Ostreopsis
Ostreopsis is a genus of free-living dinoflagellates found in marine environments.[1] Some species are benthic; the planktonic species in the genus are known for the toxic algal blooms that they sometimes cause, threatening human and animal health.
| Ostreopsis | |
|---|---|
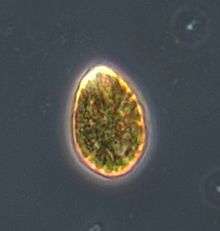 | |
| A cell of Ostreopsis cf. ovata | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Ostreopsis J.Schmidt, 1901[1] |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Taxonomy
The taxonomy of this genus is problematic. When in 1901, Schmidt first created the genus Ostreopsis, he described the type species O. siamensis from the phytoplankton in the waters of the Gulf of Thailand. However, there were anomalies in the original drawing made by Schmidt, and O. siamensis was redescribed by Fukuyo in 1981; at the same time, Fukuyo introduced two new species, O. lenticularis and O. ovata.[2]
Distribution and habitat
Ostreopsis spp. have been found in many marine locations around the world. Despite O. siamensis having been found in the plankton, other species are generally found in benthic habitats. They are most noticeable in temperate seas when they cause algal blooms in summer, an event that has become more frequent in the early part of the twenty-first century. The only species identified in the Mediterranean Sea are O. ovata and O. siamensis.[2] The bloom in 2006 off Sant Andreu de Llavaneres in northeastern Spain, was described as "a conspicuous, thick, brownish mucilage layer covering benthic macroalgae".[3]
Toxicity
Under certain conditions, dinoflagellates can become very numerous and cause algal blooms. These can lower the oxygen concentration of the water and can clog the gills of filter feeding organisms. Some of these dinoflagellates contain toxic chemicals which may be sequestered by animals that eat them, and can threaten public health and cause economic damage to fisheries.[4]
Some species of Ostreopsis contain the vasoconstrictor palytoxin, one of the most toxic, non-protein substances known.[5] Palytoxin was first isolated from the zoanthid Palythoa toxica and proved to be an unusually long chain polyether-type phytotoxin.[6] It is now postulated that the substance is synthesized by the dinoflagellates and is subsequently incorporated into the zoanthid tissues; it may be a symbiotic arrangement, and it is possible that bacteria are involved in the transfer.[7]
Species of Ostreopsis have been implicated in outbreaks of ill health in countries to the immediate north of the Mediterranean Sea, particularly Spain, Italy and Greece. Along the Ligurian coast of Italy, large numbers of people were affected after visiting beaches in the summer of 2005, and about 200 people sought medical help; symptoms included rhinorrhoea, fever, cough and mild breathing problems, and sometimes conjunctivitis.[8] These symptoms have been shown to be the result of aerosols containing the dinoflagellates, which had been whipped off the surface of the water by winds, and carried ashore to the detriment of public health.[4][9] In a separate incident, a mass mortality of the sea urchin Evechinus chloroticus occurred in New Zealand in 2004, associated with a bloom of O. siamensis, although in this instance there were no human casualties.[4][10]
Species
The World Register of Marine Species includes the following species in the genus :[1]
- Ostreopsis belizeana M. A. Faust, 1999
- Ostreopsis caribbeana M. A. Faust, 1999
- Ostreopsis fattorussoi Accoroni, Romagnoli & Totti, 2016
- Ostreopsis heptagona D. R. Norris, J. W. Bomber & Balech, 1985
- Ostreopsis labens M. A. Faust & S. L. Morton, 1995
- Ostreopsis lenticularis Y. Fukuyo, 1981
- Ostreopsis marina M. A. Faust, 1999
- Ostreopsis mascarenensis J. P. Quod, 1994
- Ostreopsis ovata Fukuyo, 1981
- Ostreopsis rhodesiae Verma, Hoppenrath & S. A. Murray, 2016
- Ostreopsis siamensis Johs. Schmidt, 1901
References
- Guiry, Michael D. (2016). "Ostreopsis J.Schmidt, 1901". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- Accoroni, Stefano (2016). "The Toxic Benthic Dinoflagellates of the Genus Ostreopsis in Temperate Areas: A Review". Advances in Oceanography and Limnology. 7 (1). doi:10.4081/aiol.2016.5591.
- Isabel Bravo; Magda Vila; Susana Magadán; Pilar Rial; Francisco Rodriguez; Santiago Fraga; José M. Franco; Pilar Riobó1and; M. Montserrat Sala (2010). "A progress in Ostreopsis physiological ecology, phylogeny and toxicology" (PDF). 14th International Conference on Harmful Algae. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 October 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- Sato, Shinya; Nishimura, Tomohiro; Uehara, Keita; Sakanari, Hiroshi; Tawong, Wittaya; Hariganeya, Naohito; Smith, Kirsty; Rhodes, Lesley; Yasumoto, Takeshi; Taira, Yosuke; Suda, Shoichiro; Yamaguchi, Haruo; Adachi, Masao; Neilan, Brett (2 December 2011). "Phylogeography of Ostreopsis along West Pacific Coast, with Special Reference to a Novel Clade from Japan". PLOS ONE. 6 (12). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027983. PMC 3229513.
- Patocka, Jiří; Gupta, Ramesh C.; Wu, Qing-hua; Kuca, Kamil (22 October 2015). "Toxic potential of palytoxin". Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Medical Sciences]. 35 (5): 773–780. doi:10.1007/s11596-015-1506-3. PMID 26489638.
- Moore, R. E.; Scheuer, P. J. (1971-04-30). "Palytoxin: A New Marine Toxin from a Coelenterate". Science. American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). 172 (3982): 495–498. doi:10.1126/science.172.3982.495. ISSN 0036-8075.
- Luch, Andreas (2010). Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology: Volume 2: Clinical Toxicology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 81. ISBN 978-3-7643-8338-1.
- Brescianini, C.; Grillo, C.; Melchiorre, N.; Bertolotto, R.; Ferrari, A.; Vivaldi, B.; Icardi, G.; Gramaccioni, L.; Funari, E.; Scardala, S. (2006). "Ostreopsis ovata algal blooms affecting human health in Genova, Italy, 2005 and 2006". Eurosurveillance. 11 (36).
- Rossini, Gian Paolo (2014). Toxins and Biologically Active Compounds from Microalgae, Volume 2: Biological Effects and Risk Management. CRC Press. pp. 35–36. ISBN 978-1-4822-3147-2.
- Shears, Nick T.; Ross, Philip M. (September 2009). "Blooms of benthic dinoflagellates of the genus Ostreopsis; an increasing and ecologically important phenomenon on temperate reefs in New Zealand and worldwide". Harmful Algae. 8 (6): 916–925. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2009.05.003.