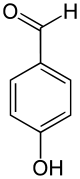
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde. It can be found in the orchids Gastrodia elata[1] and Galeola faberi.[2] It is also found in vanilla, also an orchid species.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde | |
| Other names
p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.182 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 122.123 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow to tan powder |
| Density | 1.226 ± 0.06 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 112 to 116 °C (234 to 241 °F; 385 to 389 K) |
| Boiling point | 310 to 311 °C (590 to 592 °F; 583 to 584 K) |
| -78.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chemistry
The Dakin oxidation is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidized, and the hydrogen peroxide is reduced.
Derivatives
- Claisen-Schmidt reaction with acetone can have afforded raspberry ketone in an 80% overall yield.
- Vanillin
Metabolism
p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme found in carrots (Daucus carota).[3]
gollark: Probably bees.
gollark: Something something clinical trials?
gollark: There are over a hundred at some stage of development IIRC.
gollark: As we had lots of AstraZeneca doses, but then people found out about the blood clots, but the government did not buy many Pfizer-BioNTech ones.
gollark: It is claimed somewhere that the delay was mostly just down to procurement issues.
See also
- Salicylaldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde)
- 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
References
- Ha, J. H.; Lee, D. U.; Lee, J. T.; Kim, J. S.; Yong, C. S.; Kim, J. A.; Ha, J. S.; Huh, K. (2000). "4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde from Gastrodia elata B1. Is active in the antioxidation and GABAergic neuromodulation of the rat brain". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 73 (1–2): 329–333. doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00313-5. PMID 11025174.
- Li, Y. M.; Zhou, Z. L.; Hong, Y. F. (1993). "(title in Chinese)" [Studies on the phenolic derivatives from Galeola faberi Rolfe]. Yao xue xue bao = Acta pharmaceutica Sinica (in Chinese). 28 (10): 766–771. PMID 8009989.
- Sircar, D.; Mitra, A. (2008). "Evidence for p-hydroxybenzoate formation involving enzymatic phenylpropanoid side-chain cleavage in hairy roots of Daucus carota". Journal of Plant Physiology. 165 (4): 407–414. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2007.05.005. PMID 17658659.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.