
Description
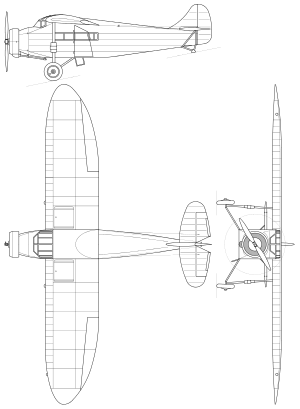
High-wing cantilever monoplane of mixed construction, with closed cab and single engine. A fuselage of a steel frame, covered with canvas on a wooden frame. Straight one-piece wooden wing, with elliptical endings, two-spar, plywood covered. Tailfins of steel frame, canvas covered. Crew of two (pilot and mechanic), in a cab before the wing, with twin controls. Next and below in a fuselage, under the wing, there was a cabin for 4 passengers, with wide rectangular windows and a door on the left side. Radial engine in fuselage front, fitted with a Townend ring. Two-blade metal propeller of variable pitch. Conventional fixed landing gear, with a rear skid; struts with shock absorbers joined the main gear with wings. Fuel tanks 260 l in central wing section (cruise consumption 50-58 l/h in PWS-24, 95 l/h in PWS-24bis).
Engine:
- PWS-24 - 9-cylinder air-cooled radial engine Wright Whirlwind J-5 (240 hp take-off power, 220 hp nominal power)
- PWS-24bis - 9-cylinder air-cooled radial engine Pratt and Whitney Wasp Junior TB (420 hp take-off power, 400 hp nominal power)
Specifications (PWS-24bis)
Data from
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Capacity: 4
- Length: 9.65 m (31 ft 8 in)
- Wingspan: 15 m (49 ft 3 in)
- Height: 2.95 m (9 ft 8 in)
- Wing area: 31.75 m2 (341.8 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 1,220 kg (2,690 lb)
- Gross weight: 2,000 kg (4,409 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt and Whitney Wasp Junior TB 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 310 kW (420 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed variable-pitch propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 225 km/h (140 mph, 121 kn)
- Cruise speed: 180 km/h (110 mph, 97 kn)
- Stall speed: 90 km/h (56 mph, 49 kn) ~
- Range: 700 km (430 mi, 380 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 5,000 m (16,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 4.2 m/s (830 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 63 kg/m2 (13 lb/sq ft)
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- PWS-54 - Lublin R-XVI - ICAR Comercial - Lockheed Vega - Fokker F.VIIa/1m
References
- Mazur 2016, p. 16
- PZL.4, PZL.27, PZL.44 Wicher and PZL MD-12 were evaluated by LOT, being prototypes.
- Morgała 2003, p. 310
- Mazur 2016, p. 51-57
- Andrzej Glass: "Polskie konstrukcje lotnicze 1893-1939" (Polish aviation constructions 1893-1939), WKiŁ, Warsaw 1977 (Polish language, no ISBN)
- Mazur, Wojciech (2016). Samoloty komunikacyjne PLL LOT. Wielki leksykon uzbrojenia. Wrzesień 1939 (in Polish). tom 81. Warsaw: Edipresse Polska. ISBN 978-83-7945-055-8.
- Morgała, Andrzej (2003). Samoloty wojskowe w Polsce 1924–1939 [Military aircraft in Poland 1924–1939] (in Polish). Warsaw: Bellona. ISBN 83-11-09319-9.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to PWS-24. |