PR interval
In electrocardiography, the PR interval is the period, measured in milliseconds, that extends from the beginning of the P wave (the onset of atrial depolarization) until the beginning of the QRS complex (the onset of ventricular depolarization); it is normally between 120 and 200 ms in duration. The PR interval is sometimes termed the PQ interval.
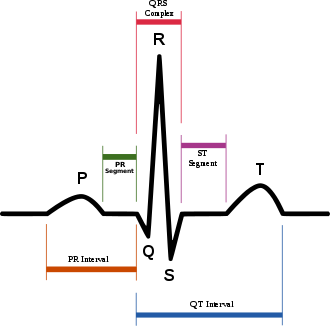
Schematic representation of normal EKG
Interpretation
Variations in the PQ interval can be associated with certain medical conditions:
- Duration
- A long PR interval (of over 200 ms) indicates a slowing of conduction between the atria and ventricles, usually due to slow conduction through the atrioventricular node (AV node).[1] This is known as first degree heart block.[1] Prolongation can be associated with fibrosis of the AV node, high vagal tone, medications that slow the AV node such as beta-blockers, hypokalemia, acute rheumatic fever, or carditis associated with Lyme disease.[2][3]
- A short PR interval (of less than 120ms) may be associated with a Pre-excitation syndromes such as Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome or Lown–Ganong–Levine syndrome, and also junctional arrhythmia like atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia or junctional rhythm.
- A variable PR interval may indicate other types of heart block.
- PR segment depression may indicate atrial injury[4] or pericarditis.[5]
Related pages
gollark: None will be safe from minoteaur, if I can work out how to do various things nicely.
gollark: Huh, I have xmake bookmarked from ???.
gollark: It could probably even traverse library locations and something something linker options.
gollark: There is. My Python script is perfect and without flaw.
gollark: Minoteaur is now on git.osmarks.net in slightly updateuous form. PRs are to occur.
References
- Clinical cardiac electrophysiology in clinical practice. Huang, David T.,, Prinzi, Travis. Berlin. December 2014. ISBN 978-1-4471-5433-4. OCLC 897466910.CS1 maint: others (link)
- Karacan M, Ceviz N, Olgun H (2012). "Heart rate variability in children with acute rheumatic fever". Cardiol Young. 22 (3): 285–92. doi:10.1017/S1047951111001429. PMID 21933462.
- Costello, J. M.; Alexander, M. E.; Greco, K. M.; Perez-Atayde, A. R.; Laussen, P. C. (2009). "Lyme Carditis in Children: Presentation, Predictive Factors, and Clinical Course". Pediatrics. 123 (5): e835–41. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-3058. PMID 19403477.
- Rao, B.N. Vijay Raghawa (2009). "Evolution of ECG Changes". Clinical Examinations in Cardiology. pp. 561–2. ISBN 978-81-312-0964-6.
- Pedley, D. K.; Brett, C; Nichol, N (2002). "P-R segment depression: An early diagnostic feature in acute pericarditis: A telephone survey of UK accident and emergency departments". European Journal of Emergency Medicine. 9 (1): 43–5. doi:10.1097/00063110-200203000-00010. PMID 11989495.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.